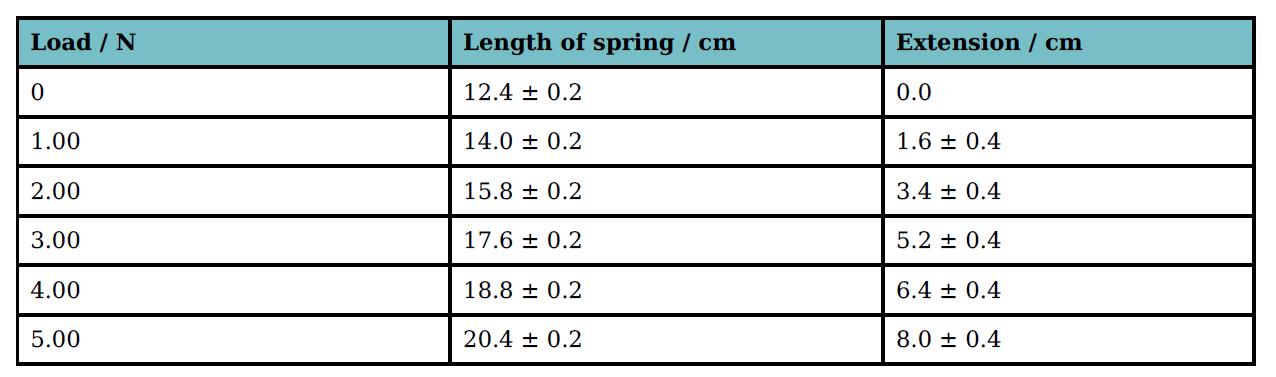
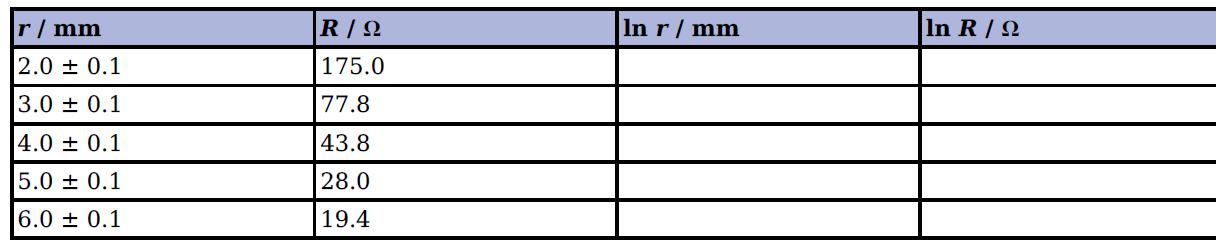
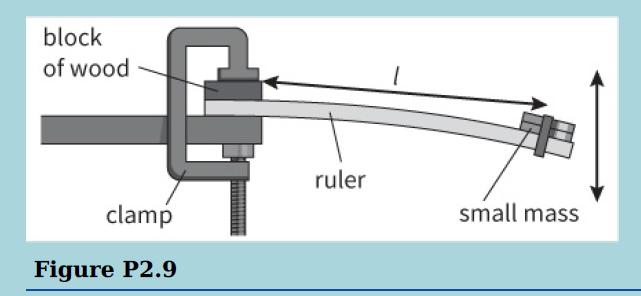
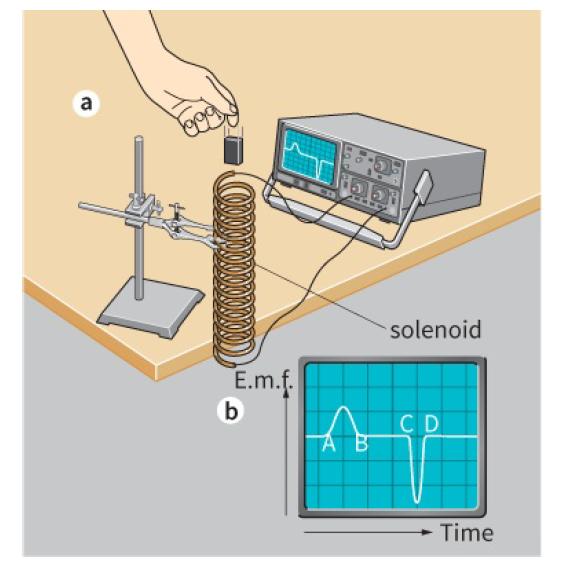
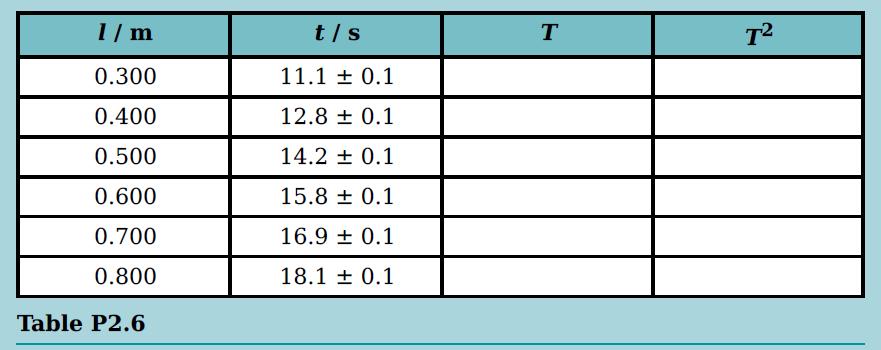
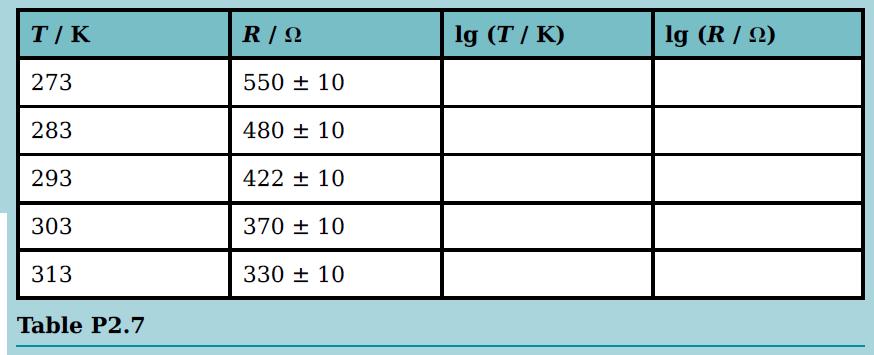
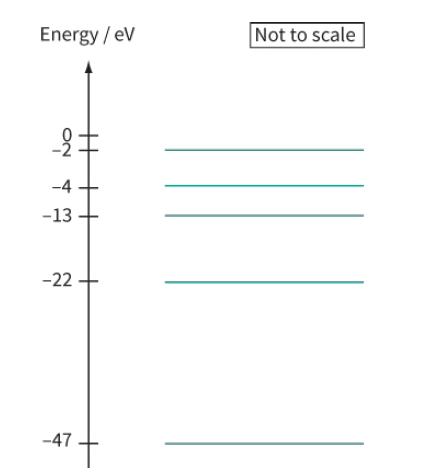
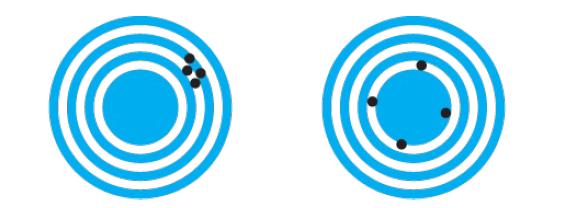
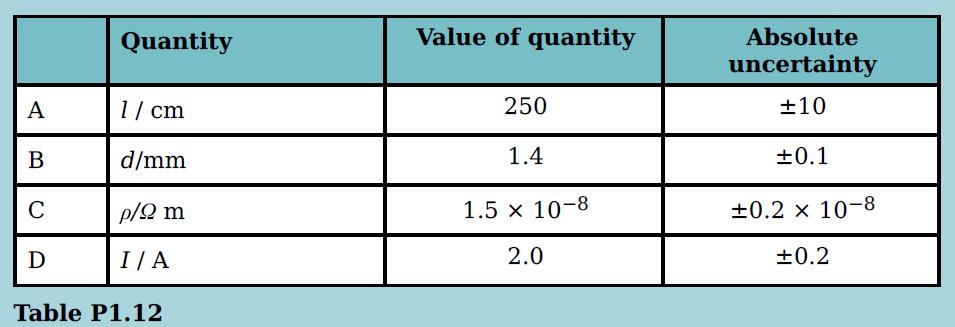
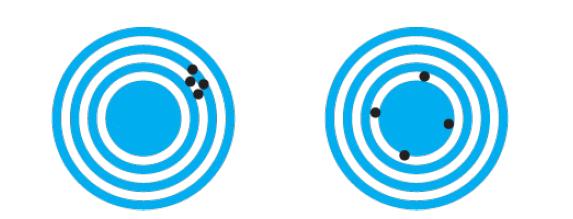
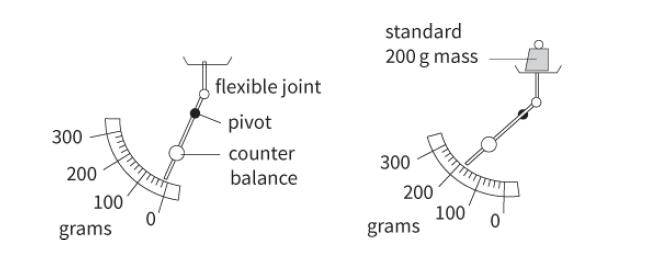
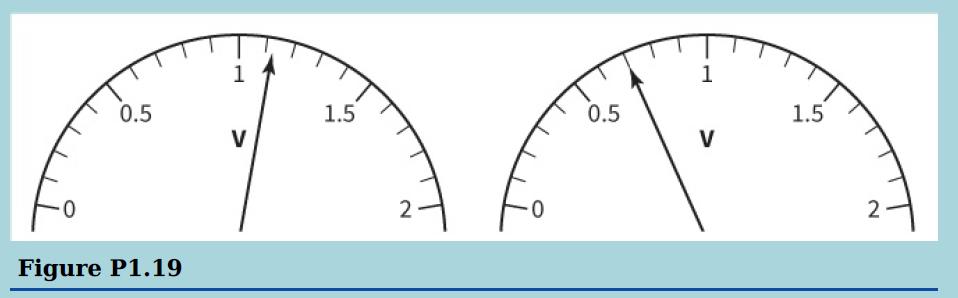
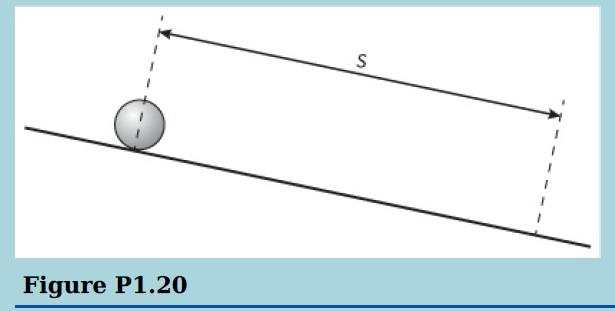
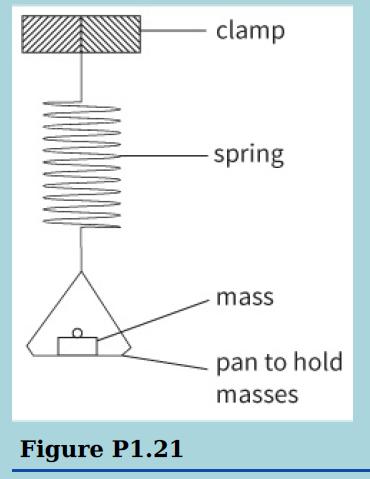
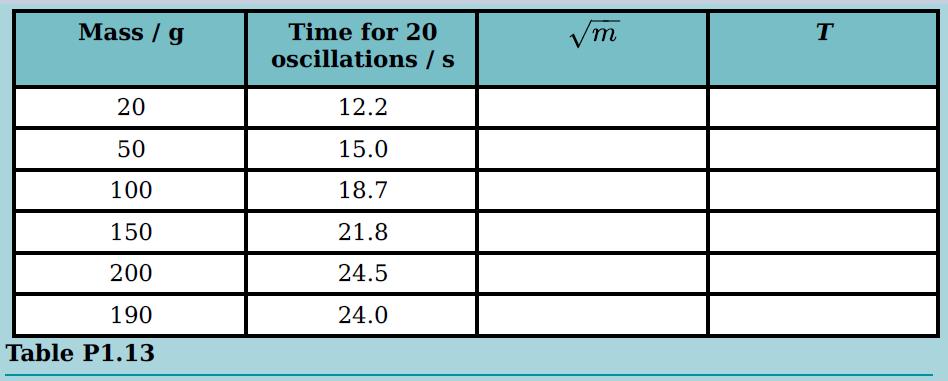
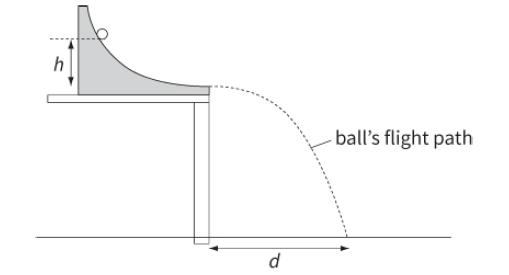
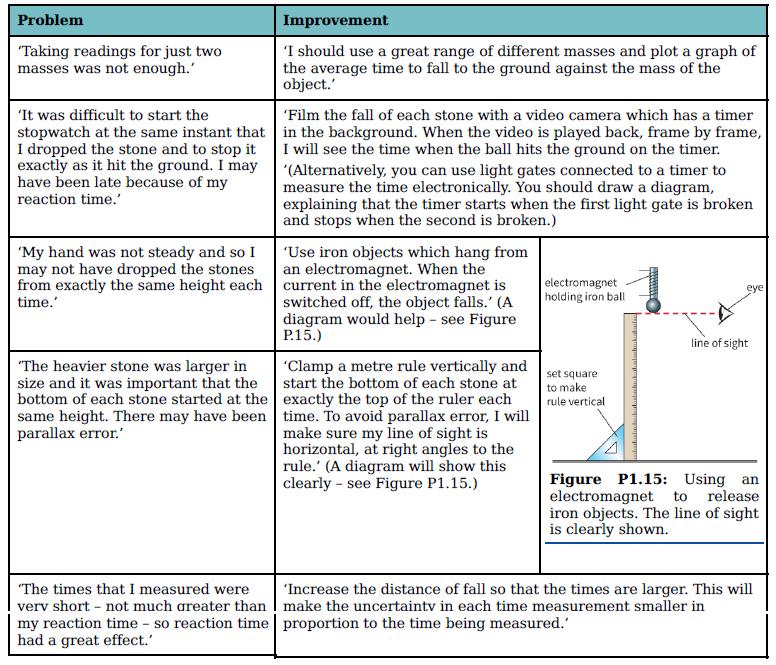
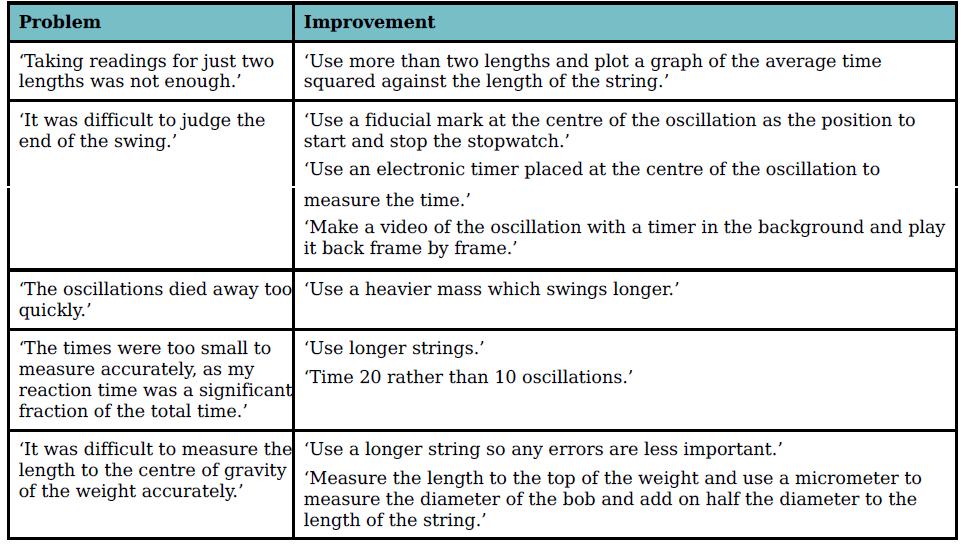
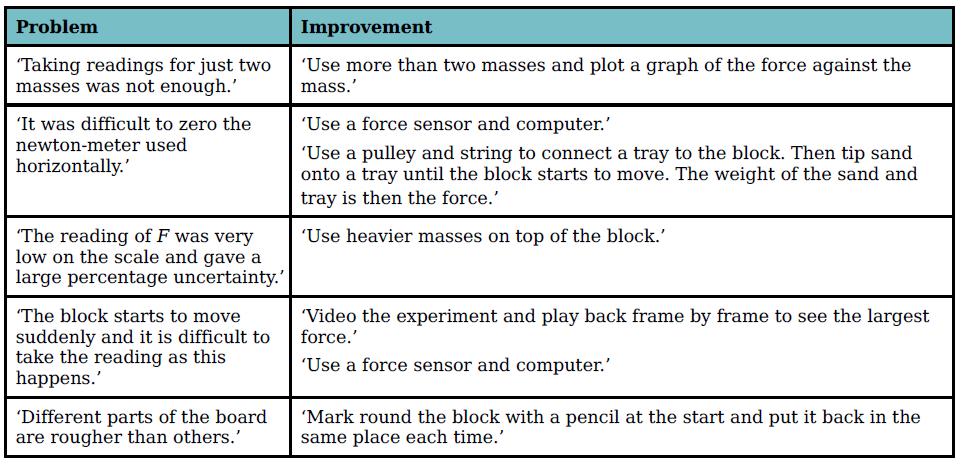
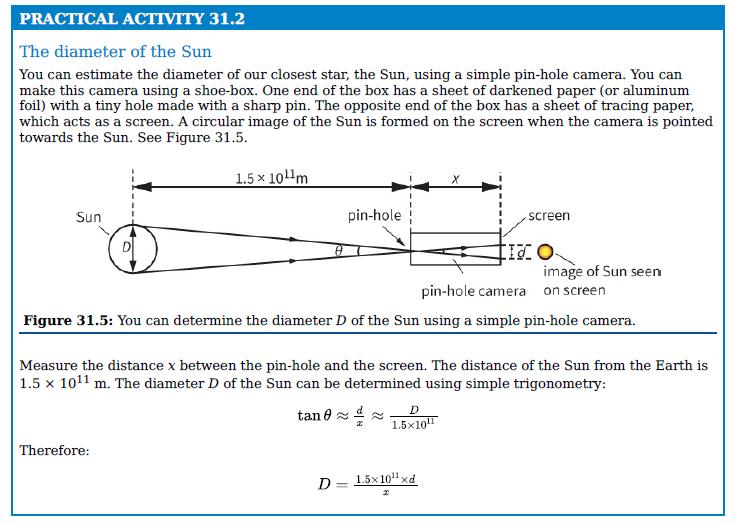
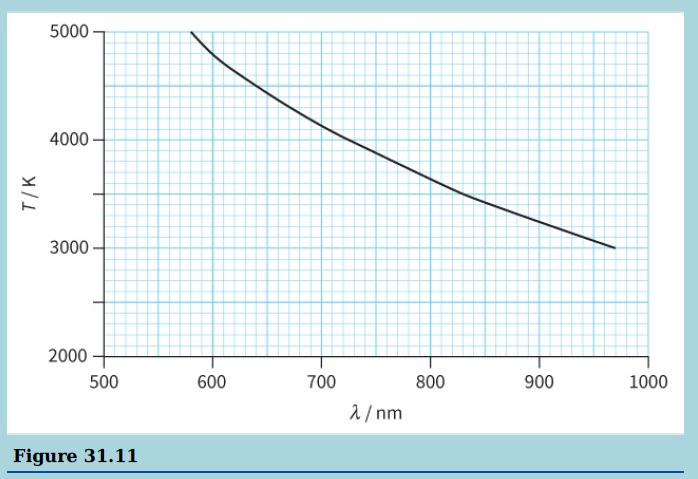
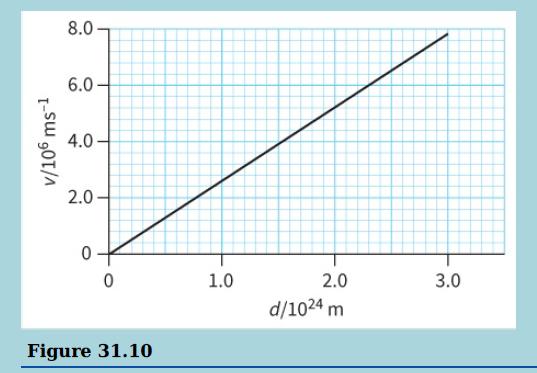
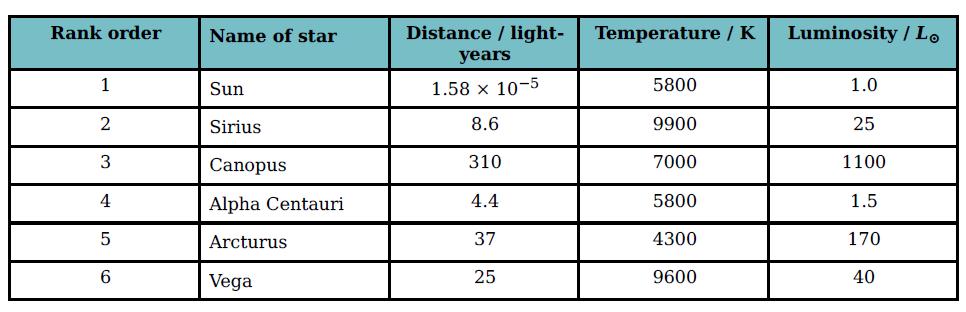
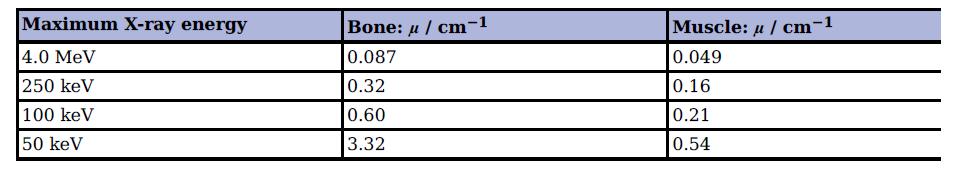
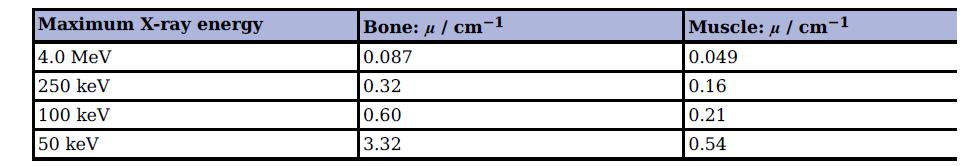
Cambridge International AS And A Level Physics Coursebook 3rd Edition David Sang, Graham Jones, Gurinder Chadha, Richard Woodside - Solutions
Unlock the full potential of your physics studies with our comprehensive solutions for the "Cambridge International AS and A Level Physics Coursebook 3rd Edition" by David Sang, Graham Jones, Gurinder Chadha, and Richard Woodside. Our online platform offers an extensive answers key and solutions manual, providing you with step-by-step answers to complex physics questions. Whether you're searching for solved problems, a test bank, or chapter solutions, we have the resources you need. Access the instructor manual and textbook solutions for free download and conquer physics with confidence. Explore our answers and solutions PDF to excel in your academic journey.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()