
Why do entities borrow in the form of debt obligations?
Economies around the world were still recovering during 2012 after the 20082009 recession. Governments and central banks continued their efforts to facilitate economic recovery. The U.S. Federal Reserve Bank (the Fed) kept interest rates at record lows. This, along with several other reasons, found the bond markets flooded with new bond issues. The following article highlights some reasons why firms issued debt obligations to raise funds.


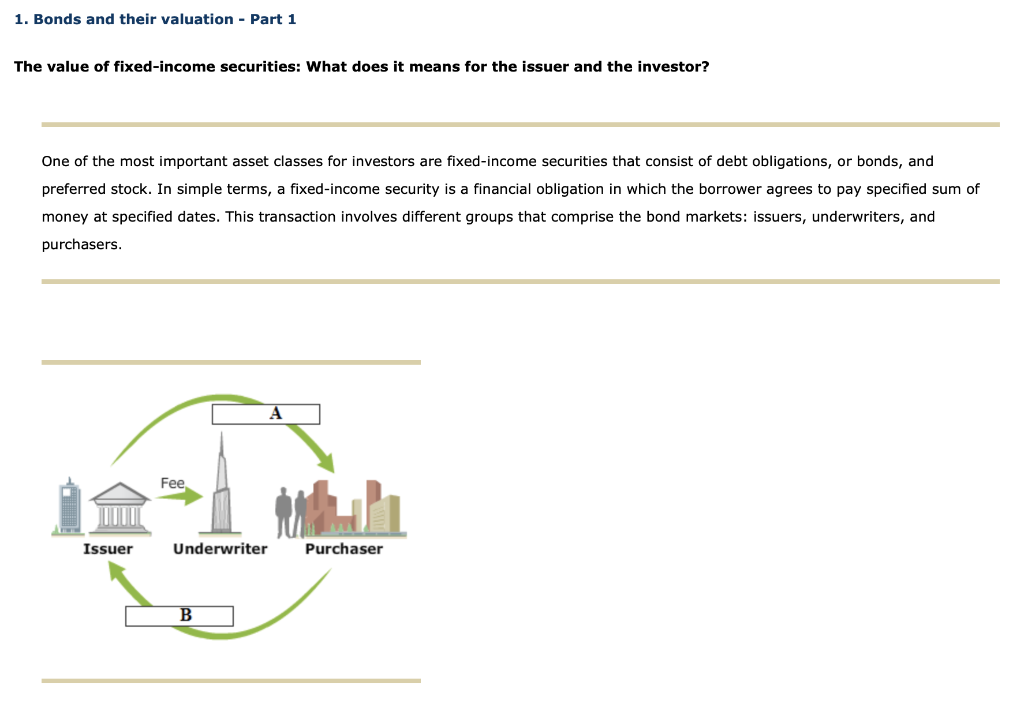
1. Bonds and their valuation - Part 1 The value of fixed-income securities: What does it means for the issuer and the investor? One of the most important asset classes for investors are fixed-income securities that consist of debt obligations, or bonds, and preferred stock. In simple terms, a fixed-income security is a financial obligation in which the borrower agrees to pay specified sum of money at specified dates. This transaction involves different groups that comprise the bond markets: issuers, underwriters, and purchasers. Fee Issuer Underwriter Purchaser B A: (Bond Price, Coupons) B: (Par Value, Bond Price) The entity issuing the debt obligation is the borrower in the transaction. Some of the biggest issuers in the bond market are (1) (central governments, supranational banks, corporations), such as the U.S. government and the government of U.K.; (2) government-related agencies, such as Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac; (2) (corporations, municipal governments, supranational banks), such as the state of California, Sakai City, Japan; (3) (corporations, central governments, municipal governments), such as British Telecom, and The Walt Disney Co. and (4) (corporations, supranational banks, central governments), such as the European Investment Bank and the World Bank. In the context of the reasons why entities borrow in the form of bond issues, which statement is correct? Check all that apply. Because of covenants, issuers often find direct borrowing from a bank more restrictive than selling debt on the bond market. When U.S Treasury yields are low and the spread between the Treasury and corporate bond yield is narrow, issuers can lock in low costs of borrowing through bond issues. When spreads are narrow, borrowers want to lock in low coupon payments for the long term; investors, however, prefer short and medium terms, to avoid losing income when interest rates rise. Bond financing dilutes shareholder equity by reducing current shareholder ownership. This makes it difficult for companies to get approval to raise funds through bond financing. Corporate-Bond Issuers Race to the Market as U.S. Yields Approach Record Low On April 25, 2011, the Fed announced that short-term interest rates would be kept near zero through late 2014. Because corporate bonds are indexed to Treasury yields and the Treasury yield hit nearly all-time lows, issuing conditions became conducive for investment-grade borrowers. Europe's debt crisis fueled the demand for relatively safer U.S. securities, and the market became more confident that Europe's crisis would not significantly disrupt recovery of the world's largest economy. This triggered issuers to announce investment-grade supply benefiting from the low borrowing costs. Companies such as IBM, Procter & Gamble, Petroleo Brasileiro SA, and Berkshire Hathaway announced more than $15.5 billion debt offerings as yields approached record lows. The spread between the Treasury bonds and investment-grade bonds was hovering at narrow levels, making it attractive for issuers to tap into low borrowing costs. According to a BusinessWeek story, "Yields have fallen to 3.55 percent, the lowest level since touching 3.53 percent on Aug. 10, and within 10 basis points of a record low 3.45 on Aug. 4, according to the Bank of America Merrill Lynch U.S. Corporate Master Index." Another factor contributing to the rising issues of investment-grade bonds was purchasers' eagerness to invest in high-quality securities. Sales of debt offerings had fallen 19% from the year before, and that made investors eager to spend cash on offerings. The relationship between corporate bond yields and Treasury yields The article highlights an important relationship between the corporate bond yields and the U.S. Treasury yields. When demand for Treasuries increases, prices rise and yields (rise, fall). All else being equal, this leads to the (widening, narrowing) of corporate bond yields because they are riskier and their yields are (higher, lower) than U.S. Treasury yields. However, this does not necessarily imply that particular changes in the Treasury yield will lead to similar changes in the corporate bond yields. A corporate bond with a narrow yield spread and high credit rating will offer a relatively (high, low) return when the bond is purchased. However, if the yield spread widens, the price of the bond will (rise, fall), thus (increasing, decreasing) the value of the fixed-income asset class in the investor's portfolio











