
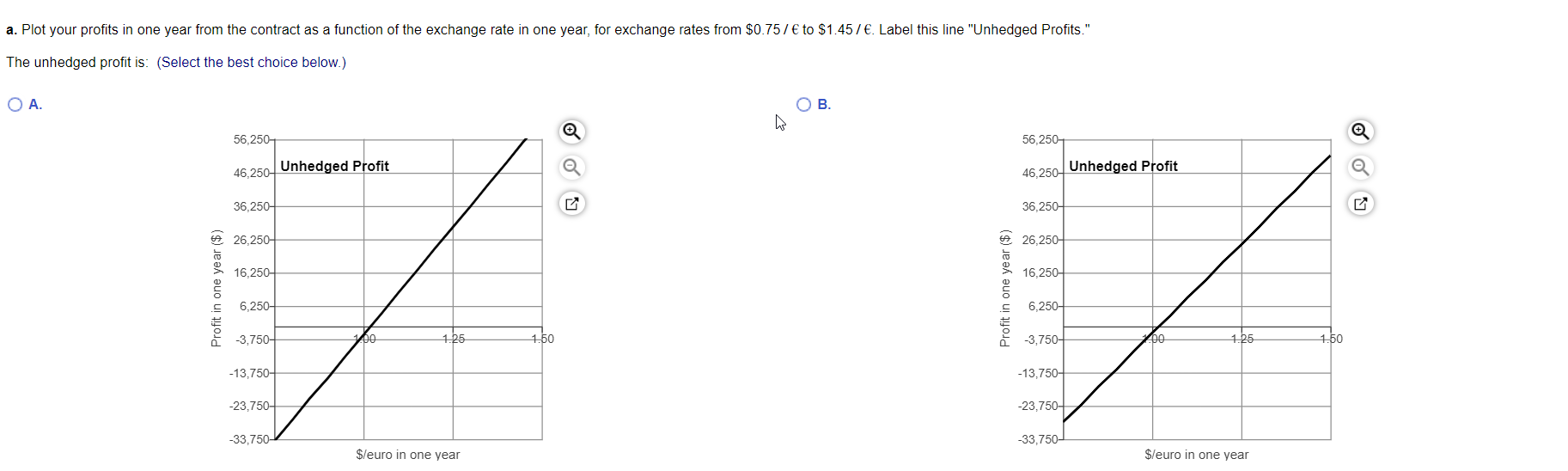
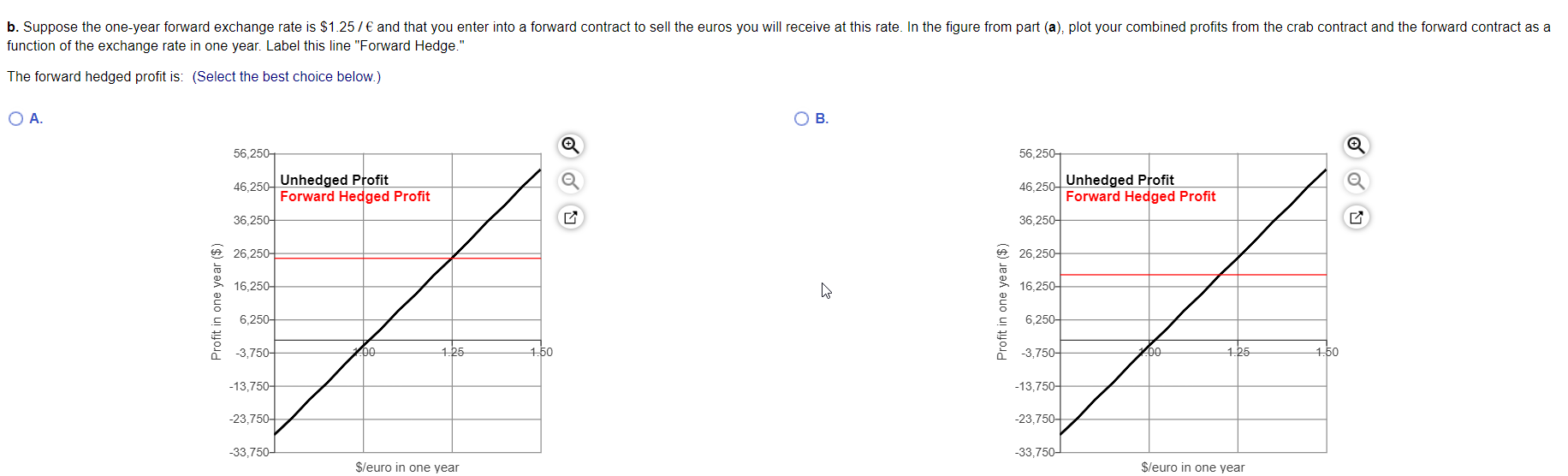
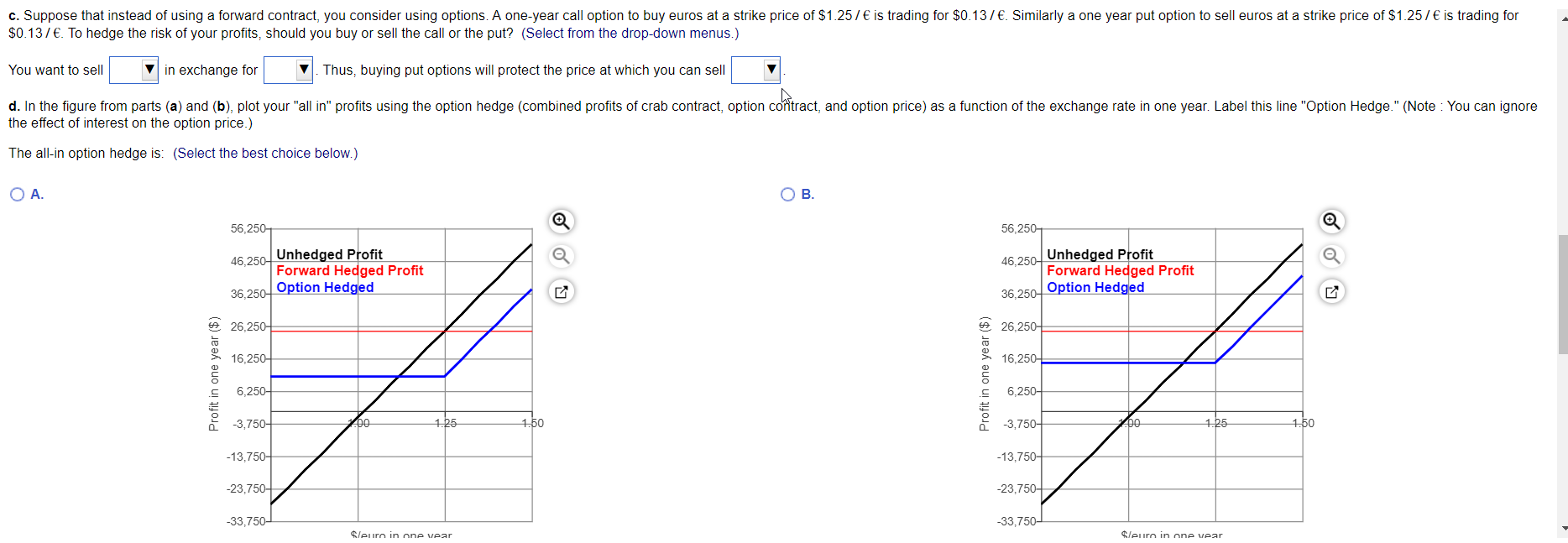

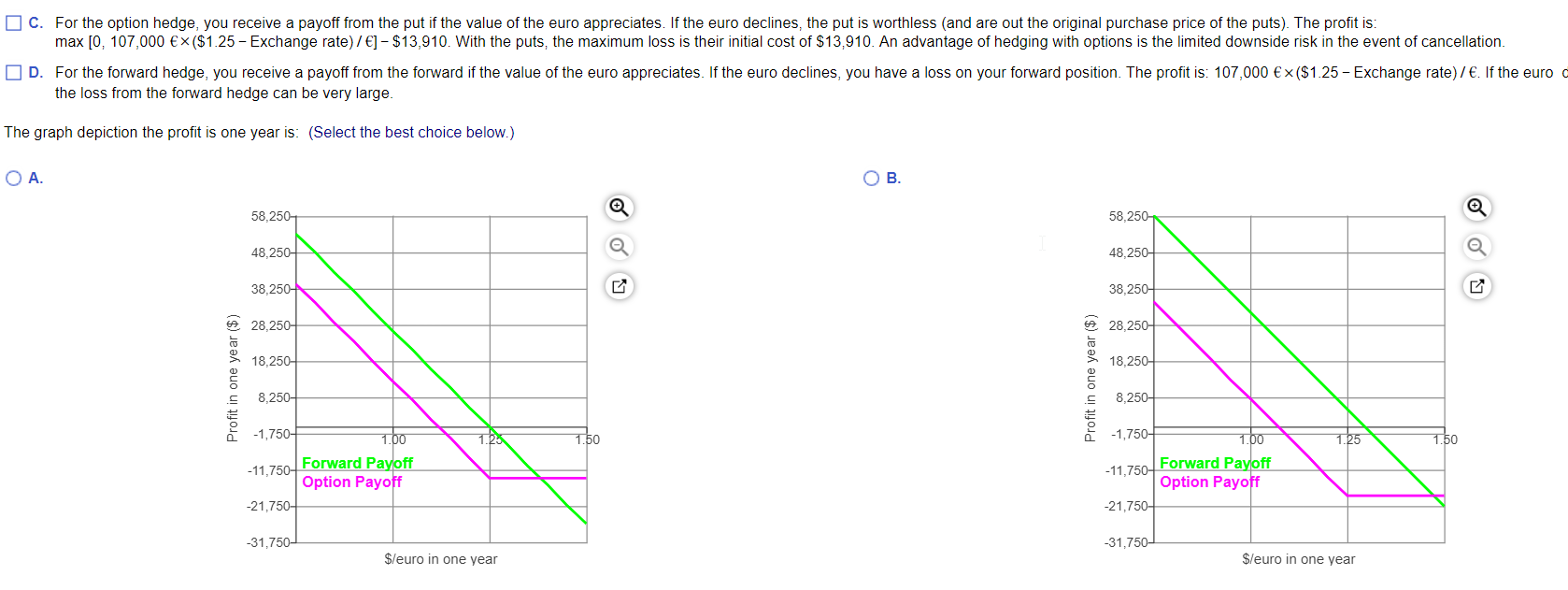
You are a broker for frozen seafood products for Choyce Products. You just signed a deal with a Belgian distributor. Under the terms of the contract, in one year you will deliver 4,000 kilograms of frozen king crab for 107,000 euros. Your cost for obtaining the king crab is $109,000. All cash flows occur in exactly one year. a. Plot your profits in one year from the contract as a function of the exchange rate in one year, for exchange rates from $0.75 / to $1.45/ . Label this line "Unhedged Profits." b. Suppose the one-year forward exchange rate is $1.25/ and that you enter into a forward contract to sell the euros you will receive at this rate. In the figure from part (a), plot your combined profits from the crab contract and the forward contract as a function of the exchange rate in one year. Label this line "Forward Hedge." c. Suppose that instead of using a forward contract, you consider using options. A one-year call option to buy euros at a strike price of $1.257 is trading for $0.137. Similarly a one year put option to sell euros at a strike price of $1.257 is trading for $0.137. To hedge the risk of your profits, should you buy or sell the call or the put? d. In the figure from parts (a) and (b), plot your "all in" profits using the option hedge (combined profits of crab contract, option contract, and option price) as a function of the exchange rate in one year. Label this line "Option Hedge." (Note: You can ignore the effect of interest on the option price.) e. Suppose that by the end of the year, a trade war erupts, leading to a European embargo on U.S. food products. As a result, your deal is cancelled, and you don't receive the euros or incur the costs of procuring the crab. However, you still have the profits (or losses) associated with your forward or options contract. In a new figure, plot the profits associated with the forward hedge and the options hedge (labeling each line). When there is a risk of cancellation, which type of hedge has the least downside risk? Explain briefly. " a. Plot your profits in one year from the contract as a function of the exchange rate in one year, for exchange rates from $0.75/ to $1.457 . Label this line "Unhedged Profits." The unhedged profit is: (Select the best choice below.) . B. 56,250 56,250 46,250 Unhedged Profit 46,250 Unhedged Profit 36,250 36,250 6 26,250 26,250 16.250 16,250 Profit in one year ($) Profit in one year ($) 6,250 6,250- -3,750- Do 1.25 1.50 -3,750- 00 1.25 1.50 -13,750 -13,750- -23.750- -23,750+ -33,750- -33,750- $/euro in one year $/euro in one year b. Suppose the one-year forward exchange rate is $1.25/ and that you enter into a forward contract to sell the euros you will receive at this rate. In the figure from part (a), plot your combined profits from the crab contract and the forward contract as a function of the exchange rate in one year. Label this line "Forward Hedge." The forward hedged profit is: (Select the best choice below.) OA B. 56,250 56,250 46,250+ Unhedged Profit Forward Hedged Profit 36,250 46,250 Unhedged Profit Forward Hedged Profit 36,250 26,250 6 26,250 16,250 W 16,250 Profit in one year ($) Profit in one year ($) 6,250- 6,250- -3,750- po 1.25 1.50 -3,750- 00 1.25 1.50 -13,750- -13,750- -23,750-4 -23,750+ -33,750 -33,750- $/euro in one year $/euro in one year c. Suppose that instead of using a forward contract, you consider using options. A one-year call option to buy euros at a strike price of $1.25/ is trading for $0.137 . Similarly a one year put option to sell euros at a strike price of $1.25/ is trading for $0.137. To hedge the risk of your profits, should you buy or sell the call or the put? (Select from the drop-down menus.) You want to sell v in exchange for V. Thus, buying put options will protect the price at which you can sell d. In the figure from parts (a) and (b), plot your "all in" profits using the option hedge (combined profits of crab contract, option contract, and option price) as a function of the exchange rate in one year. Label this line "Option Hedge." (Note: You can ignore the effect of interest on the option price.) The all-in option hedge is: (Select the best choice below.) OA OB. 56,250-1 56,2501 46,250- Unhedged Profit Forward Hedged Profit 36,250 Option Hedged 46,250 Unhedged Profit Forward Hedged Profit 36,250 Option Hedged 26,250 26,250- 16,250-4 16,250 Profit in one year ($) Profit in one year ($) 6,250 6,250- -3,750 200 1.25 1.50 -3,750- 200 1.25 1.50 -13,750- -13,750- -23,750+ -23,750- -33,750- -33,750- leur in one vear leur in one vear e. Suppose that by the end of the year, a trade war erupts, leading to a European embargo on U.S. food products. As a result, your deal is cancelled, and you don't receive the euros or incur the costs of procuring the crab. However, you still have the profits (or losses) associated with your forward or options contract. In a new figure, plot the profits associated with the forward hedge and the options hedge (labeling each line). When there is a risk of cancellation, which type of hedge has the least downside risk Explain briefly (Select all the choices that apply.) A. For the option hedge, you receive a payoff from the put if the value of the euro declines. If the euro appreciates, the put is worthless (and are out the original purchase price of the puts). The profit is: max [0, 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / ] - $13,910. With the puts, the maximum loss is their initial cost of $13,910. An advantage of hedging with options is the limited downside risk in the event of cancellation. B. For the forward hedge, you receive a payoff from the forward if the value of the euro declines. If the euro appreciates, you have a loss on your forward position. The profit is: 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / . If the euro appreciates significantly, the loss from the forward hedge can be very large. O C. For the option hedge, you receive a payoff from the put if the value of the euro appreciates. If the euro declines, the put is worthless (and are out the original purchase price of the puts). The profit is: max [0, 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / ] - $13,910. With the puts, the maximum loss is their initial cost of $13,910. An advantage of hedging with options is the limited downside risk in the event of cancellation. D. For the forward hedge, you receive a payoff from the forward if the value of the euro appreciates. If the euro declines, you have a loss on your forward position. The profit is: 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / . If the euro declines significantly, the loss from the forward hedge can be very large. O C. For the option hedge, you receive a payoff from the put if the value of the euro appreciates. If the euro declines, the put is worthless (and are out the original purchase price of the puts). The profit is: max [0, 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / ] - $13,910. With the puts, the maximum loss is their initial cost of $13,910. An advantage of hedging with options is the limited downside risk in the event of cancellation. D. For the forward hedge, you receive a payoff from the forward if the value of the euro appreciates. If the euro declines, you have a loss on your forward position. The profit is: 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / . If the euro the loss from the forward hedge can be very large. The graph depiction the profit is one year is: (Select the best choice below.) OA. . 58,250 58.250 48,250- 48.250 38,250- 38,250 28,2504 6 28,250- 18,250 18,250 Profit in one year ($) Profit in one year ($) 8,2504 8,250- 1.25 1.50 -1,750- 1.00 1.25 1.50 -1,750- 1.00 -11,750 Forward Payoff Option Payoff -21,750 -11,750 Forward Payoff Option Payoff -21,7507 -31,750- -31,750 $/euro in one year $/euro in one year You are a broker for frozen seafood products for Choyce Products. You just signed a deal with a Belgian distributor. Under the terms of the contract, in one year you will deliver 4,000 kilograms of frozen king crab for 107,000 euros. Your cost for obtaining the king crab is $109,000. All cash flows occur in exactly one year. a. Plot your profits in one year from the contract as a function of the exchange rate in one year, for exchange rates from $0.75 / to $1.45/ . Label this line "Unhedged Profits." b. Suppose the one-year forward exchange rate is $1.25/ and that you enter into a forward contract to sell the euros you will receive at this rate. In the figure from part (a), plot your combined profits from the crab contract and the forward contract as a function of the exchange rate in one year. Label this line "Forward Hedge." c. Suppose that instead of using a forward contract, you consider using options. A one-year call option to buy euros at a strike price of $1.257 is trading for $0.137. Similarly a one year put option to sell euros at a strike price of $1.257 is trading for $0.137. To hedge the risk of your profits, should you buy or sell the call or the put? d. In the figure from parts (a) and (b), plot your "all in" profits using the option hedge (combined profits of crab contract, option contract, and option price) as a function of the exchange rate in one year. Label this line "Option Hedge." (Note: You can ignore the effect of interest on the option price.) e. Suppose that by the end of the year, a trade war erupts, leading to a European embargo on U.S. food products. As a result, your deal is cancelled, and you don't receive the euros or incur the costs of procuring the crab. However, you still have the profits (or losses) associated with your forward or options contract. In a new figure, plot the profits associated with the forward hedge and the options hedge (labeling each line). When there is a risk of cancellation, which type of hedge has the least downside risk? Explain briefly. " a. Plot your profits in one year from the contract as a function of the exchange rate in one year, for exchange rates from $0.75/ to $1.457 . Label this line "Unhedged Profits." The unhedged profit is: (Select the best choice below.) . B. 56,250 56,250 46,250 Unhedged Profit 46,250 Unhedged Profit 36,250 36,250 6 26,250 26,250 16.250 16,250 Profit in one year ($) Profit in one year ($) 6,250 6,250- -3,750- Do 1.25 1.50 -3,750- 00 1.25 1.50 -13,750 -13,750- -23.750- -23,750+ -33,750- -33,750- $/euro in one year $/euro in one year b. Suppose the one-year forward exchange rate is $1.25/ and that you enter into a forward contract to sell the euros you will receive at this rate. In the figure from part (a), plot your combined profits from the crab contract and the forward contract as a function of the exchange rate in one year. Label this line "Forward Hedge." The forward hedged profit is: (Select the best choice below.) OA B. 56,250 56,250 46,250+ Unhedged Profit Forward Hedged Profit 36,250 46,250 Unhedged Profit Forward Hedged Profit 36,250 26,250 6 26,250 16,250 W 16,250 Profit in one year ($) Profit in one year ($) 6,250- 6,250- -3,750- po 1.25 1.50 -3,750- 00 1.25 1.50 -13,750- -13,750- -23,750-4 -23,750+ -33,750 -33,750- $/euro in one year $/euro in one year c. Suppose that instead of using a forward contract, you consider using options. A one-year call option to buy euros at a strike price of $1.25/ is trading for $0.137 . Similarly a one year put option to sell euros at a strike price of $1.25/ is trading for $0.137. To hedge the risk of your profits, should you buy or sell the call or the put? (Select from the drop-down menus.) You want to sell v in exchange for V. Thus, buying put options will protect the price at which you can sell d. In the figure from parts (a) and (b), plot your "all in" profits using the option hedge (combined profits of crab contract, option contract, and option price) as a function of the exchange rate in one year. Label this line "Option Hedge." (Note: You can ignore the effect of interest on the option price.) The all-in option hedge is: (Select the best choice below.) OA OB. 56,250-1 56,2501 46,250- Unhedged Profit Forward Hedged Profit 36,250 Option Hedged 46,250 Unhedged Profit Forward Hedged Profit 36,250 Option Hedged 26,250 26,250- 16,250-4 16,250 Profit in one year ($) Profit in one year ($) 6,250 6,250- -3,750 200 1.25 1.50 -3,750- 200 1.25 1.50 -13,750- -13,750- -23,750+ -23,750- -33,750- -33,750- leur in one vear leur in one vear e. Suppose that by the end of the year, a trade war erupts, leading to a European embargo on U.S. food products. As a result, your deal is cancelled, and you don't receive the euros or incur the costs of procuring the crab. However, you still have the profits (or losses) associated with your forward or options contract. In a new figure, plot the profits associated with the forward hedge and the options hedge (labeling each line). When there is a risk of cancellation, which type of hedge has the least downside risk Explain briefly (Select all the choices that apply.) A. For the option hedge, you receive a payoff from the put if the value of the euro declines. If the euro appreciates, the put is worthless (and are out the original purchase price of the puts). The profit is: max [0, 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / ] - $13,910. With the puts, the maximum loss is their initial cost of $13,910. An advantage of hedging with options is the limited downside risk in the event of cancellation. B. For the forward hedge, you receive a payoff from the forward if the value of the euro declines. If the euro appreciates, you have a loss on your forward position. The profit is: 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / . If the euro appreciates significantly, the loss from the forward hedge can be very large. O C. For the option hedge, you receive a payoff from the put if the value of the euro appreciates. If the euro declines, the put is worthless (and are out the original purchase price of the puts). The profit is: max [0, 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / ] - $13,910. With the puts, the maximum loss is their initial cost of $13,910. An advantage of hedging with options is the limited downside risk in the event of cancellation. D. For the forward hedge, you receive a payoff from the forward if the value of the euro appreciates. If the euro declines, you have a loss on your forward position. The profit is: 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / . If the euro declines significantly, the loss from the forward hedge can be very large. O C. For the option hedge, you receive a payoff from the put if the value of the euro appreciates. If the euro declines, the put is worthless (and are out the original purchase price of the puts). The profit is: max [0, 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / ] - $13,910. With the puts, the maximum loss is their initial cost of $13,910. An advantage of hedging with options is the limited downside risk in the event of cancellation. D. For the forward hedge, you receive a payoff from the forward if the value of the euro appreciates. If the euro declines, you have a loss on your forward position. The profit is: 107,000 ($1.25 - Exchange rate) / . If the euro the loss from the forward hedge can be very large. The graph depiction the profit is one year is: (Select the best choice below.) OA. . 58,250 58.250 48,250- 48.250 38,250- 38,250 28,2504 6 28,250- 18,250 18,250 Profit in one year ($) Profit in one year ($) 8,2504 8,250- 1.25 1.50 -1,750- 1.00 1.25 1.50 -1,750- 1.00 -11,750 Forward Payoff Option Payoff -21,750 -11,750 Forward Payoff Option Payoff -21,7507 -31,750- -31,750 $/euro in one year $/euro in one year












