Answered step by step
Verified Expert Solution
Question
1 Approved Answer
Your Fan retails computer fans in two sizes: small and large. The business has provided you with the following information for a regular month
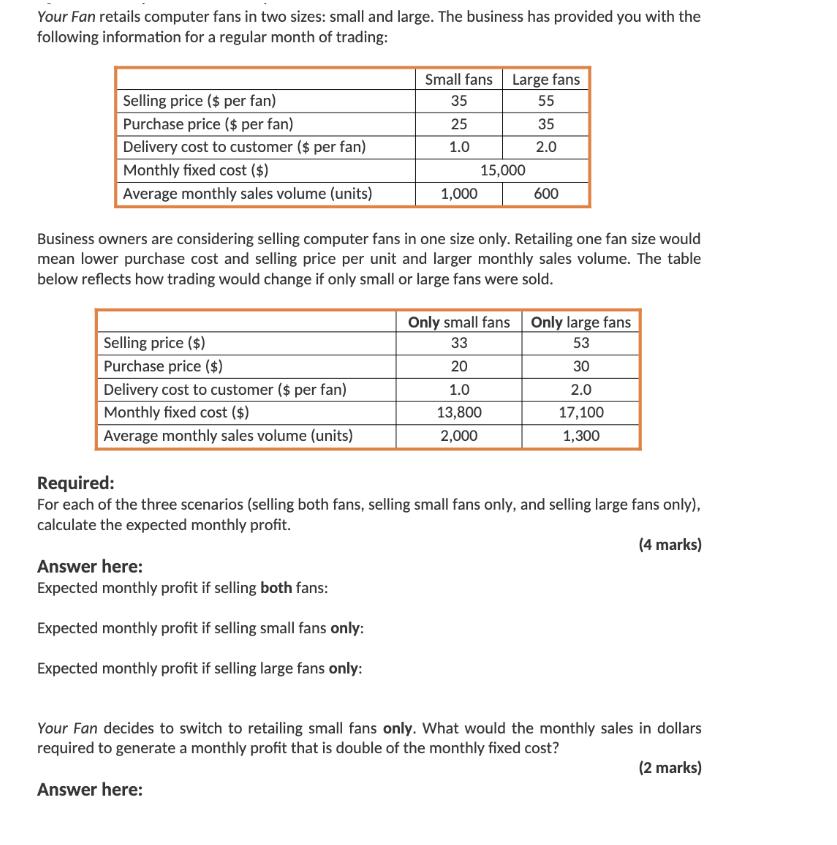
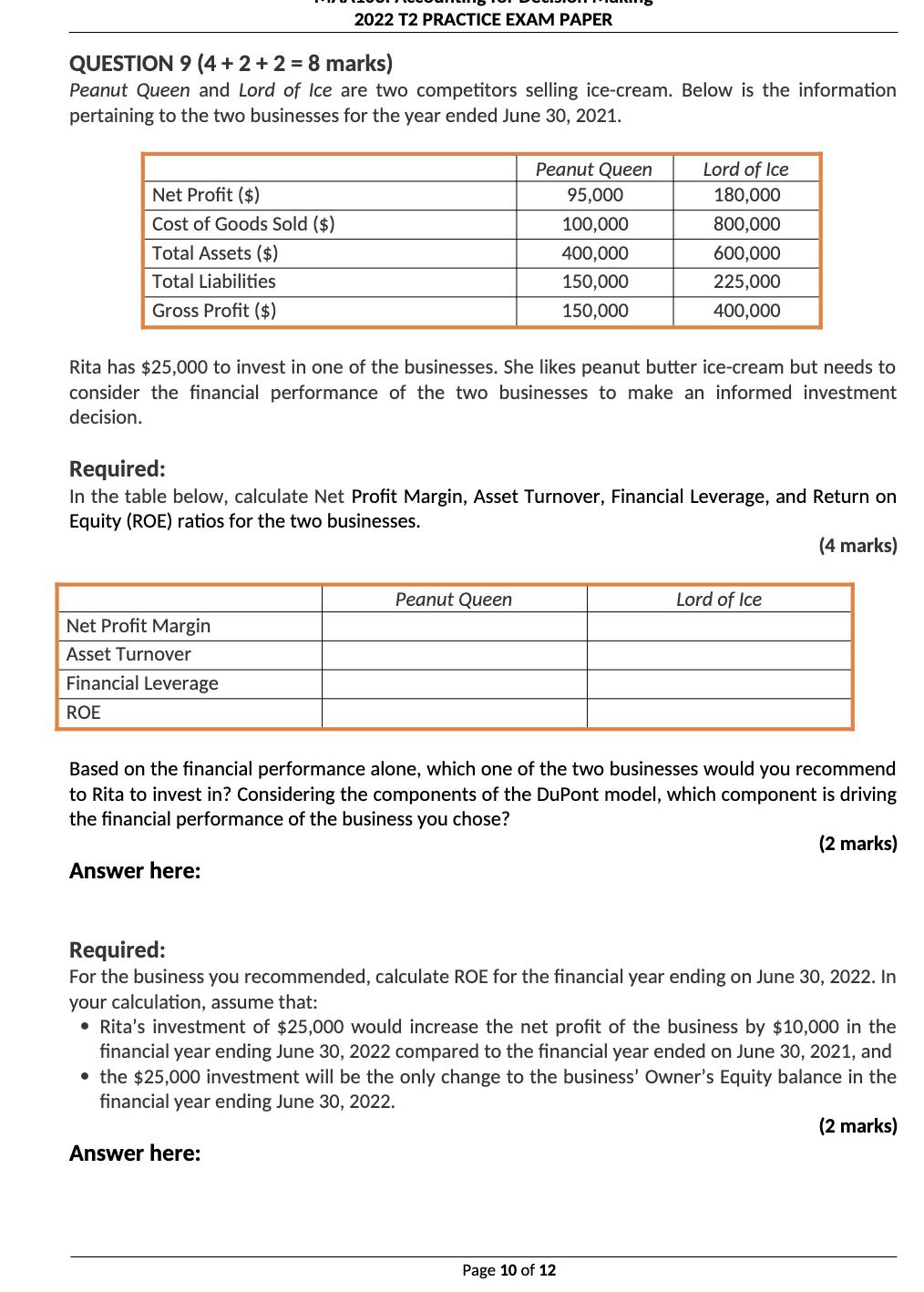

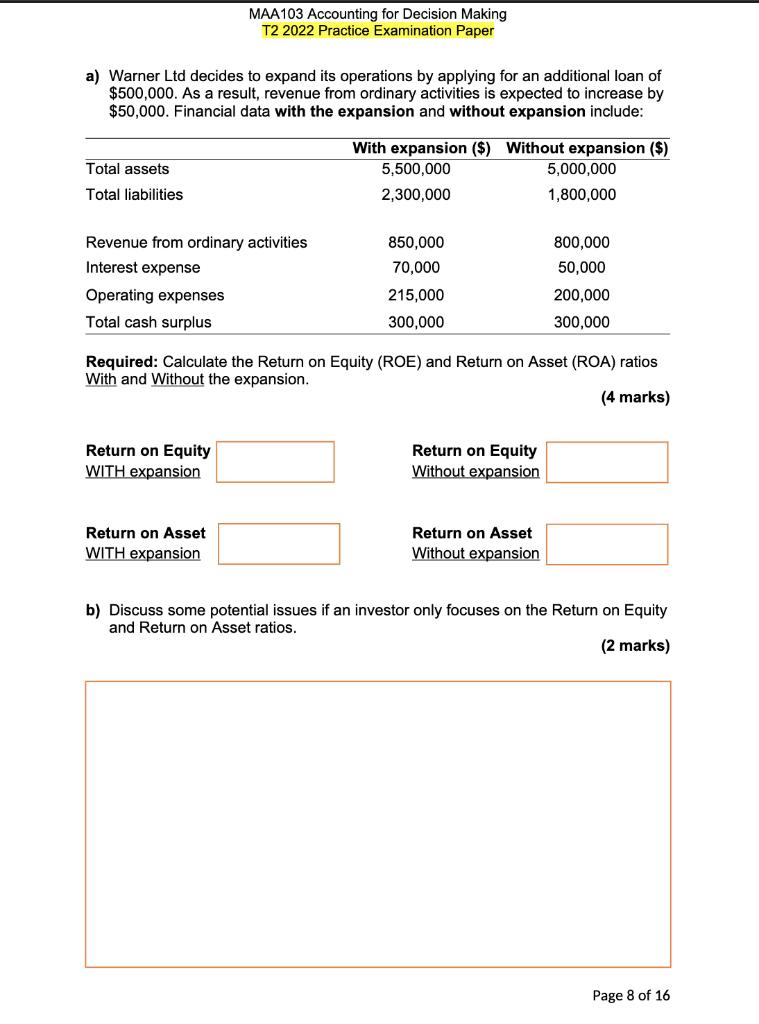
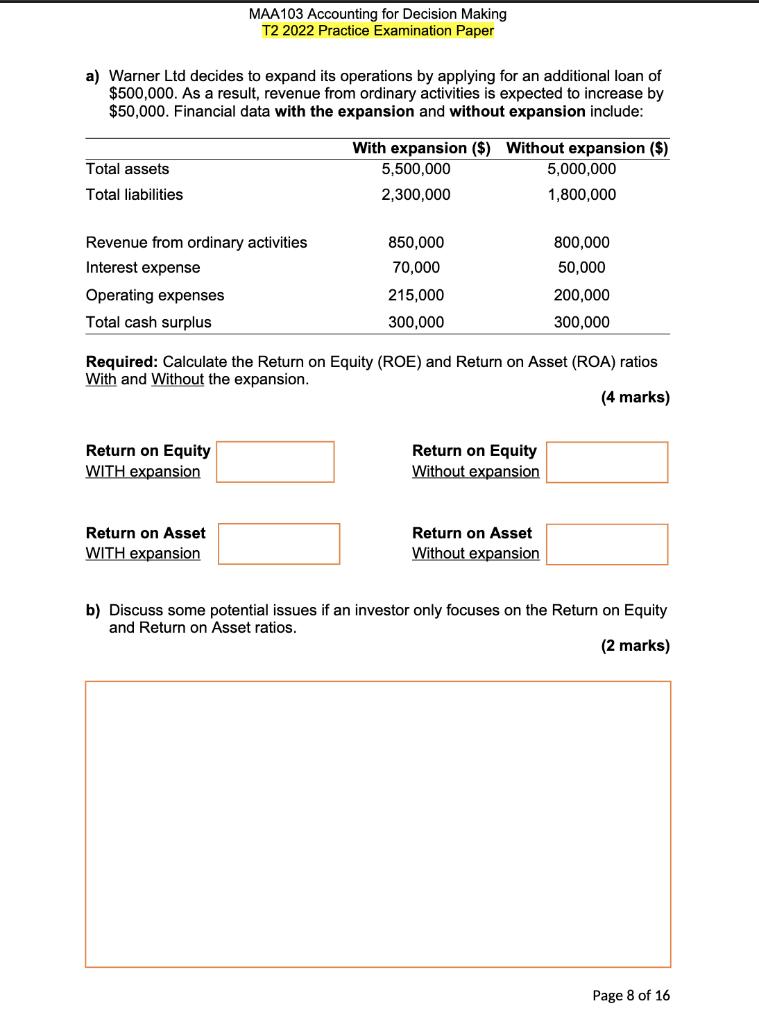

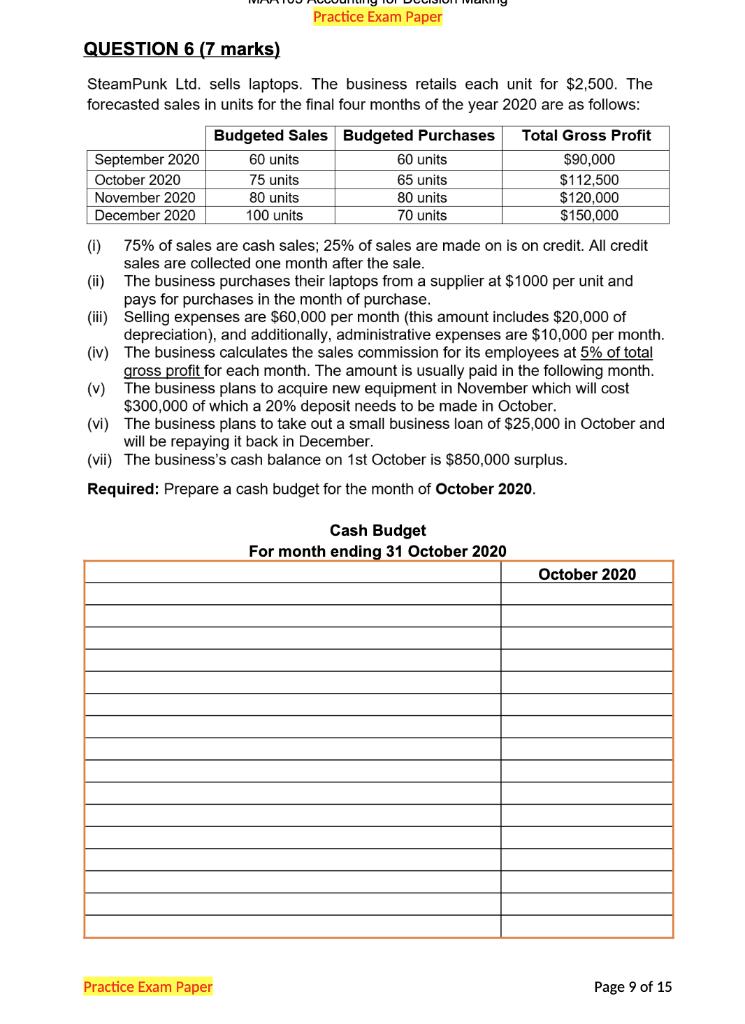
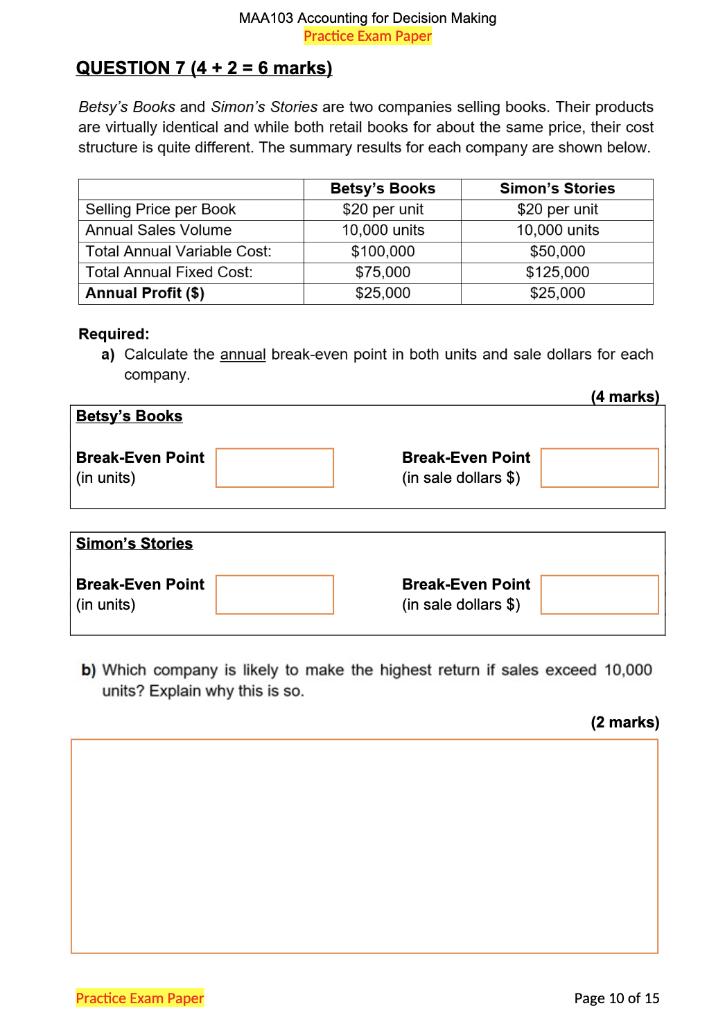
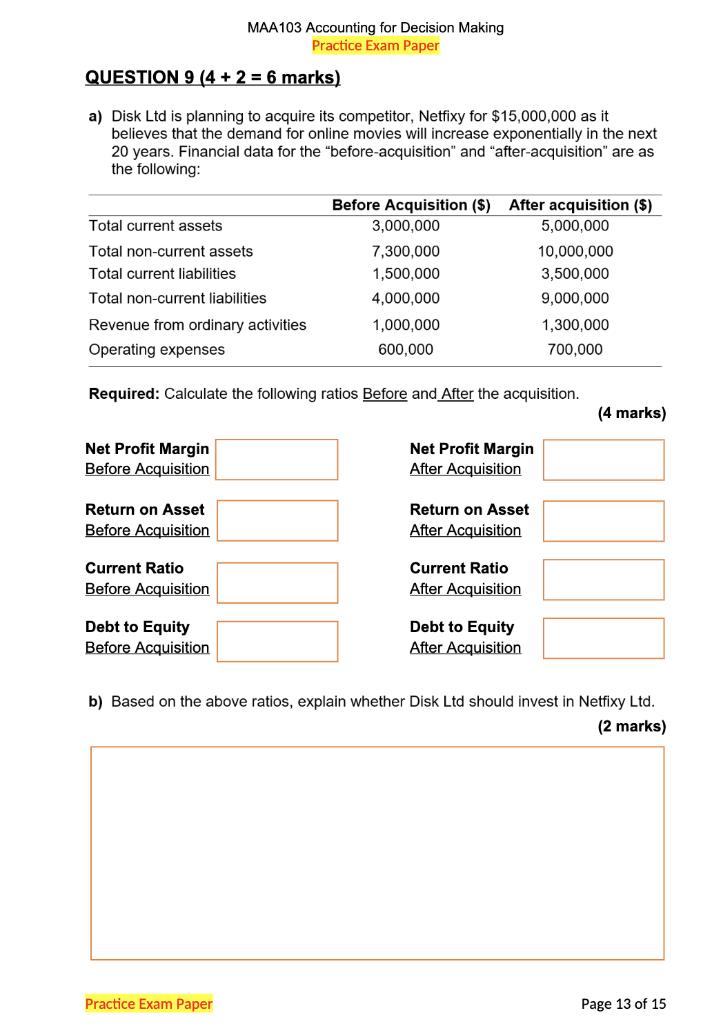
Your Fan retails computer fans in two sizes: small and large. The business has provided you with the following information for a regular month of trading: Selling price ($ per fan) Purchase price ($ per fan) Delivery cost to customer ($ per fan) Monthly fixed cost ($) Average monthly sales volume (units) Selling price ($) Purchase price ($) Delivery cost to customer ($ per fan) Monthly fixed cost ($) Average monthly sales volume (units) Small fans Large fans 35 55 35 2.0 25 1.0 Answer here: Expected monthly profit if selling both fans: Expected monthly profit if selling small fans only: Expected monthly profit if selling large fans only: 1,000 15,000 Business owners are considering selling computer fans in one size only. Retailing one fan size would mean lower purchase cost and selling price per unit and larger monthly sales volume. The table below reflects how trading would change if only small or large fans were sold. 600 Only small fans Only large fans 53 33 30 2.0 17,100 1,300 20 1.0 13,800 2,000 Required: For each of the three scenarios (selling both fans, selling small fans only, and selling large fans only), calculate the expected monthly profit. (4 marks) Your Fan decides to switch to retailing small fans only. What would the monthly sales in dollars required to generate a monthly profit that is double of the monthly fixed cost? (2 marks) Answer here: QUESTION 9 (4 + 2 + 2 = 8 marks) Peanut Queen and Lord of Ice are two competitors selling ice-cream. Below is the information pertaining to the two businesses for the year ended June 30, 2021. Net Profit ($) Cost of Goods Sold ($) Total Assets ($) Total Liabilities Gross Profit ($) 2022 T2 PRACTICE EXAM PAPER Net Profit Margin Asset Turnover Financial Leverage ROE Rita has $25,000 to invest in one of the businesses. She likes peanut butter ice-cream but needs to consider the financial performance of the two businesses to make an informed investment decision. Peanut Queen 95,000 100,000 400,000 150,000 150,000 Required: In the table below, calculate Net Profit Margin, Asset Turnover, Financial Leverage, and Return on Equity (ROE) ratios for the two businesses. (4 marks) Answer here: Peanut Queen Lord of Ice 180,000 800,000 600,000 225,000 400,000 Based on the financial performance alone, which one of the two businesses would you recommend to Rita to invest in? Considering the components of the DuPont model, which component is driving the financial performance of the business you chose? (2 marks) Lord of Ice Required: For the business you recommended, calculate ROE for the financial year ending on June 30, 2022. In your calculation, assume that: Page 10 of 12 Rita's investment of $25,000 would increase the net profit of the business by $10,000 in the financial year ending June 30, 2022 compared to the financial year ended on June 30, 2021, and the $25,000 investment will be the only change to the business' Owner's Equity balance in the financial year ending June 30, 2022. (2 marks) Answer here: QUESTION 2 (4 marks) Olivia Ltd is a business registered for GST and it lodges its Business Activity Statement (BAS) at the end of each quarter. For month of June 2020, Olivia Ltd recorded the following transactions: Transactions Made sales to customers on credit Provided services to customers on cash basis Owners withdrew cash from the business Paid for various operating expenses (not including wages) Paid for wages (gross) PAYG Withheld Paid suppliers for an amount owed on 1 March 2020 MAA103 Accounting for Decision Making T2 2022 Practice Examination Paper Note: the above amounts include GST where appropriate GST Paid ($) Additional information: On 1 June 2020, GST Paid and GST Collected opening balances were $9,000 and $5,000 respectively. PAYG Withheld opening balance was $2,000. GST Collected ($) Required: Based on the above information, record the total GST Paid, GST Collected, PAYG Withheld, the Net Amount Payable/Refundable, and clearly indicate whether the Net Amount is payable to the ATO or refundable to the business for the April to June 2020 quarter in the space provided. (4 marks) PAYG Withheld ($) $ 13,200 12,100 20,000 Net Amount Payable/Refundable ($) 79,200 48,590 7,500 22,000 Is the Net Amount Payable to the ATO or Refundable to the Business? a) Warner Ltd decides to expand its operations by applying for an additional loan of $500,000. As a result, revenue from ordinary activities is expected to increase by $50,000. Financial data with the expansion and without expansion include: Total assets Total liabilities Revenue from ordinary activities Interest expense Operating expenses Total cash surplus MAA103 Accounting for Decision Making T2 2022 Practice Examination Paper Return on Equity WITH expansion Return on Asset WITH expansion With expansion ($) Without expansion ($) 5,500,000 2,300,000 850,000 70,000 215,000 300,000 Required: Calculate the Return on Equity (ROE) and Return on Asset (ROA) ratios With and Without the expansion. (4 marks) Return on Equity Without expansion. 5,000,000 1,800,000 Return on Asset Without expansion 800,000 50,000 200,000 300,000 b) Discuss some potential issues if an investor only focuses on the Return on Equity and Return on Asset ratios. (2 marks) Page 8 of 16 a) Warner Ltd decides to expand its operations by applying for an additional loan of $500,000. As a result, revenue from ordinary activities is expected to increase by $50,000. Financial data with the expansion and without expansion include: Total assets Total liabilities Revenue from ordinary activities Interest expense Operating expenses Total cash surplus MAA103 Accounting for Decision Making T2 2022 Practice Examination Paper Return on Equity WITH expansion Return on Asset WITH expansion With expansion ($) Without expansion ($) 5,500,000 2,300,000 850,000 70,000 215,000 300,000 Required: Calculate the Return on Equity (ROE) and Return on Asset (ROA) ratios With and Without the expansion. (4 marks) Return on Equity Without expansion. 5,000,000 1,800,000 Return on Asset Without expansion 800,000 50,000 200,000 300,000 b) Discuss some potential issues if an investor only focuses on the Return on Equity and Return on Asset ratios. (2 marks) Page 8 of 16 QUESTION 9 (5 + 3 = 8 marks) a) Snoozy Suzie Ltd retails beds. Each bed currently sells for $700 and costs $200 to purchase from suppliers. On average, the business expects to sell 60 beds per month and the total annual fixed cost to be $60,000. Snoozy Suzie are considering the following options to help their business grow. OPTION A: To increase profits, the business could increase the selling price to $800 per bed. The manager estimates that by increasing the selling price, expected sales volume would decrease to 50 beds per month. Fixed cost and the cost price per unit would remain the same. OPTION B: Snoozy Suzie could expand the current business by launching an online store. The manager estimates that if they open for business online, sales volume would increase to 80 beds per month. However, fixed costs will also need to increase to $90,000 per year. Selling price and cost price per unit would remain the same. MAA103 Accounting for Decision Making T2 2022 Practice Examination Paper Required: Calculate the 'annual break-even point' in units and 'expected annual profits' for both Option A and Option B. Record your answers in the box provided below. (5 marks) OPTION A Break-Even Point (in units) OPTION B Break-Even Point (in units) Annual Expected Profit ($) Annual Expected Profit ($) QUESTION 6 (7 marks) SteamPunk Ltd. sells laptops. The business retails each unit for $2,500. The forecasted sales in units for the final four months of the year 2020 are as follows: Total Gross Profit $90,000 $112,500 $120,000 $150,000 September 2020 October 2020 November 2020 December 2020 Practice Exam Paper Budgeted Sales Budgeted Purchases 60 units 75 units 80 units 100 units Practice Exam Paper 60 units 65 units 80 units 70 units (1) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The business plans to take out a small business loan of $25,000 in October and will be repaying it back in December. (vii) The business's cash balance on 1st October is $850,000 surplus. Required: Prepare a cash budget for the month of October 2020. 75% of sales are cash sales; 25% of sales are made on is on credit. All credit sales are collected one month after the sale. The business purchases their laptops from a supplier at $1000 per unit and pays for purchases in the month of purchase. Selling expenses are $60,000 per month (this amount includes $20,000 of depreciation), and additionally, administrative expenses are $10,000 per month. The business calculates the sales commission for its employees at 5% of total gross profit for each month. The amount is usually paid in the following month. The business plans to acquire new equipment in November which will cost $300,000 of which a 20% deposit needs to be made in October. Cash Budget For month ending 31 October 2020 October 2020 Page 9 of 15 QUESTION 7 (4+2 = 6 marks) Betsy's Books and Simon's Stories are two companies selling books. Their products are virtually identical and while both retail books for about the same price, their cost structure is quite different. The summary results for each company are shown below. Selling Price per Book Annual Sales Volume Total Annual Variable Cost: Total Annual Fixed Cost: Annual Profit ($) Betsy's Books Break-Even Point (in units) MAA103 Accounting for Decision Making Practice Exam Paper Simon's Stories Break-Even Point (in units) Required: a) Calculate the annual break-even point in both units and sale dollars for each company. Betsy's Books $20 per unit 10,000 units Practice Exam Paper $100,000 $75,000 $25,000 Simon's Stories $20 per unit 10,000 units $50,000 $125,000 $25,000 Break-Even Point (in sale dollars $) Break-Even Point (in sale dollars $) (4 marks) b) Which company is likely to make the highest return if sales exceed 10,000 units? Explain why this is so. (2 marks) Page 10 of 15 QUESTION 9 (4+2= 6 marks) a) Disk Ltd is planning to acquire its competitor, Netfixy for $15,000,000 as it believes that the demand for online movies will increase exponentially in the next 20 years. Financial data for the "before-acquisition" and "after-acquisition" are as the following: Total current assets Total non-current assets Total current liabilities. Total non-current liabilities Net Profit Margin Before Acquisition Return on Asset Before Acquisition MAA103 Accounting for Decision Making Practice Exam Paper Revenue from ordinary activities Operating expenses Required: Calculate the following ratios Before and After the acquisition. Current Ratio Before Acquisition Debt to Equity Before Acquisition Before Acquisition ($) After acquisition ($) 3,000,000 5,000,000 7,300,000 1,500,000 4,000,000 1,000,000 600,000 Practice Exam Paper Net Profit Margin After Acquisition Return on Asset After Acquisition Current Ratio After Acquisition 10,000,000 3,500,000 9,000,000 1,300,000 700,000 Debt to Equity After Acquisition (4 marks) b) Based on the above ratios, explain whether Disk Ltd should invest in Netfixy Ltd. (2 marks) Page 13 of 15
Step by Step Solution
★★★★★
3.54 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
ANSWER Expected monthly profit if selling both fans Epected p...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


