Question: Write a C++ program consisting of the six related classes presented in the UML diagram below and complete the program with the provided driver program
Write a C++ program consisting of the six related classes presented in the UML diagram below and complete the program with the provided driver program (driver.cpp
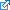 - no modifications are necessary).
- no modifications are necessary).
Examine the UML diagram closely to determine which parts are public and which are private, to determine what functions must be included in each class, and the type and the order of all arguments
Initialize all member variables via constructor calls and initializer lists
Define each class in a separate header (i.e., .h) file and begin and end each header file with an appropriate #ifndef and #endif preprocessor directive or you may use #pragma once
The Address and Date classes are simple and the same as those appearing in the Actor and Vet examples - you may copy them from the examples but notice that the relationships with Employee are reversed from those in the examples)
Employee class (see the Actor example and the Dog class in the vet example)
add variables to implement the class relationships with Date and Address (note that these variables are not shown in the diagram but are assumed from the connector lines; you must choose appropriate variable names). Take care to set the variable implementing the aggregation relation with Address to NULL (see the Dog initializer list)
constructor must initialize the name member variable and the composed Date (the Date information must be included with the Employee constructor arguments)
add a setAddress function as specified in the UML diagram (see the setShots function in dog.h of the vet example)
display function print the name and display the composed Date and aggregated Address by calling their display functions.
the operator
define a destructor that deletes the aggregated Address object (see the Dog class)
SalariedEmployeeconstructor
uses a_salary to initialize the salary member variable and all Date information
calls the Employee constructor and passes to it name and all Date information
display function and operator
must call the Employee display function and operator
must print the salary
SalesEmployeeconstructor
uses a_commission and a_sales arguments to initialize the commission and sales member variables respectively
calls the SalariedEmployee constructor and passes to it name, salary, and all Date information - see the vet example
display function and operator
must call the SalariedEmployee display function and operator
must print the commission and sales
WagedEmployee constructor calls the Employee constructor
uses a_wage and a_hours to initialize the wage and hours member variables respectively
calls the Employee constructor and passes to it name and the Date information
display function and operator
must call the Employee display function and operator
must print the wage and hours
***DRIVER.CPP***
#include "Employee.h"
#include "SalariedEmployee.h"
#include "SalesEmployee.h"
#include "WagedEmployee.h"
#include "Date.h"
#include "Address.h"
#include
#include
using namespace std;
void prompt(const char* message, string& variable);
void prompt(const char* message, int& number);
void prompt(const char* message, double& number);
int main()
{
while (true)
{
cout
cout
cout
cout
//cout
a future lab
cout
cout
char c;
cin >> c;
cin.ignore();
string name; // variables used by
all employee types
int year;
int month;
int day;
string street;
string city;
switch (c)
{ case '1' : // waged employee
{
double wage;
double hours;
prompt("Name", name);
prompt("Wage", wage);
prompt("Hours", hours);
prompt("Year", year);
prompt("Month", month);
prompt("Day", day);
prompt("Street", street);
prompt("City", city);
WagedEmployee* we = new
WagedEmployee(name, year, month, day, wage, hours);
we->setAddress(street,
city);
cout
we->display();
break;
}
case '2' : // salaried employee
{
double salary;
prompt("Name", name);
prompt("Salary", salary);
prompt("Year", year);
prompt("Month", month);
prompt("Day", day);
prompt("Street", street);
prompt("City", city);
SalariedEmployee* se = new
SalariedEmployee(name, year, month, day, salary);
se->setAddress(street,
city);
cout
se->display();
break;
}
case '3' : // sales employee
{
double salary;
double commission;
double sales;
prompt("Name", name);
prompt("Salary", salary);
prompt("Commission",
commission);
prompt("Sales", sales);
prompt("Year", year);
prompt("Month", month);
prompt("Day", day);
prompt("Street", street);
prompt("City", city);
SalesEmployee* se = new
SalesEmployee(name, year, month, day,
salary,
commission, sales);
se->setAddress(street,
city);
cout
se->display();
break;
}
//case '4' :
// break;
case '5' :
exit(0);
}
}
return 0;
}
void prompt(const char* message, string& variable)
{
cout
getline(cin, variable);
}
void prompt(const char* message, int& number)
{
cout
cin >> number;
cin.ignore(); // discard following number
}
void prompt(const char* message, double& number)
{
cout
cin >> number;
cin.ignore(); // discard following number
}
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


