Question
Your task is to compare the memory efficiency of four different styles of instruction set architectures. The architecture styles are: AccumulatorAll operations occur between
Your task is to compare the memory efficiency of four different styles of instruction set architectures. The architecture styles are:
■ Accumulator—All operations occur between a single register and a memory location.
■ Memory-memory—All instruction addresses reference only memory locations.
■ Stack—All operations occur on top of the stack. Push and pop are the only instructions that access memory; all others remove their operands from the stack and replace them with the result. The implementation uses a hardwired stack for only the top two stack entries, which keeps the processor circuit very small and low in cost. Additional stack positions are kept in memory locations, and access to these stack positions requires memory references.
■ Load-store—All operations occur in registers, and register-to-register instructions have three register names per instruction.
To measure memory efficiency, make the following assumptions about all four instruction sets:
■ All instructions are an integral number of bytes in length.
■ The opcode is always one byte (8 bits).
■ Memory accesses use direct, or absolute, addressing.
■ The variables A, B, C, and D are initially in memory.
a. Invent your own assembly language mnemonics (Figure A.2 provides a useful sample to generalize), and for each architecture write the best equivalent assembly language code for this high-level language code sequence:
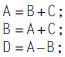
b. Label each instance in your assembly codes for part (a) where a value is loaded from memory after having been loaded once. Also, label each instance in your code where the result of one instruction is passed to another instruction as an operand, and further classify these events as involving storage within the processor or storage in memory.
c. Assume that the given code sequence is from a small, embedded computer application that uses a 16-bit memory address and data operands. If a load-store architecture is used, assume it has 16 general-purpose registers. For each architecture answer, the following questions: How many instruction bytes are fetched? How many bytes of data are transferred from/to memory? Which architecture is most efficient as measured by total memory traffic (code + data)?
d. Now assume a processor with 64-bit memory addresses and data operands. For each architecture answer the questions of part (c). How have the relative merits of the architectures changed for the chosen metrics?
A=B+C; B=A+C; D=A-B;
Step by Step Solution
3.46 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1
a Accumulator ABC BAC DAB Memorymemory LD AB ADD AC ST ATEMP LD BA ADD BC ST BA LD ATEMP SUB AB ST A...
Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


