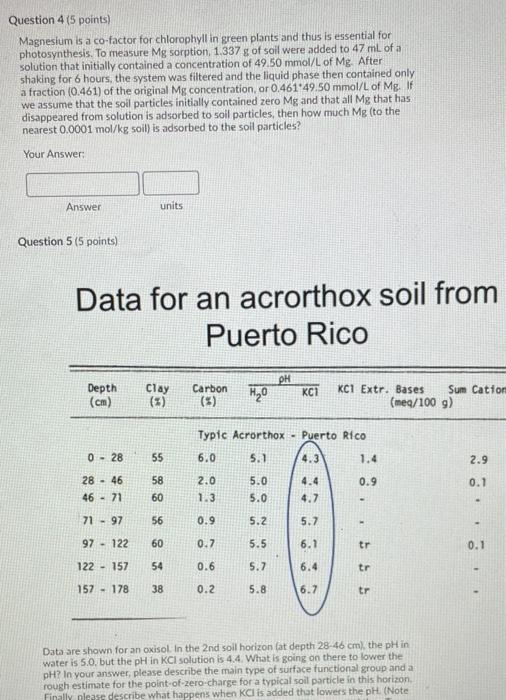
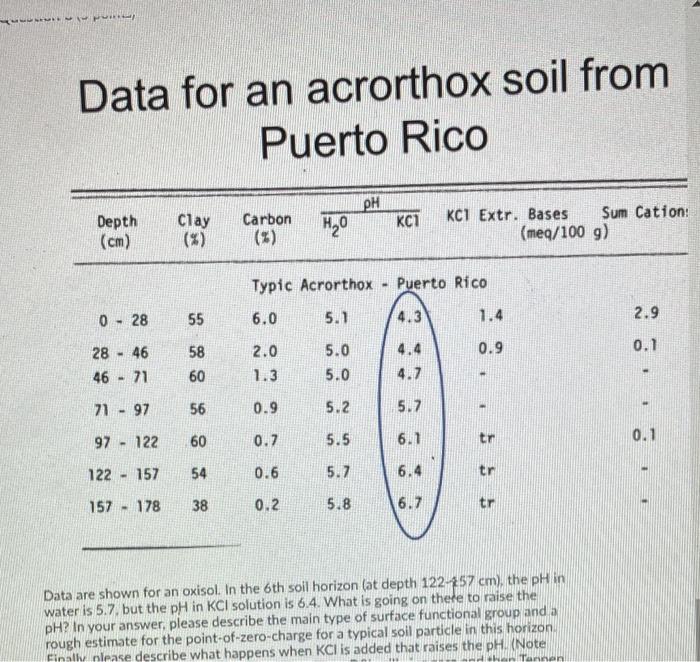
You wish to make a phosphate solution for sorption studies so you dissolve 2.50 grams potassium dihydrogen phosphate in water as follows (it is completely soluble KH2PO46) -> K+ (aq) + H2PO4 (aq) After the salt is fully dissolved, the volume is made up to 700 ml. What is the concentration of the resulting solution in moles P per Lof solution? > Your Answer: Answer units Question 2 (4 points) You wish to make a phosphate standard solution for sorption studies that is initially 45 ppm P, and you plan to dissolve sodium dihydrogen phosphate salt in water as follows (it is completely soluble): NaH2PO43) -> Na*(aq) + H2PO4 (aa) The meaning of 45 ppm Pin solution is 45 mg P per kg solution, which in this case) is very close to 45 mg P per L solution. We use mg Prather than ing phosphate because the molecular weight of phosphate depends on pH and other factors, After the salt is fully dissolved, the volume will be made up to 150 mL How much NaH2PO4 salt (in mg) should you weigh out to make a final solution that contains 45 ppm P Your Answer: Answer units Question 3 (5 points) Magnesium is a co-factor for chlorophyll in green plants and thus is essential for photosynthesis. To measure Mg sorption, 0.541 g of soil were added to 0.0418 L of a solution that initially contained a concentration of 45,89 mmol/L of Mg. After shaking for 6 hours, the system was filtered and the liquid phase then contained only a fraction (0.513) of the original Mg concentration, or 0.513-45.89 mmol/L of Mg. If we assume that the soil particles initially contained zero Mg and that all Mg that has disappeared from solution is adsorbed to soil particles, then how much Mg (to the nearest 0,1 mmol/kg soil) is adsorbed to the soil particles? Your Answer: Answer units Question 4 (5 points) Magnesium is a co-factor for chlorophyll in green plants and thus is essential for photosynthesis. To measure Mg sorption, 1.337 g of soil were added to 47 ml. of a solution that initially contained a concentration of 49.50 mmol/L of Mg. After shaking for 6 hours, the system was filtered and the liquid phase then contained only a fraction (0.461) of the original Mg concentration, or 0.461'49.50 mmol/L of Mg. If we assume that the soil particles initially contained zero Mg and that all Mg that has disappeared from solution is adsorbed to soil particles, then how much Mg (to the nearest 0.0001 mol/kg soil) is adsorbed to the soil particles? Your Answer: Answer units Question 5 (5 points) Data for an acrorthox soil from Puerto Rico PH Carbon Depth (cm) Clay (5) HO KC1 KCI Extr. Bases Sum Cation (meg/100 g) Typic Acrorthox - Puerto Rico 6.0 5.1 4.3 1.4 0 - 28 55 2.9 2.0 0.9 0.1 28 - 46 46 - 71 58 60 5.0 5.0 4.4 4.7 1.3 71 - 97 56 0.9 5.2 5.7 97 - 122 60 0.7 5.5 6.1 tr 0.1 122 - 157 54 0.6 5.7 6.4 tr 157 - 178 38 0.2 5.8 6.7 tr Data are shown for an oxisol. In the 2nd soll horizon (at depth 28-46 cm), the pH in water is 5.0, but the pH in KCl solution is 4.4 What is going on there to lower the pH? in your answer, please describe the main type of surface functional group and a rough estimate for the point-of-zero charge for a typical soil particle in this horizon Finally please describe what happens when KCl is added that lowers the pH. (Note HIN Data for an acrorthox soil from Puerto Rico . Depth Clay Carbon HO KC7 KCI Extr. Bases Sum Cation: (meg/100 g) (cm) Typic Acrorthox Puerto Rico 0 - 28 55 6.0 5.1 4.3 1.4 2.9 0.9 0.1 28 - 46 46 71 58 60 2.0 1.3 5.0 5.0 4.4 4.7 71 - 97 56 - 0.9 5.2 5.7 60 97 - 122 0.7 5.5 6.1 tr 0.1 122 157 54 - 0.6 5.7 6.4 tr 55 157 - 178 38 0.2 5.8 6.7 tr Data are shown for an oxisol. In the 6th soil horizon (at depth 122-57 cm), the pH in water is 5.7, but the pH in KCl solution is 6.4. What is going on there to raise the pH? In your answer, please describe the main type of surface functional group and a rough estimate for the point-of-zero-charge for a typical soil particle in this horizon Finally please describe what happens when KCl is added that raises the pH. (Note Tannen Question 7 (5 points) Previous research on a soil like yours measured an isotherm for the sorption of P by the soil. The isotherm was Langmuir-type with best-fit values of b - 143 mg p/kg soil, and KF - 1.11 L/mg P. If a water extract indicates that the soil solution concentration of Pis 3.2 mg P/L (at equilibrium), then what is the expected amount of Psorbed by this soil. in mg p/kg soil