
 Widget Case
Widget Case
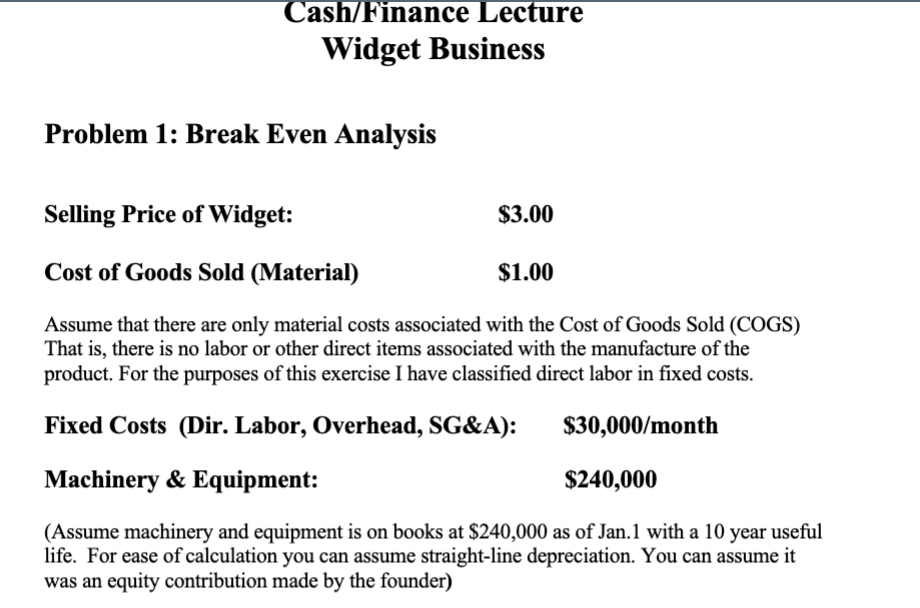
Cash/Finance Lecture Widget Business Problem 1: Break Even Analysis Selling Price of Widget: $3.00 Cost of Goods Sold (Material) $1.00 Assume that there are only material costs associated with the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) That is, there is no labor or other direct items associated with the manufacture of the product. For the purposes of this exercise I have classified direct labor in fixed costs. Fixed Costs (Dir. Labor, Overhead, SG&A): $30,000/month Machinery & Equipment: $240,000 (Assume machinery and equipment is on books at $240,000 as of Jan.1 with a 10 year useful life. For ease of calculation you can assume straight-line depreciation. You can assume it was an equity contribution made by the founder) Problem 3: Cash Flow, Income Statement and Balance Sheet Assume all of the cost and expense assumptions remain as in problem 2 and you need to replenish your inventory so that you keep at least one month buffer of inventory on hand at all times. However, in this scenario, you've been granted 30 day terms with your suppliers and you must also give your customers 30 days to pay. So here is the specific scenario: 1) Payment for goods is made 30 days after receipt of goods. So you pay for the widgets you buy in the following month 2) Your customers pay you 30 days after shipment (in the following month) Therefore, you start the business on Jan 1st and the sequence of events is as follows: Events in January a) On Jan 1, you order 2 month's worth of material. b) Goods will be received on Jan 10th and must be paid for on Feb. 10th c) During January you ship the number of widgets you need to reach profit break even Events in February a) On Feb 1, you order 1 months worth of material to replenish January shipments. b) Goods will be received on Feb 10th and must be paid for on March 10th. c) You pay the bill for inventory you bought in January. d) During February you ship the widgets you need to reach profit break even Events in March a) On March 1, you order 1 month's worth of material to replenish February shipments. b) Goods will be received on March 10th and must be paid for on April 10th. c) You pay the bill for the inventory you bought in February d) During March you ship the widgets you need to reach profit break even Events in April a) On April 1, you order 1 month's worth of material to replenish March shipments. b) Goods will be received on April 10th and must be paid for on May 10th. c) You pay the bill for the inventory you bought in March d) During April you ship the widgets you need to reach profit break even Question Set 3: Develop a monthly Income Statement as of the end of each month Calculate your cash generation/usage for each month Develop an ending balance sheet for each month Report on your cumulative cash generation/usage at the end of each month Report on your total profit for the entire 4 month period Compare total cash generation/usage vs. profits over the period


 Widget Case
Widget Case





