Question
With the ECB mode, if there is an error in a block of the transmitted ciphertext, only the corresponding plaintext block is affected. However, in
With the ECB mode, if there is an error in a block of the transmitted ciphertext, only the corresponding plaintext block is affected. However, in the CBC mode, this error propagates. Lets study the error propagation for CBC mode.
Given we have a cipher that first flips (i.e. convert 1 to 0 and 0 to 1) and then right shifts two bits (circular shift). If we use this cipher in encryption, then the decryption process would be left shift two bits and do a flip. We use this cipher with CBC mode. Assume we have a plaintext as following: 10101100 01110001 11000101, block size is 8. So the plaintext can be divided into three blocks. IV is 01000111. The basic CBC diagram is shown as following (25 points total)
Find ciphertext based on part (a) of the diagram. (5 points)
Generate the recovered plaintext based on part (b) of the diagram. Show your steps. The recovered plaintext should be same as the original plaintext (5 points)
Assuming No. 7 bit in the plaintext got bit error (i.e. flipped by accident), the plaintext becomes: 10101110 01110001 11000101. For this plaintext, find the ciphertext and the recovered plaintext again. (10 points)
Compare the results of the ciphertext and the recovered plaintext from b and c. How does one-bit difference in the first plaintext block affect the ciphertext result and recovered plaintext result? (5 points)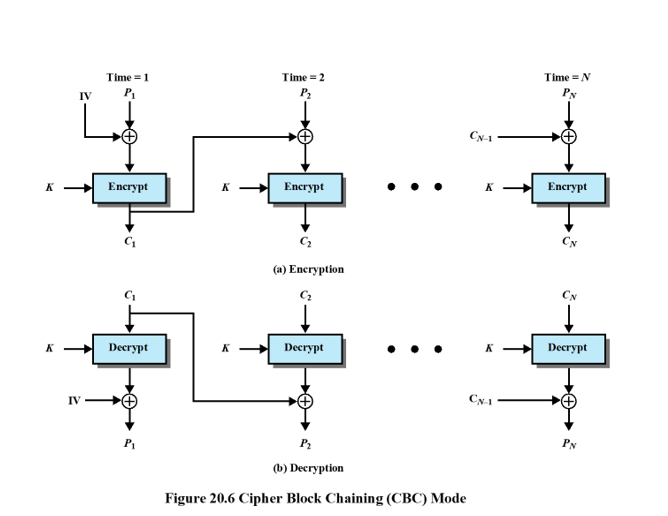
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


