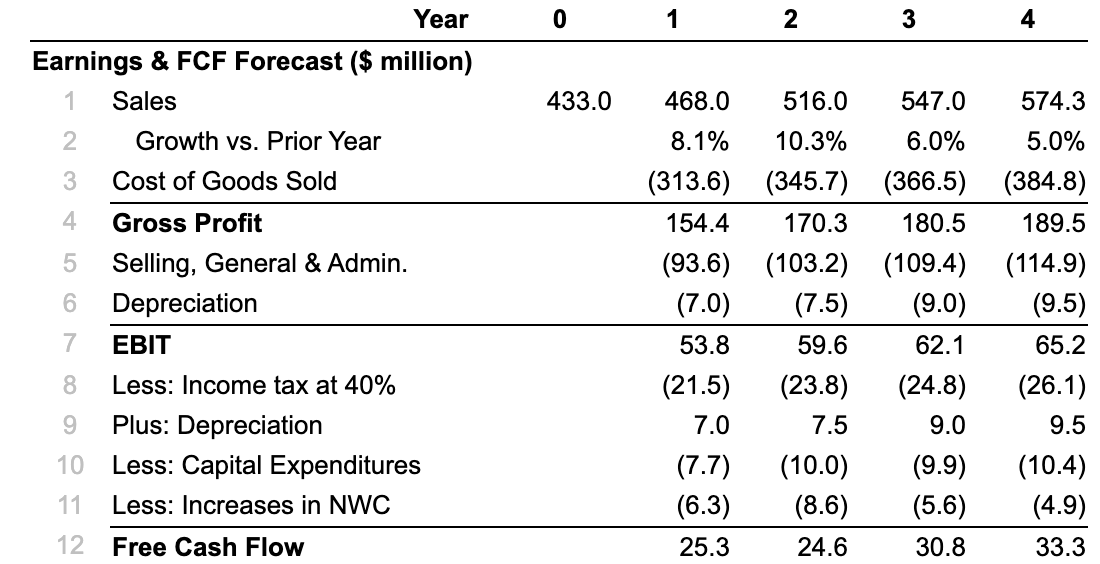
Year Earnings & FCF Forecast (5 million) 5:3(omwmmeMx Sales Growth vs. Prior Year Cost of Goods Sold Gross Profit Selling, General &Admin. Depreciation EBIT Less: Income tax at 40% Plus: Depreciation Less: Capital Expenditures Less: Increases in NWC Free Cash Flow 433.0 458.0 8.1% (313.5) 154.4 (93.5) (7.0) 53.8 (21.5) 7.0 (7.7) (6.3) 25.3 515.0 10.3% (345.7) 170.3 (103.2) (7.5) 59.5 (23.8) 7.5 (10.0) (8.5) 24.5 547.0 5.0% (355.5) 180.5 (109.4) (9.0) 52.1 (24.8) 9.0 (9.9) (5.5) 30.8 574.3 5.0% (384.8) 189.5 (114.9) (9.5) 55.2 (25.1) 9.5 (10.4) (4.9) 33.3 Sora Industries has 60 million outstanding shares, $121 million in debt, $55 million in cash, and the following projected free cash ow for the next four years. a. Suppose Sora's revenue and free cash ow are expected to grow at a 4.5% rate beyond year 4. If Sora's weighted average cost of capital is 13.0%, what is the value of Sora's stock based on this information? b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? c. Let's return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, now suppose Sora reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (which is their current level in year 0). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions remain as in part (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash ow in year 1.) The stock price for this case is $ 4.48 . (Round to two decimal places.) b. Sora's cost of goods sold was assumed to be 67% of sales. If its cost of goods sold is actually 70% of sales, how would the estimate of the stock's value change? The stock price for this case, when COGS increases, is $ 2.71 . (Round to two decimal places.) c. Let's return to the assumptions of part (a) and suppose Sora can maintain its cost of goods sold at 67% of sales. However, now suppose Sora reduces its selling, general, and administrative expenses from 20% of sales to 16% of sales. What stock price would you estimate now? (Assume no other expenses, except taxes, are affected.) The stock price for this case, when selling and SG&A costs decrease, is $ 6.83 . (Round to two decimal places.) d. Sora's net working capital needs were estimated to be 18% of sales (which is their current level in year 0). If Sora can reduce this requirement to 12% of sales starting in year 1, but all other assumptions remain as in part (a), what stock price do you estimate for Sora? (Hint: This change will have the largest impact on Sora's free cash ow in year 1.) The stock price for this case, when working capital needs are reduced, is $ . (Round to two decimal places.)