Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Write a Python function to implement the k-Nearest Neighbors algorithm using Numpy 1. Write a Python function that uses the k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) algorithm

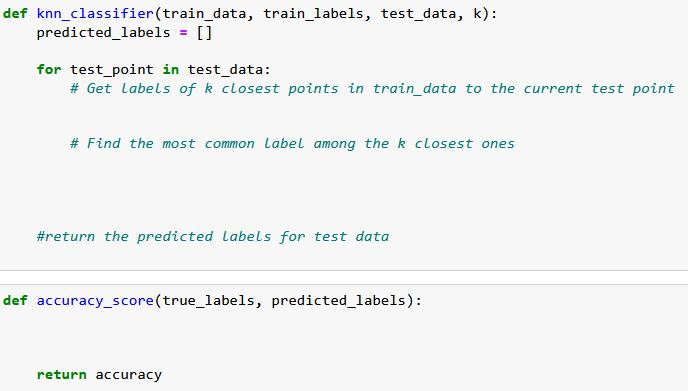
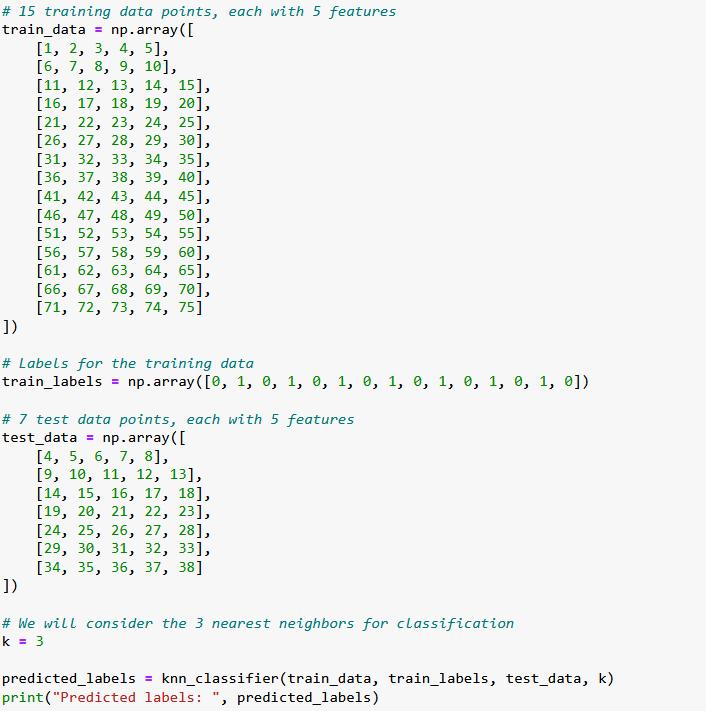
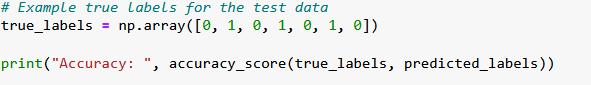
Write a Python function to implement the "k-Nearest Neighbors" algorithm using Numpy 1. Write a Python function that uses the k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN) algorithm to classify a given set of test data based on a given set of training data and labels. The function should be named knn_classifier and it should take four arguments: A. train_data: A 2D numpy array where each row is a separate data point in the training dataset. B. train_labels: A 1D numpy array where each element is the class label of the corresponding row in train_data. C. test_data: A 2D numpy array where each row is a separate data point in the test dataset. The function should predict and return class labels for these data points. D. k: The number of nearest neighbors to be considered. The knn_classifier function should return test_labels, a 1D numpy array where each element is the predicted class label of the corresponding row in test_data. Use the Euclidean distance to calculate the distance between data points. The class of each test point is determined by the class of k closest training points (in terms of Euclidean distance). If there's a tie in the voting process, break the tie by choosing the class with the closest representative among the k nearest neighbors. You may use the k_closest_points and closest_labels functions from the previous question in your implementation. You are not allowed to use any external libraries except for Numpy and Python's standard library. 2. Write a function accuracy_score that calculates and returns the accuracy of the knn_classifier function's predictions. The function should take two parameters: true_labels: The actual labels of the test data. predicted_labels: The labels predicted by the knn_classifier function. The accuracy score is the proportion of correct predictions over total predictions. def knn_classifier (train_data, train_labels, test_data, k): predicted labels = [] for test_point in test_data: # Get Labels of k closest points in train_data to the current test point # Find the most common Label among the k closest ones #return the predicted Labels for test data def accuracy_score (true_labels, predicted_labels): return accuracy # 15 training data points, each with 5 features train_data = np.array([ [1, 2, 3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8, 9, 10], [11, 12, 13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18, 19, 20], [21, 22, 23, 24, 25], [26, 27, 28, 29, 30], [31, 32, 33, 34, 35], [36, 37, 38, 39, 40], [41, 42, 43, 44, 45], [46, 47, 48, 49, 50], [51, 52, 53, 54, 55], [56, 57, 58, 59, 60], [61, 62, 63, 64, 65], [66, 67, 68, 69, 70], [71, 72, 73, 74, 75] ]) # Labels for the training data train_labels = np.array([0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]) # 7 test data points, each with 5 features test_data = np.array([ ]) [4, 5, 6, 7, 8], [9, 10, 11, 12, 13], [14, 15, 16, 17, 18], [19, 20, 21, 22, 23], [24, 25, 26, 27, 28], [29, 30, 31, 32, 33], [34, 35, 36, 37, 38] # We will consider the 3 nearest neighbors for classification k = 3 predicted_labels = knn_classifier (train_data, train_labels, test_data, k) print("Predicted labels: ", predicted_labels) # Example true Labels for the test data true_labels = np.array([0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0]) print("Accuracy: accuracy_score (true_labels, predicted_labels))
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


