Question
ZAGG, Zealous About Great Gadgets, began designing protective plastic shields for wristwatches in 2005. Today, the company is a market leader in mobile device accessories.
ZAGG, "Zealous About Great Gadgets," began designing protective plastic shields for wristwatches in 2005. Today, the company is a market leader in mobile device accessories. ZAGG's patented invisibleSHIELD film protects tablet and smart phone screens around the world. Their product list also includes mobile keyboards, cases, headphones, and portable power. In 2016, ZAGG acquired iFrogz, a manufacturer of digital audio accessories in order to grow their product lines and expand distribution. ZAGG is currently traded on the NASDAQ.
Learning Objectives
Understand the concepts underlying deferred income tax accounting.
Understand and interpret the three primary disclosures provided in the income tax footnote to the financial statements.
Use deferred income tax asset and liability information to infer the magnitude of differences between book and tax income and asset values.
Understand the purpose of a deferred income tax asset valuation allowance.
Understand how changes in income tax rates impact deferred income tax assets and liabilities.
Refer to the 2017 financial statements and footnote excerpts of ZAGG, Inc. at the end of this document.
The third table in Note 8 discloses the details of ZAGG's deferred income tax assets and liabilities that arise from various temporary differences. Use the information in this table to answer questions g and h. Where necessary, you may assume that ZAGG's total statutory income tax rate is the sum of its federal statutory tax rate of 35% and a blended state statutory tax rate of 3%.
g. The largest component of ZAGG's deferred income tax liability, labeled "Property and equipment," relates to differences between book and tax depreciation expense.
a. As of December 31, 2017, which system recognized a greater expense over time relating to depreciation book or tax? Describe what information you sued to make this assessment.
b. Estimate the dollar magnitude of the cumulative difference in depreciation expense between the two systems as of December 31, 2017 using the chart below. Begin with step 1 and work backwards.
| Cumulative difference in book and tax depreciation expense | Statutory income tax rate | = | Deferred income tax liability relating to property and equipment at 12/31/2017 | |
| Step 3 | Step 2 | Step 1 | ||
|
|
c. Using the information in the chart above, determine the balance in "Property and equipment, net" on the balance sheet at December 31, 2017 if tax depreciation had been used through the assets' lives instead of the reported method.
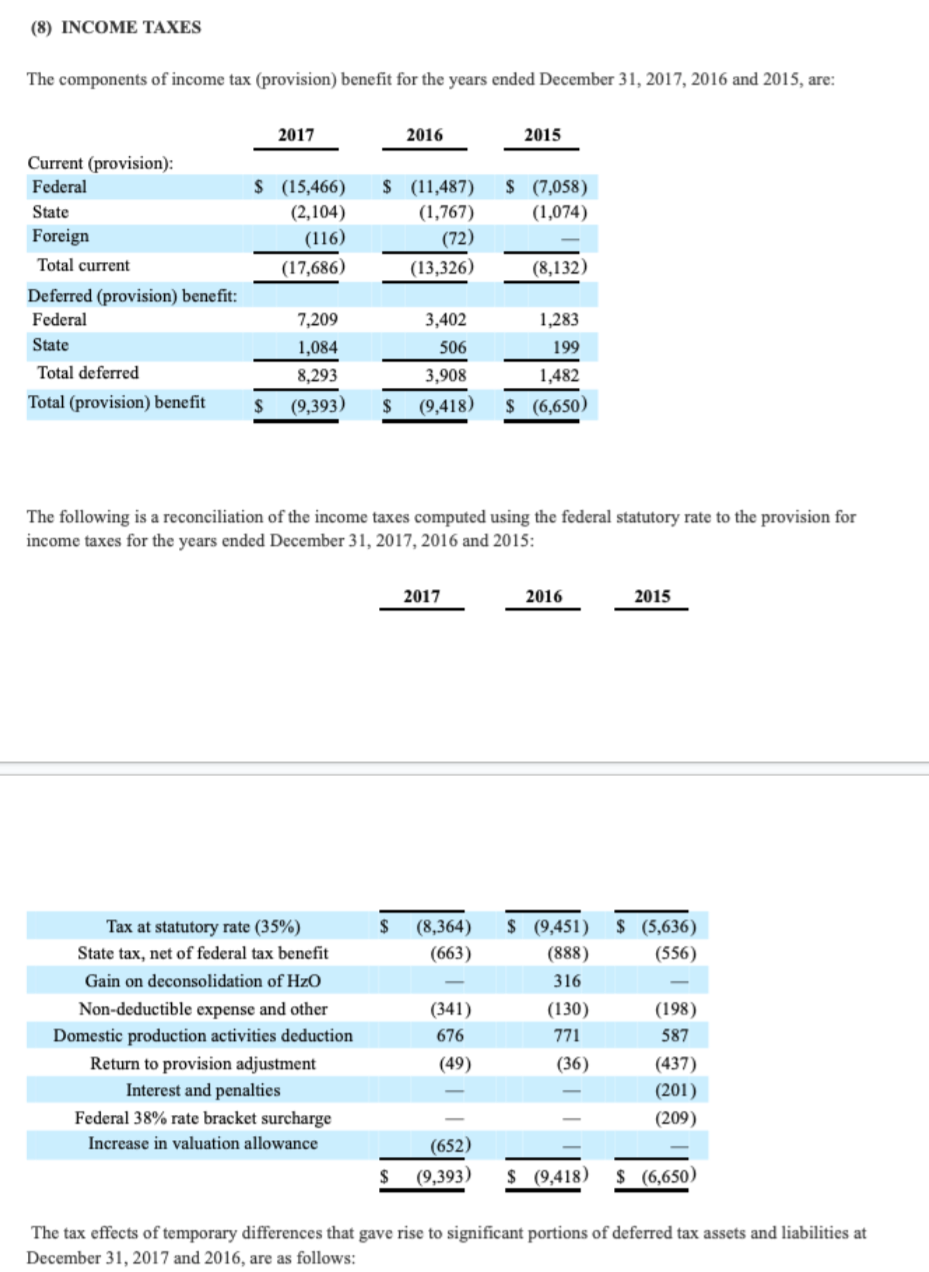
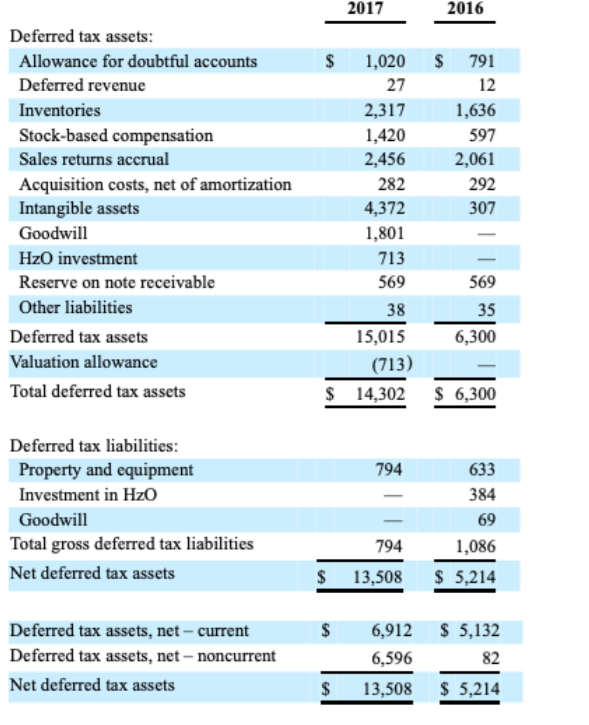 (8) INCOME TAXES The components of income tax (provision) benefit for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, are: The following is a reconciliation of the income taxes computed using the federal statutory rate to the provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2017,2016 and 2015: 201720162015 The tax effects of temporary differences that gave rise to significant portions of deferred tax assets and liabilities at December 31, 2017 and 2016, are as follows: (8) INCOME TAXES The components of income tax (provision) benefit for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, are: The following is a reconciliation of the income taxes computed using the federal statutory rate to the provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2017,2016 and 2015: 201720162015 The tax effects of temporary differences that gave rise to significant portions of deferred tax assets and liabilities at December 31, 2017 and 2016, are as follows
(8) INCOME TAXES The components of income tax (provision) benefit for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, are: The following is a reconciliation of the income taxes computed using the federal statutory rate to the provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2017,2016 and 2015: 201720162015 The tax effects of temporary differences that gave rise to significant portions of deferred tax assets and liabilities at December 31, 2017 and 2016, are as follows: (8) INCOME TAXES The components of income tax (provision) benefit for the years ended December 31, 2017, 2016 and 2015, are: The following is a reconciliation of the income taxes computed using the federal statutory rate to the provision for income taxes for the years ended December 31, 2017,2016 and 2015: 201720162015 The tax effects of temporary differences that gave rise to significant portions of deferred tax assets and liabilities at December 31, 2017 and 2016, are as follows Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
Step: 1

Get Instant Access to Expert-Tailored Solutions
See step-by-step solutions with expert insights and AI powered tools for academic success
Step: 2

Step: 3

Ace Your Homework with AI
Get the answers you need in no time with our AI-driven, step-by-step assistance
Get Started


