Question: Write an abstract superclass encapsulating a shape. A shape has two abstract methods: one returning the perimeter of the shape one returning the area of
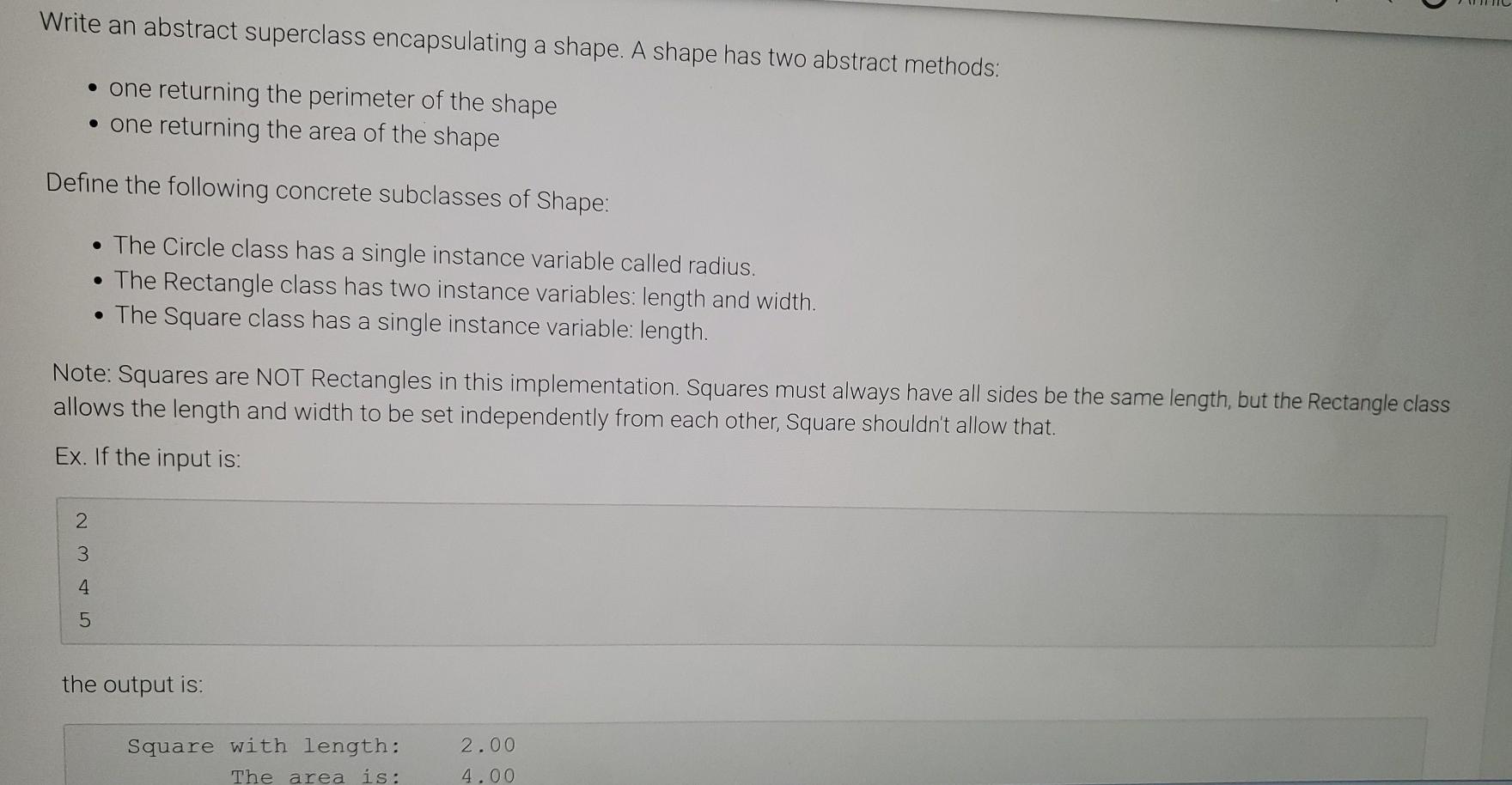
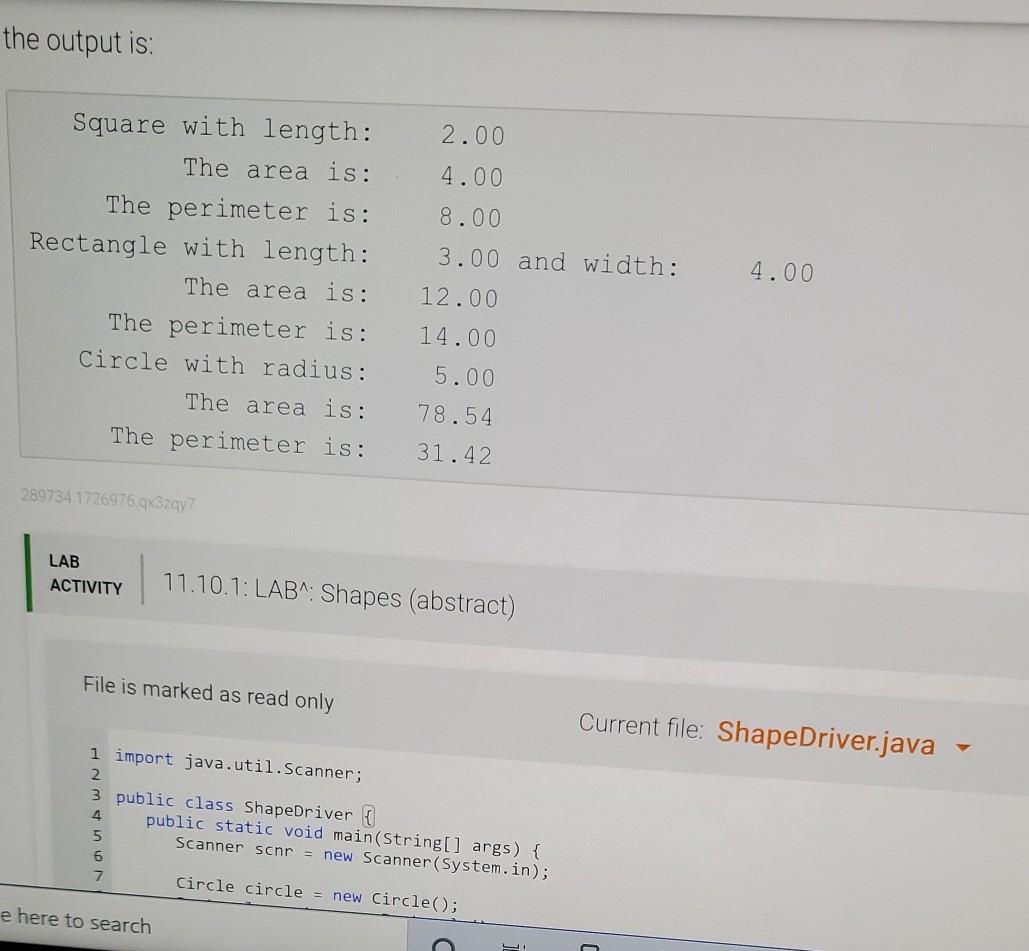
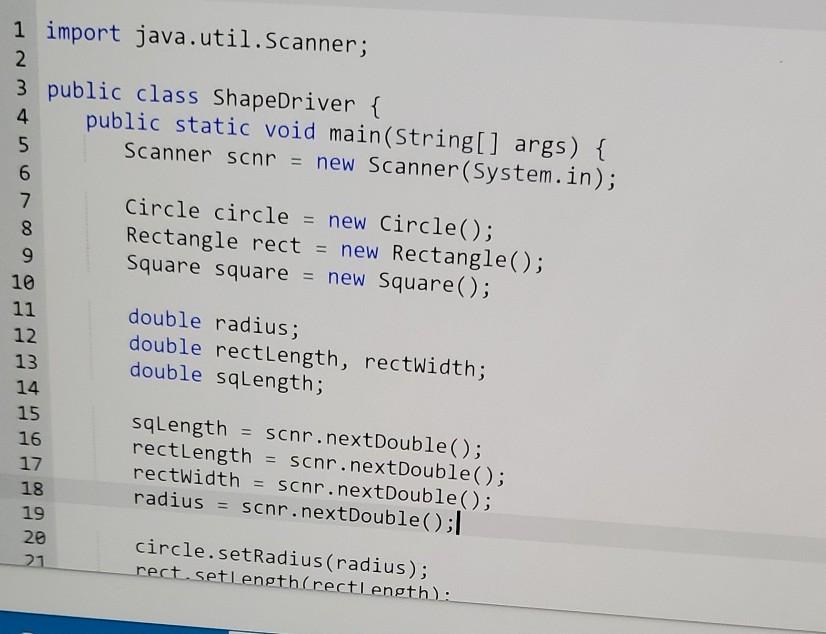
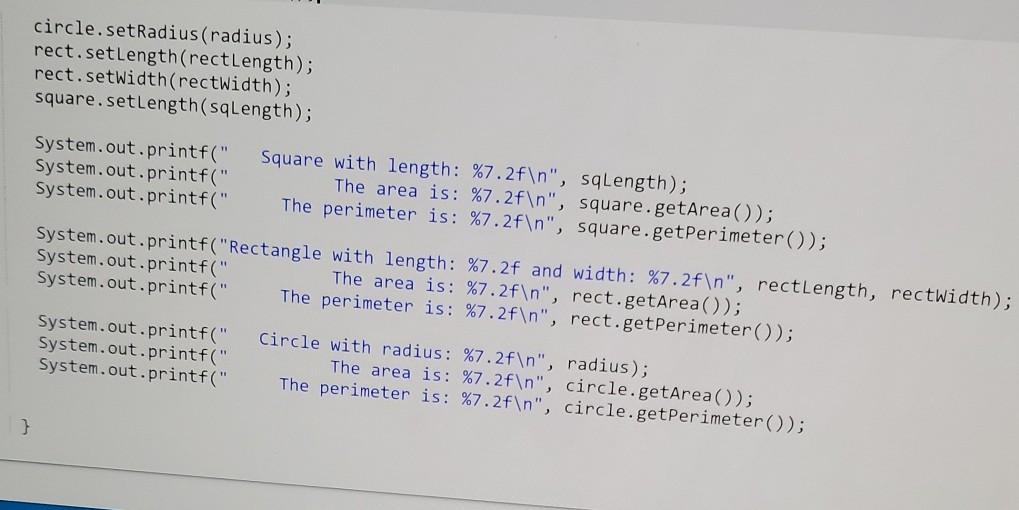
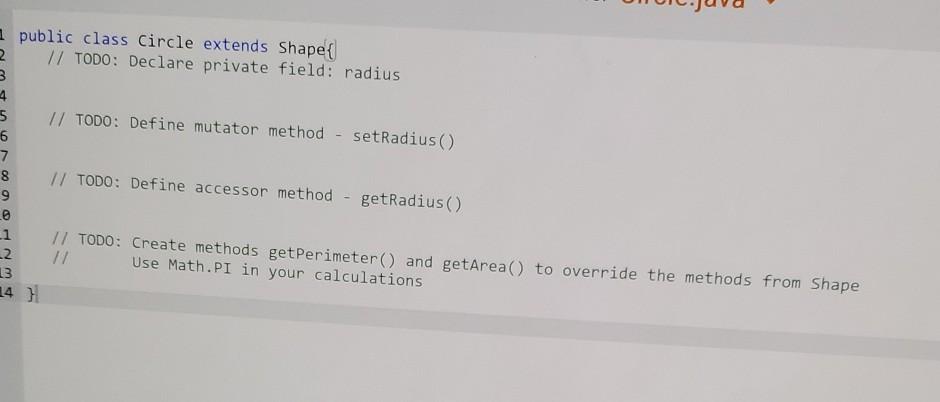
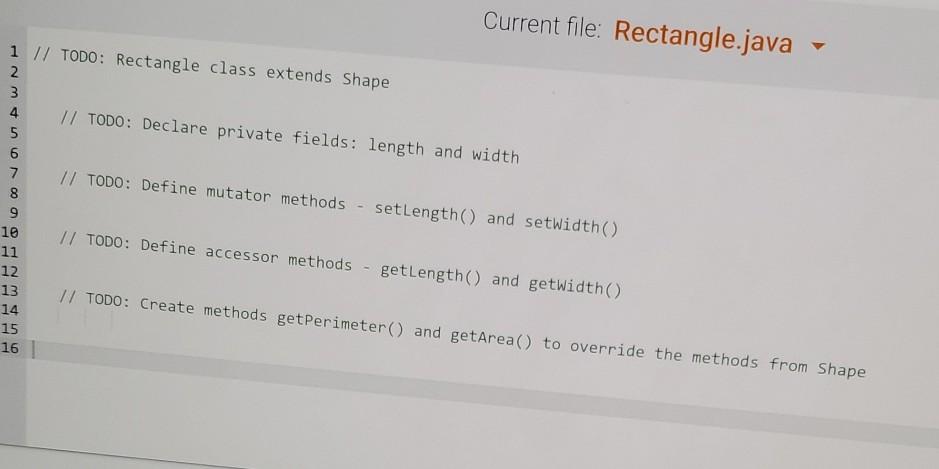
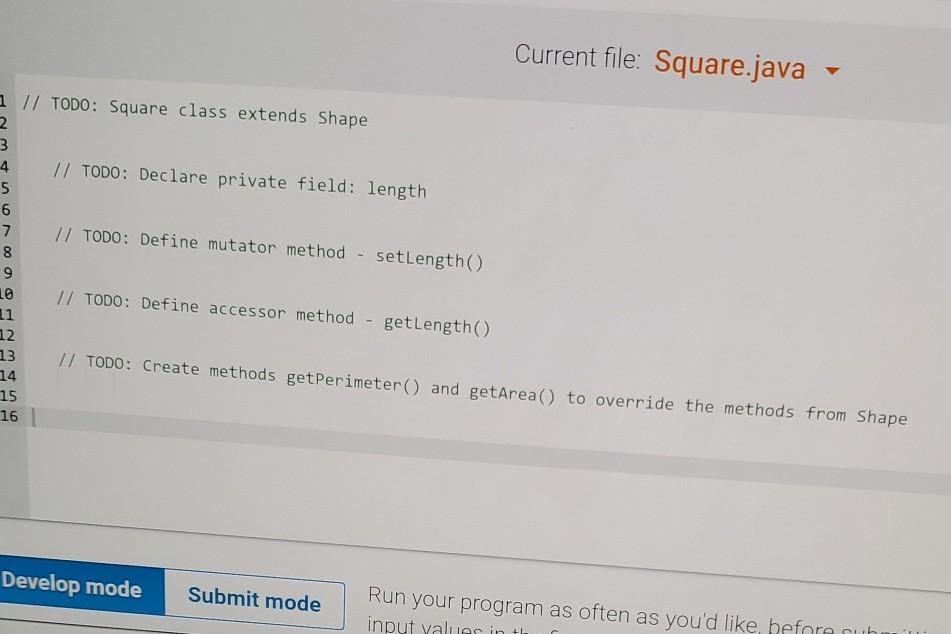
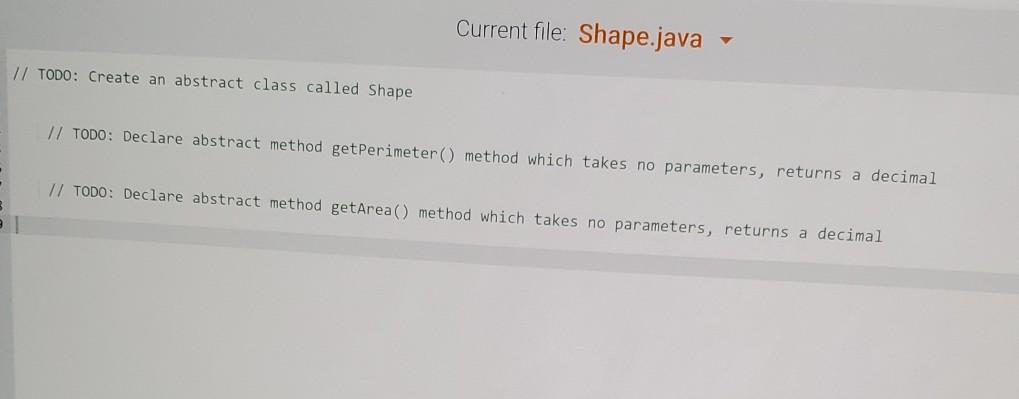
Write an abstract superclass encapsulating a shape. A shape has two abstract methods: one returning the perimeter of the shape one returning the area of the shape Define the following concrete subclasses of Shape: The Circle class has a single instance variable called radius. The Rectangle class has two instance variables: length and width. The Square class has a single instance variable: length. Note: Squares are NOT Rectangles in this implementation. Squares must always have all sides be the same length, but the Rectangle class allows the length and width to be set independently from each other, Square shouldn't allow that. Ex. If the input is: 2 3 4 5 the output is: Square with length: The area is: 2.00 4.00 the output is: Square with length: The area is: The perimeter is: Rectangle with length: The area is: The perimeter is: Circle with radius: The area is: The perimeter is: 4.00 2.00 4.00 8.00 3.00 and width: 12.00 14.00 5.00 78.54 31.42. 289734 1726976 qx3zqy7 LAB ACTIVITY 11.10.1: LAB: Shapes (abstract) File is marked as read only Current file: ShapeDriver.java 1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class ShapeDriver 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner scnr = new Scanner(System.in); 6 7 Circle circle = new Circle(); e here to search 1 import java.util.Scanner; 2 3 public class ShapeDriver { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 Scanner scnr = new Scanner(System.in); 6 7 Circle circle = new Circle(); 8 Rectangle rect = new Rectangle(); Square square = new Square(); 10 11 12 double rectLength, rectWidth; 13 9 double radius; double sqLength; 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 SqLength = scnr.nextDouble(); rectLength = scnr.nextDouble(); rectWidth = scnr.nextDouble(); radius = scnr.nextDouble(); 21 circle.setRadius (radius); rect.setlength(rectLength: circle.setRadius (radius); rect.setLength(rectLength); rect.setWidth(rectWidth); square.setLength(sqlength); System.out.printf(" System.out.printf(" System.out.printf(" Square with length: %7.2f ", sqLength); The area is: %7.2f ", square.getArea()); The perimeter is: %7.2f ", square.getPerimeter()); System.out.printf("Rectangle with length: %7.2f and width: %7.2f ", rectLength, rectWidth); System.out.printf(" The area is: %7.2f ", rect.getArea()); System.out.printf(" The perimeter is: %7.2f ", rect.getPerimeter(); System.out.printf(" System.out.printf(" System.out.printf(" Circle with radius: %7.2f ", radius); The area is: %7.2f ", circle.getArea()); The perimeter is: %7.2f ", circle.getPerimeter()); } public class Circle extends Shape{ // TODO: Declare private field: radius 2 3 4 5 6 // TODO: Define mutator method - setRadius() 7 8 9 // TODO: Define accessor method getRadius() NO // TODO: Create methods getPerimeter() and getArea() to override the methods from Shape Use Math.PI in your calculations 13 Current file: Rectangle.java 1 // TODO: Rectangle class extends Shape // TODO: Declare private fields: length and width // TODO: Define mutator methods 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 setLength() and setWidth() // TODO: Define accessor methods - getLength() and getWidth() // TODO: Create methods getPerimeter() and getArea() to override the methods from Shape Current file: Square.java 1 // TODO: Square class extends Shape 2. 3 4 // TODO: Declare private field: length 5 6 7 // TODO: Define mutator method - setLength() 8 9 10 // TODO: Define accessor method 11 getLength() 12 13 // TODO: Create methods getPerimeter() and getArea() to override the methods from Shape 14 15 16 Develop mode Submit mode Run your program as often as you'd like before ruhi input values in the -- Current file: Shape.java // TODO: Create an abstract class called Shape // TODO: Declare abstract method getPerimeter() method which takes no parameters, returns a decimal // TODO: Declare abstract method getArea() method which takes no parameters, returns a decimal
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


