Write in C++
Please make sure it works for negatives. I will upvote if your answer is correct

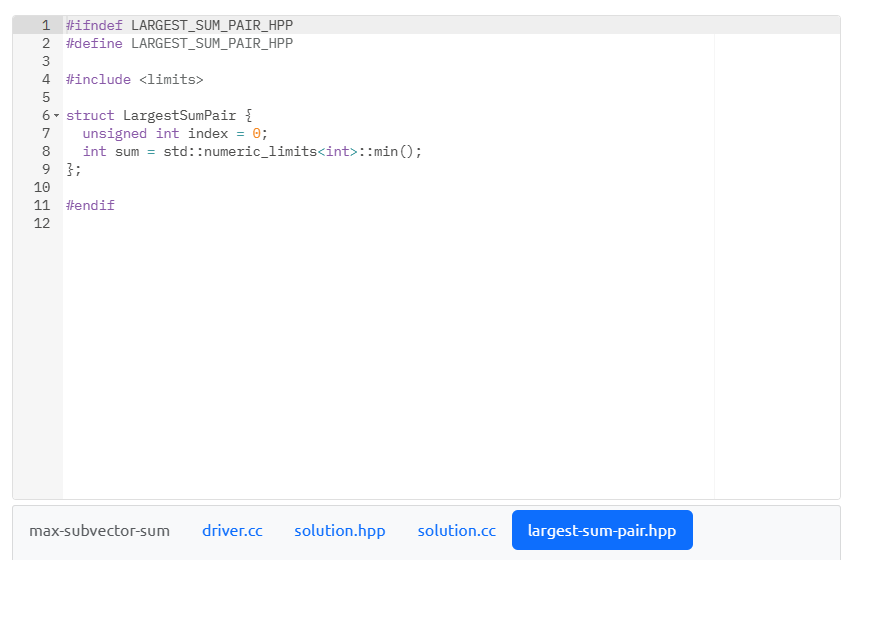
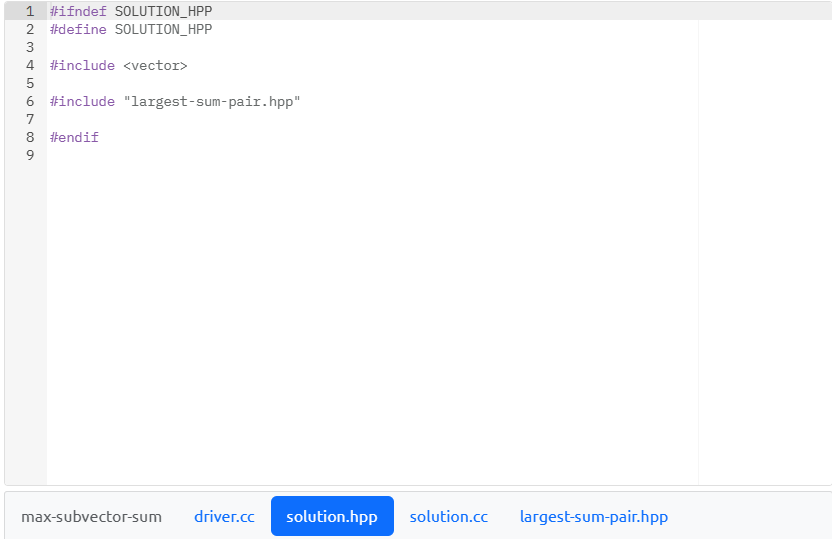
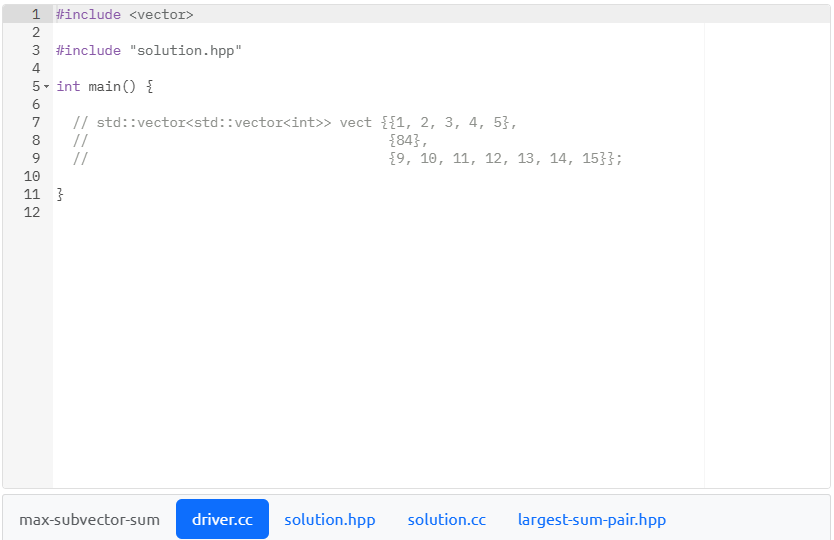
In this problem, using the C++ conventions introduced in the daily lessons, you will declare a function named LargestVectorSum in the header file (solution.hpp) and define this function in the corresponding source file (solution.cc). Your LargestVectorsum function must be defined with a single parameter, a two-dimensional std: :vector of ints; this function will return an object typed LargestSumpair. We define this structured type (i.e., the function's return type) in largest-sum-pair. hpp; please do not change that definition. Now that the return type and signature of Largestvectorsum have been specified, let's discuss what this function is to do and how the returned object will be composed. LargestVectorSum will examine the non-rectangular two-dimensional vector of integers passed to it subvector-bysubvector. For clarity: \( \begin{array}{rr}1 & \text { std: :vector> my_2d_vector }\{ \\ 2 & \{1,2,4\},\{4,1,-1\},\{6,8,-10,-9\},\{-1\}\} ; / / \text { declares + initializes a non-rectangu } \\ 3 & \text { my_2d_vector.at }(0) ; / / \text { returns the subvector }\{1,2,4\}\end{array} \) Your function will track the index into the subvector whose contents sum to the largest (most positive) integer value and record what that sum was. Keep in mind that the subvector may have positive and negative values. Since the two-dimensional vector is non-rectangular, you cannot assume that the subvectors contain an equal number of elements: the number of elements stored in one subvector can (and will) differ. If more than one subvector sums to the same value and that value is the largest sum, record the subvector with the smaller index. What does a smaller index mean? Given a two-dimensional vector indexed as vect. at(subvector_idx). at(subvector_ele_idx), we mean the subvector residing at the smaller value of subvector_idx. Once you're finished examining the twodimensional vector, create a new LargestSumPair object, initializing the data member index with the index to the subvector whose contents sum to the largest (most positive) integer value and sum with the sum calculated for that subvector. Assume the two-dimensional vector passed to your function will have at least one subvector. max-subvector-sum driver.cc solution.hpp solution.cc largest-sum-pair.hpp 12 max-subvector-sum driver.cc solution.hpp solution.cc largest-sum-pair.hpp max-subvector-sum driver.cc solution.hpp solution.cc largest-sum-pair.hpp \} max-subvector-sum driver.cc solution.hpp solution.cc largest-sum-pair.hpp In this problem, using the C++ conventions introduced in the daily lessons, you will declare a function named LargestVectorSum in the header file (solution.hpp) and define this function in the corresponding source file (solution.cc). Your LargestVectorsum function must be defined with a single parameter, a two-dimensional std: :vector of ints; this function will return an object typed LargestSumpair. We define this structured type (i.e., the function's return type) in largest-sum-pair. hpp; please do not change that definition. Now that the return type and signature of Largestvectorsum have been specified, let's discuss what this function is to do and how the returned object will be composed. LargestVectorSum will examine the non-rectangular two-dimensional vector of integers passed to it subvector-bysubvector. For clarity: \( \begin{array}{rr}1 & \text { std: :vector> my_2d_vector }\{ \\ 2 & \{1,2,4\},\{4,1,-1\},\{6,8,-10,-9\},\{-1\}\} ; / / \text { declares + initializes a non-rectangu } \\ 3 & \text { my_2d_vector.at }(0) ; / / \text { returns the subvector }\{1,2,4\}\end{array} \) Your function will track the index into the subvector whose contents sum to the largest (most positive) integer value and record what that sum was. Keep in mind that the subvector may have positive and negative values. Since the two-dimensional vector is non-rectangular, you cannot assume that the subvectors contain an equal number of elements: the number of elements stored in one subvector can (and will) differ. If more than one subvector sums to the same value and that value is the largest sum, record the subvector with the smaller index. What does a smaller index mean? Given a two-dimensional vector indexed as vect. at(subvector_idx). at(subvector_ele_idx), we mean the subvector residing at the smaller value of subvector_idx. Once you're finished examining the twodimensional vector, create a new LargestSumPair object, initializing the data member index with the index to the subvector whose contents sum to the largest (most positive) integer value and sum with the sum calculated for that subvector. Assume the two-dimensional vector passed to your function will have at least one subvector. max-subvector-sum driver.cc solution.hpp solution.cc largest-sum-pair.hpp 12 max-subvector-sum driver.cc solution.hpp solution.cc largest-sum-pair.hpp max-subvector-sum driver.cc solution.hpp solution.cc largest-sum-pair.hpp \} max-subvector-sum driver.cc solution.hpp solution.cc largest-sum-pair.hpp











