
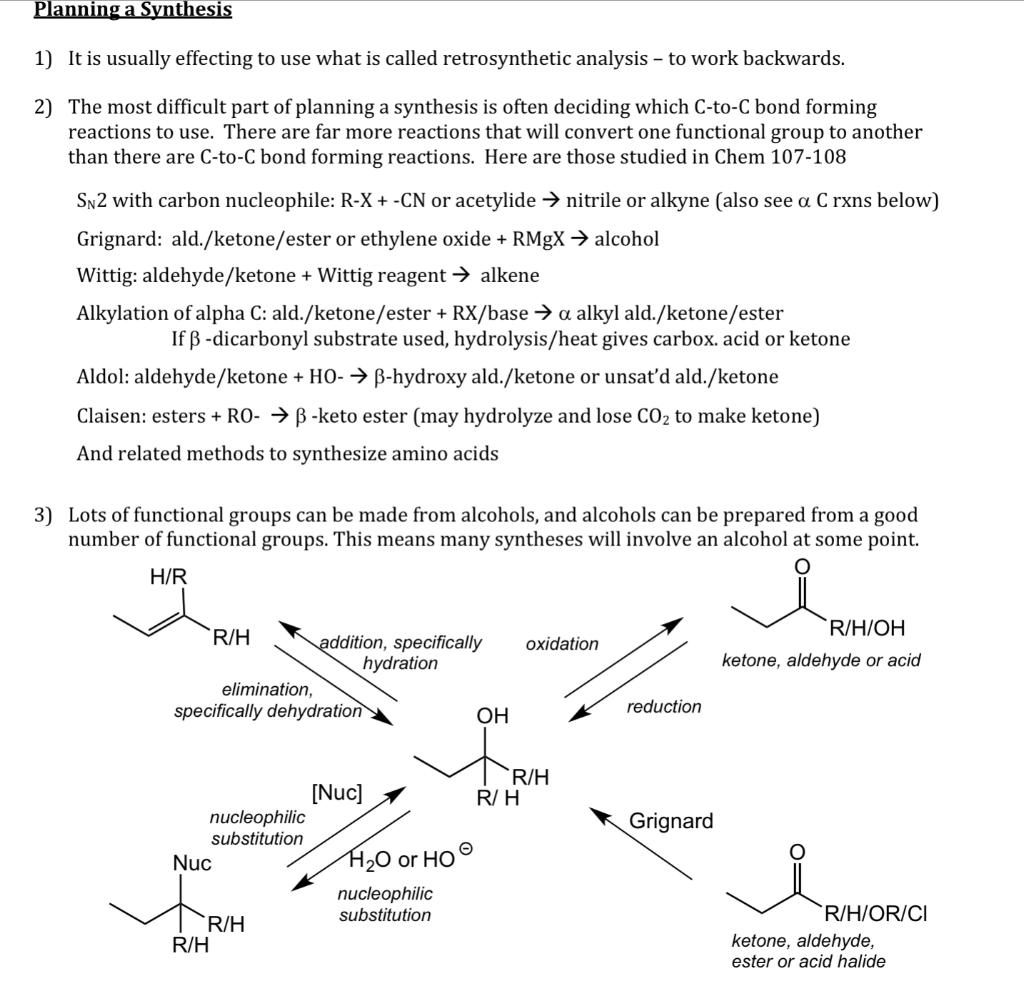


Your Assignment Propose reasonable laboratory syntheses for four compounds (including 2 of 4 compounds in question 3) on the report form starting with any of the following (may need more than one of these): KCN, CO2, ethylene oxide bromobenzene, benzoic acid, phenol, or aniline diethyl malonate or ethyl acetoacetate or diethyl amidomalonate and/or any alkyne, alcohol, alkyl halide, or carboxylic acid, Wittig with 4 carbons or fewer (not counting Ph's of Wittig) You may also use any other reagent (e.g. KN3 or NaBH3CN), solvent, acid or base required by your reactions, provided any carbons in the reagent/solvent are not incorporated into the final product. Once you have made a compound, you may use it for subsequent syntheses. Just mark the compound as from part_. Just turn in pages 3 and 4. There is more than one reasonable pathway for synthesizing most of these compounds. Please submit only one pathway for each of the 4 compounds. Planning a Synthesis 1) It is usually effecting to use what is called retrosynthetic analysis - to work backwards. 2) The most difficult part of planning a synthesis is often deciding which C-to-C bond forming reactions to use. There are far more reactions that will convert one functional group to another than there are C-to-C bond forming reactions. Here are those studied in Chem 107-108 Sn2 with carbon nucleophile: R-X + -CN or acetylide nitrile or alkyne (also see a C rxns below) Grignard: ald./ketone/ester or ethylene oxide + RMgX alcohol Wittig: aldehyde/ketone + Wittig reagent alkene Alkylation of alpha C: ald./ketone/ester + RX/base a alkyl ald./ketone/ester If B-dicarbonyl substrate used, hydrolysis/heat gives carbox. acid or ketone Aldol: aldehyde/ketone + HO- B-hydroxy ald./ketone or unsat'd ald./ketone Claisen: esters + RO- B-keto ester (may hydrolyze and lose CO2 to make ketone) And related methods to synthesize amino acids 3) Lots of functional groups can be made from alcohols, and alcohols can be prepared from a good number of functional groups. This means many syntheses will involve an alcohol at some point. H/R oxidation R/H/OH ketone, aldehyde or acid R/H addition, specifically hydration elimination, specifically dehydration OH reduction ti Grignard R/H [Nuc] R/H nucleophilic substitution o Nuc H2O or HO nucleophilic R/H substitution R/H R/H/OR/CI ketone, aldehyde, ester or acid halide #1) synthesis of benzyl phenyl ether #2) 1,3-diphenyl-2-propanol #3) Prepare any two of the following: ethyl 3-phenylapropanoate &/or 1,5-diphenyl-1,4-pentadiene-3-one &/ or &/ or N-isopropyl-3-phenyl-propanamine 2-amino-4-phenylbutanoic acid










