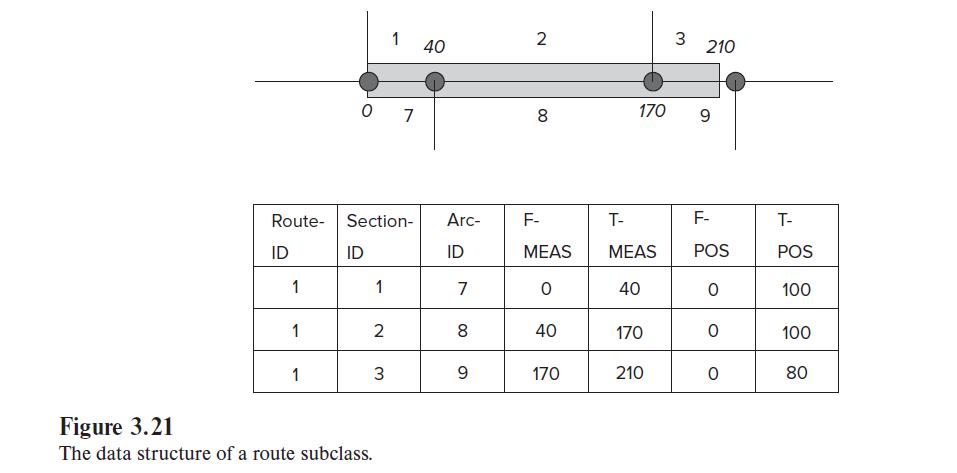
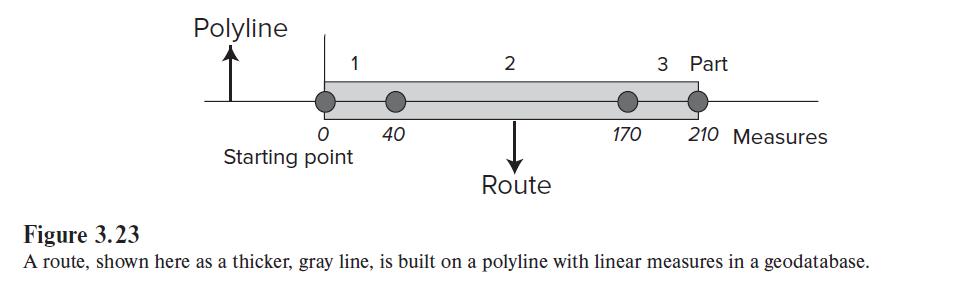
Introduction To Geographic Information Systems 9th Edition Kang-tsung Chang - Solutions
The "Introduction to Geographic Information Systems 9th Edition" by Kang-tsung Chang is a vital resource for students and professionals eager to deepen their GIS knowledge. Explore our comprehensive collection featuring a wide array of solved problems and step-by-step answers. Our online platform provides an extensive answers key, solutions manual, and solutions PDF, catering to all your needs. Access the instructor manual and test bank for detailed chapter solutions and questions and answers. Enhance your learning with our textbook solutions, available for free download, ensuring you have the best resources at your fingertips.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


![[Create a new selection] "cost"> 8 of 10 records selected [Add to current selection] "soiltype" = 'N3' OR](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1701/2/5/7/692656721dcc97de1701257692267.jpg)