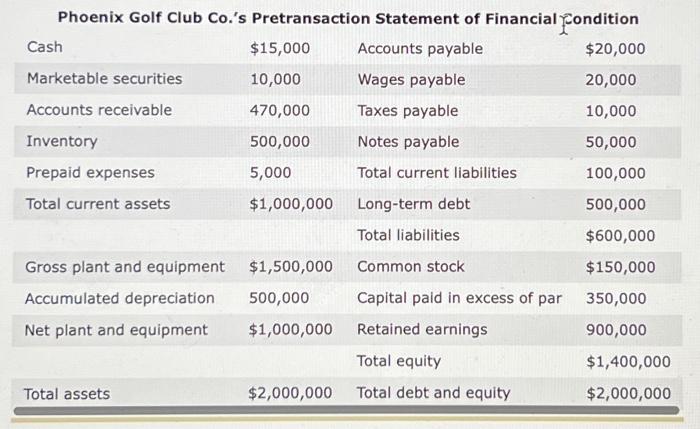
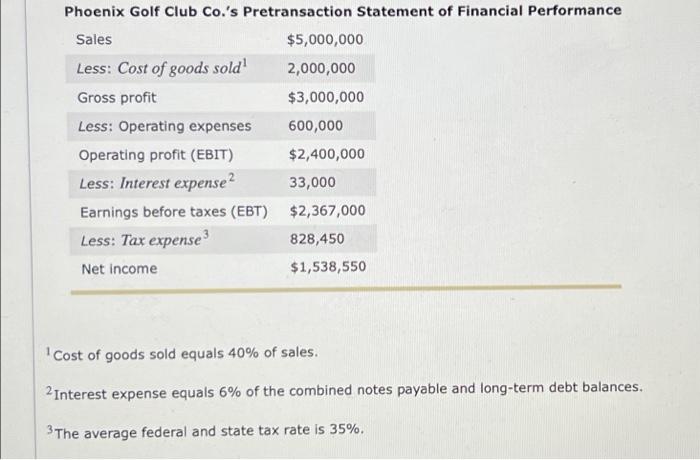
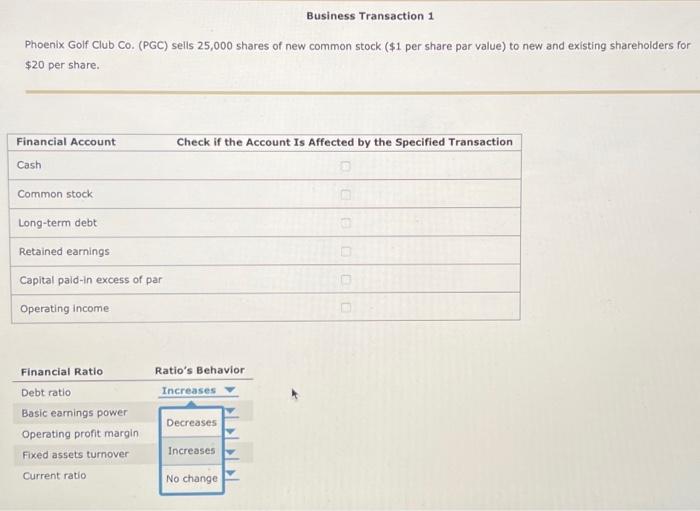
You've been asked to tutor Gavin, a finance student who doesn't feel comfortable about his understanding of the relationship between a company's business activities, its financial accounts, and the company's financial ratios. To better appreciate these relationships, you've created the following exercises for Gavin to complete. The purpose of these exercises is to help Gavin (1) understand the effect of business transactions on financial statement-such as balance sheet and income statement-accounts and (2) how these changes in the numerators and denominators of financial ratios affect the ratios' values. However, before using these exercises in your tutoring session later today, you'll want to run the calculations on the following two business transactions, to verify the accuracy of your answers. To provide a consistent frame of reference for the company's financial statements and ratios, assume that the following balance sheet and income statement reflect the company's pretransaction condition and performance. Phoenix Golf Club Co.'s Pretransaction Statement of Financial Condition Cash $15,000 Accounts payable $20,000 Marketable securities 10,000 Wages payable 20,000 Accounts receivable 470,000 Taxes payable 10,000 Inventory 500,000 Notes payable 50,000 Prepaid expenses 5,000 Total current liabilities 100,000 Total current assets $1,000,000 Long-term debt 500,000 Total liabilities $600,000 Gross plant and equipment $1,500,000 Common stock $150,000 Accumulated depreciation 500,000 Capital paid in excess of par 350,000 Net plant and equipment $1,000,000 Retained earnings 900,000 Total equity $1,400,000 Total assets $2,000,000 Total debt and equity $2,000,000 Phoenix Golf Club Co.'s Pretransaction Statement of Financial Performance Sales $5,000,000 Less: Cost of goods sold! 2,000,000 Gross profit $3,000,000 Less: Operating expenses 600,000 Operating profit (EBIT) $2,400,000 Less: Interest expense? 33,000 Earnings before taxes (EBT) $2,367,000 Less: Tax expense 828,450 Net Income $1,538,550 Cost of goods sold equals 40% of sales. 2 Interest expense equals 6% of the combined notes payable and long-term debt balances. 3 The average federal and state tax rate is 35%. Business Transaction 1 Phoenix Golf Club Co. (PGC) sells 25,000 shares of new common stock ($1 per share par value) to new and existing shareholders for $20 per share. Check if the Account Is Affected by the Specified Transaction Financial Account Cash Common stock Long-term debt Retained earnings Capital pald-in excess of par Operating income Ratio's Behavior Increases Financial Ratio Debt ratio Basic earnings power Operating profit margin Decreases Fixed assets turnover Increases Current ratio No change Business Transaction 2 Phoenix Golf Club Co. (PGC)'s labor force goes on strike for two months, reducing the company's sales by 20.00% Ratio's Behavior Financial Ratio Basic earning power Inventory turnover Average collection period Operating profit margin Decreases Increases Debt ratio No change