Question
write the function named roundTrip(). The function takes one input parameter: a vector of Stars that represents a travel itinerary. /** CS 150 Vectors and
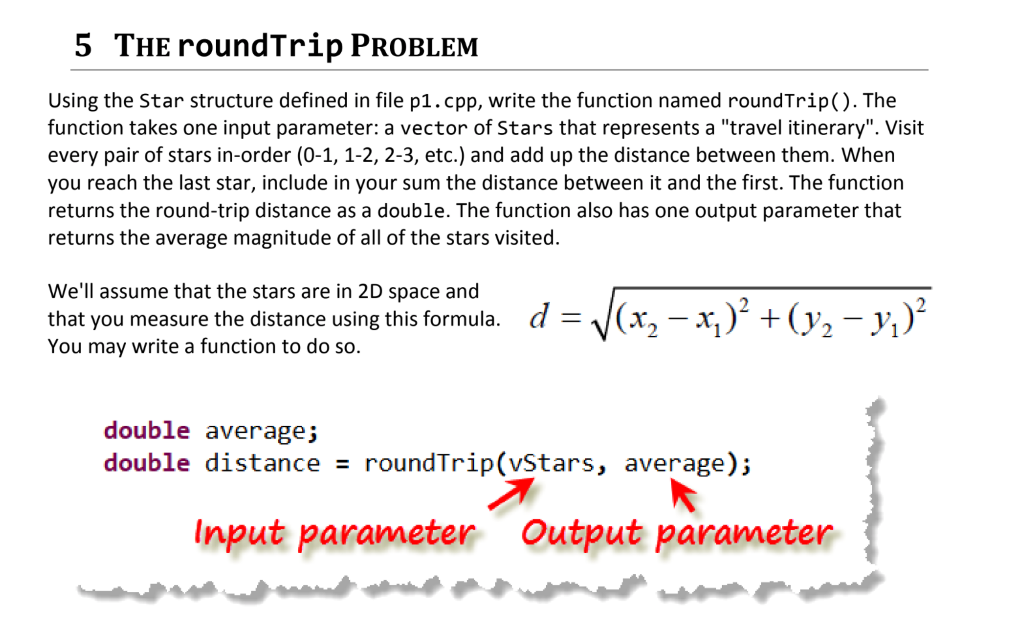
write the function named roundTrip(). The function takes one input parameter: a vector of Stars that represents a "travel itinerary".
/**
CS 150 Vectors and Structures
Below you'll find a definition for a Star structure
similar to the one we used in class, but a little simpler.
Write the function called starsInSector(), following the
instructions in your handout.
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
// The structure (don't change these)
struct Star {
double x, y;
double magnitude;
int draperNumber;
string names;
};
///////////////// WRITE YOUR FUNCTION BELOW THIS LINE ///////////////////////
function here
///////////////// WRITE YOUR FUNCTION ABOVE THIS LINE ///////////////////////
ostream& operator&);
void studentTests()
{
cout
cout
const vector
{-0.516566, -0.340233, 4.53, 124675, "BOO KAPPA"},
{-0.391537, 0.791148, 1.16, 62509, "POLLUX; GEM BETA"},
{-0.798418, 0.601749, 4.54, 82446, "HYA TAU"},
{0.544153, 0.174444, 4.34, 6961, "CAS THETA"},
{-0.843478, 0.099816, 3.54, 100407, "HYA XI"},
{-0.455459, -0.603227, 4.98, 138629, "BOO NU"},
{-0.298198, 0.387683, 3.35, 71369, "MUSCIDA; UMA OMICRON"},
{-0.696134, 0.155399, 3, 96833, "UMA PSI"},
{-0.916842, 0.246614, 4.08, 95272, "ALKES"},
{0.11301, 0.945279, 2.58, 36673, "ARNEB"},
{0.214075, -0.813927, 3.25, 176437, "SULAFAT; LYR GAMMA"},
{0.305802, 0.232677, 4.46, 15089, "CAS IOTA"},
{0.658924, -0.733896, 3.78, 198001, "ALBALI"},
{0.820248, 0.448325, 2.64, 11636, "SHERATAN"},
{-0.263867, 0.822592, 4.41, 54719, "GEM TAU"},
{0.148253, -0.755971, 5.37, 173608, "LYR EPSILON"},
{-0.741021, -0.628146, 3.78, 129246, "BOO ZETA"},
{-0.188502, -0.981846, 5.89, 156247, "U OPH"},
{0.147985, -0.755362, 6.02, 173583, "LYR EPSILON"},
{-0.317623, 0.871206, 3.5, 56986, "WASAT; GEM DELTA"},
};
vector
starsInSector(vStars, names, -1, -1);
cout
cout [BOO KAPPA, BOO NU, BOO ZETA, U OPH]"
cout "
cout
cout
}
ostream& operator& v)
{
out
int len = v.size();
if (len > 0)
{
out
for (int i = 1; i
out
}
out
return out;
}
5 THE roundTrip PROBLEM Using the Star structure defined in file p1.cpp, write the function named roundTrip(). The function takes one input parameter: a vector of Stars that represents a "travel itinerary". Visit every pair of stars in-order (0-1, 1-2, 2-3, etc.) and add up the distance between them. When you reach the last star, include in your sum the distance between it and the first. The function returns the round-trip distance as a double. The function also has one output parameter that returns the average magnitude of all of the stars visited. We'll assume that the stars are in 2D space and that you measure the distance using this formula. d-V(x,-x,) +(y2 -y) You may write a function to do so double average; double distance- roundTrip(vStars, average); Input parameter Output parameterStep by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


