Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
You will write your own version of the String class and call it the MyString class. Your MyString class will have only one data member:
You will write your own version of the String class and call it the MyString class. Your MyString class will have only one data member:
private char[] letters;
It will be a very simplified version which will implement only these public methods: (you may write private helper methods)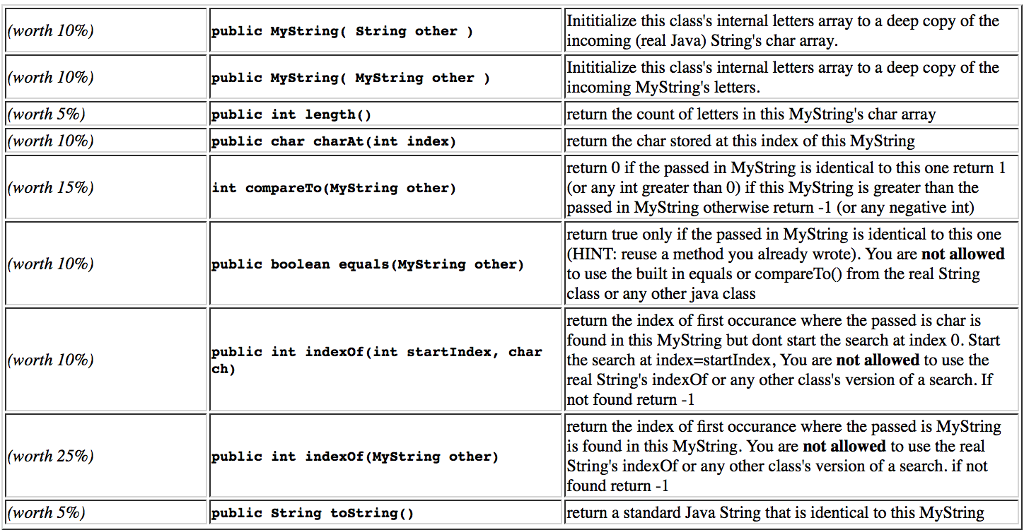
Here is the starter file that is to be modified:
public class MyString { private char[] letters; public MyString( String other ) { // MUST BE DEEP COPY: USE REAL STRING'S BUILT IN METHOD // TO RETURN A DEEP COPY OF THE THE UNDERLYING CHAR ARRAY } public MyString( MyString other ) { // RE-USE THE ABOVE CONSTRUCTOR. // LIKE FRACTION CONSTRUCTORS - RE-USED THE FULL CONSTRUCTOR } public int length() { return 0; } public char charAt(int index) // IF INDEX OUT OF BOUNDS. EXIT PROGRAM! (dont return the null char) { return '\0'; // THE null CHAR JUST TO MAKE It COMPILE } int compareTo(MyString other) { return 0; } public boolean equals(MyString other) { return false; } // LOOKING for c but starting at [startIndex], not at [0] // You should use this in your other Indexof Method public int indexOf(int startIndex, char ch) { return -1; } public int indexOf(MyString other) { // RE-USE the indexOf( int startIndex, char ch) method above in here return -1; } public String toString() { return null; } } // END MYSTRING CLASS Here is the tester file DO NOT MODIFY:
public class MyStringTester { public static void main( String[] args ) { MyString s1 = new MyString("Hello World"); System.out.println( "s1=" + s1 ); MyString s2 = new MyString(s1); System.out.println( "s2=" + s2 ); if ( s1.equals( s2 ) ) System.out.println( s1 + " identical to " + s2 ); else System.out.println( s1 + " not identical to " + s2 ); MyString s3 = new MyString( "GoodBye World" ); System.out.println( "s3='" + s3 + "' and its length is: " + s3.length() ); if ( s1.equals( s3 ) ) System.out.println( s2 + " identical to " + s3 ); else System.out.println( s1 + " not identical to " + s3 ); s1=new MyString("albert"); s2=new MyString("alpha"); System.out.println( "s1=" + s1 + " s2=" + s2 ); System.out.println( "s1.compareTo(s2) ==> " + s1.compareTo(s2) ); // since "albert" " + s1.compareTo(s2) ); // since "zebrano" > "zebra" returns 1 s1=new MyString("cattle"); s2=new MyString("catty"); System.out.println( "s1=" + s1 + " s2=" + s2 ); System.out.println( "s1.compareTo(s2) ==> " + s1.compareTo(s2) ); // since "cattle" " + s1.compareTo(s2) ); // returns 0 they are same string value System.out.println( "[4]'th letter of " + s3 + " is " + s3.charAt(4) ); MyString key = new MyString("rld"); System.out.println( key + " found in " + s3 + " at index: " + s3.indexOf( key ) ); // SAME THING BUT WITHOUT USING A MyString VAR FOR THE KEY System.out.println( new MyString("Goo") + " found in " + s3 + " at index: " + s3.indexOf( new MyString("Goo") ) ); System.out.println( new MyString("Bye") + " found in " + s3 + " at index: " + s3.indexOf( new MyString("Bye") ) ); System.out.println( new MyString("zorp") + " found in " + s3 + " at index: " + s3.indexOf( new MyString("zorp") ) ); } } 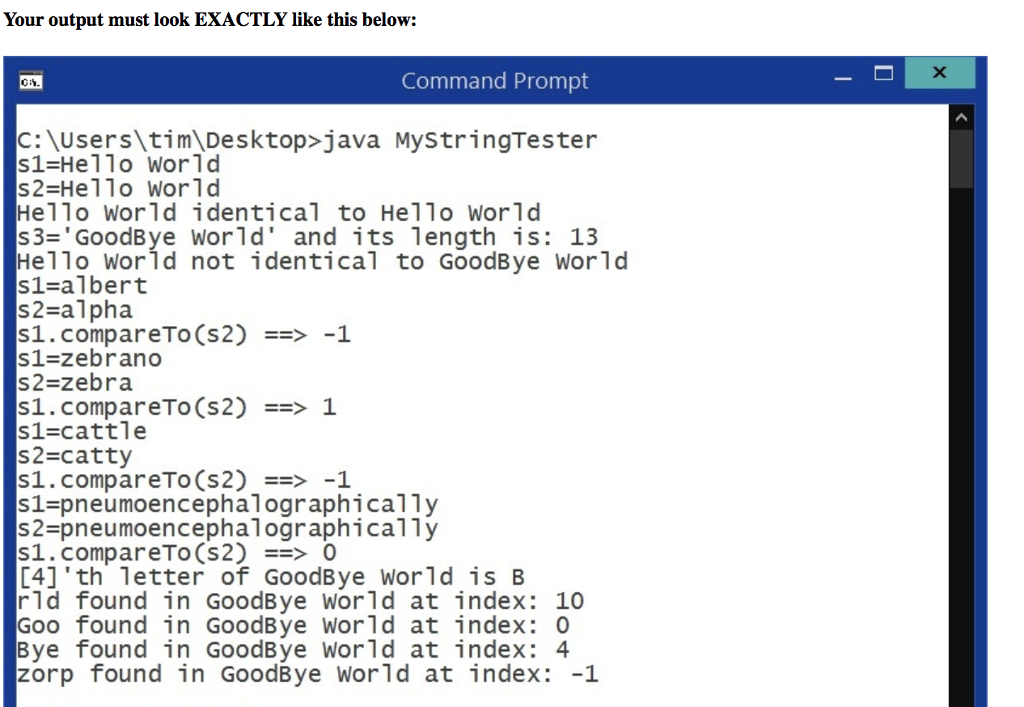
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


