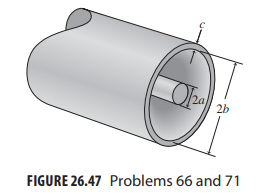
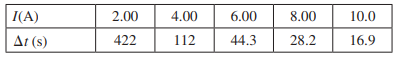
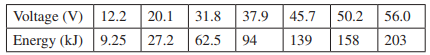
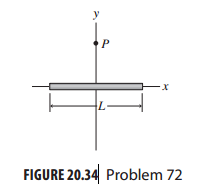
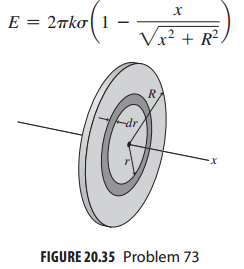
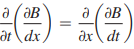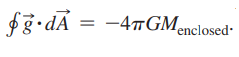Essential University Physics 3rd Edition Volume 2 Richard Wolfsonby - Solutions
Unlock the complete understanding of "Essential University Physics 3rd Edition Volume 2" by Richard Wolfson with our comprehensive solutions and answers. Access the online solutions manual, featuring step-by-step answers and solved problems. Dive into the chapter solutions and test bank to enhance your learning experience. Whether you're looking for answers or the instructor manual, our resources provide everything you need. Download the solutions PDF for free and explore the textbook's depth effortlessly. With our answers key, mastering physics concepts has never been easier. Discover the perfect companion to your academic journey today!
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()