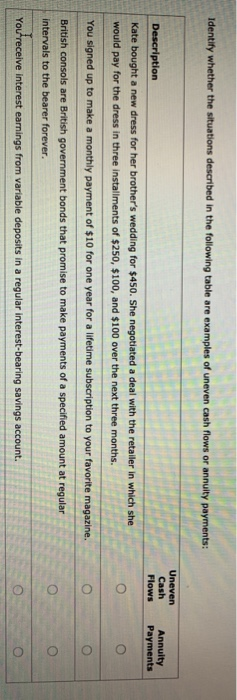
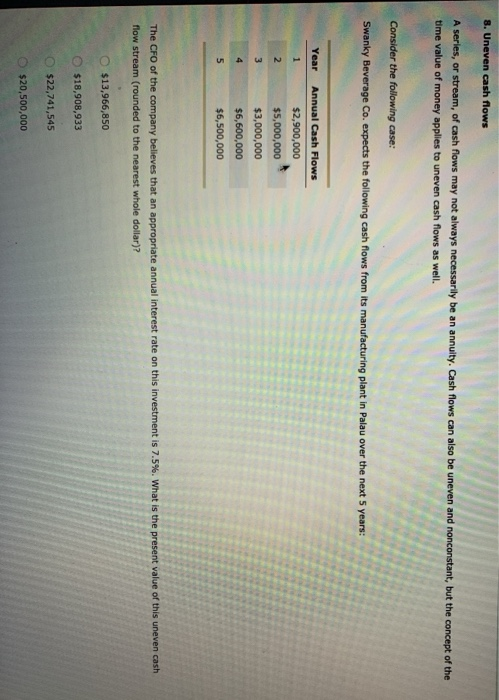
Your broker called earlier today and offered you the opportunity to invest in a security. As a friend, she suggested that you compare the current present value, cost of the security and the discounted value of its expected future cash flows before deciding whether or not to invest. The decis rule that should be used to decide whether or not to invest should be: O Everything else being equal, you should invest if the present value of the security's expected future cash flows is less than the current cost of the security. O Everything else being equal, you should invest if the current cost of the security is greater than the present value of the security's expected future cash flows. expected future cash flows. equal to the current cost of the security. Everything else being equal, you should invest if the discounted value of the security's expected future cash flows is greater than or equal to the current cost of the security. Now that you've thought about the decision rule that should be applied to your decision, apply it to the following security offered by your broker: Jing Associates, LLC, a large law firm in Denver, is building a new office complex. To pay for the construction, Ding Associates is selling a security that will pay the investor the lump sum of $6,750 in five years. The current market price of the security is $5,896. Assuming that you can earn an annual return of 3.75% on your next most attractive investment, how much is the security worth to you today? $5,334 $5,615 $7.019 From strictly a financial perspective, should you invest in the Jing security? O No Yes Why or why not? Because the discounted value of the security's future cash flows is greater than the cost of the security. Because the cost (market value) of the security is greater than the discounted value of the security's future cash flows. 7. Calculate annuity cash flows Your goal is to have $17,500 in your bank account by the end of four years. If the interest rate remains constant at 5% and you want to make annual identical deposits, you'll have to deposit into your account at the end of each year to reach your goal. If you If your deposits were made at the beginning of each year rather than an at the end, the amount of your deposit would change by still wanted to reach your financial goal by the end of four years. A series, or stream, of cash flows may not always necessarily be an annuity. Cash flows can also be uneven and nonconstant, but the concept of the time value of money applies to uneven cash flows as well. Consider the following case: Swanky Beverage Co. expects the following cash flows from its manufacturing plant in Palau over the next 5 years: Year Annual Cash Flows $2,900,000 $5,000,000 $3,000,000 $6,600,000 $6,500,000 The CFO of the company believes that an appropriate annual interest rate on this investment is 7.5%. What is the present value of this uneven cash flow stream (rounded to the nearest whole dollar)? $13,966,850 $18,908,933 $22,741,545 $20.500.000 Identify whether the situations described in the following table are examples of uneven cash flows or annuity payments: Description Flows Payments Kate bought a new dress for her brother's wedding for $450. She negotiated a deal with the retailer in which she would pay for the dress in three installments of $250, $100, and $100 over the next three months. You signed up to make a monthly payment of $10 for one year for a lifetime subscription to your favorite magazine British consols are British government bonds that promise to make payments of a specified amount at regular intervals to the bearer forever. You receive interest earnings from variable deposits in a regular interest-bearing savings account. 8. Uneven cash flows A series, or stream, of cash flows may not always necessarily be an annuity. Cash flows can also be uneven and nonconstant, but the concept of the time value of money applies to uneven cash flows as well. Consider the following case: Swanky Beverage Co. expects the following cash flows from its manufacturing plant in Palau over the next 5 years: Year Annual Cash Flows $2,900,000 $5,000,000 $3,000,000 $6,600,000 $6,500,000 The CFO of the company believes that an appropriate annual interest rate on this investment is 7.5%. What is the present value of this uneven cash flow stream (rounded to the nearest whole dollar)? O $13,966,850 $18,908,933 O $22,741,545 $20,500,000 Your broker called earlier today and offered you the opportunity to invest in a security. As a friend, she suggested that you compare the current, or present value, cost of the security and the discounted value of its expected future cash flows before deciding whether or not to invest. The decision rule that should be used to decide whether or not to invest should be: O Everything else being equal, you should invest if the present value of the security's expected future cash flows is less than the current cost of the security. Everything else being equal, you should invest if the current cost of the security is greater than the present value of the security's expected future cash flows. Everything else being equal, you should invest if the discounted value of the security's expected future cash flows is greater than or equal to the current cost of the security. Jing Associates, LLC, a large law firm in Denver, is building a new office complex. To pay for the construction, Jing Associates is selling a security that will pay the investor the lump sum of $6,750 in five years. The current market price of the security is $5,896. Assuming that you can earn an annual return of 3.75% on your next most attractive investment, how much is the security worth to you today? O $5,334 O $5,615 $7,019 From strictly a financial perspective, should you invest in the Jing security? No Yes Why or why not? Because the discounted value of the security's future cash flows is greater than the cost of the security. Because the cost (market value) of the security greater than the discounted value of the security's future cash flows