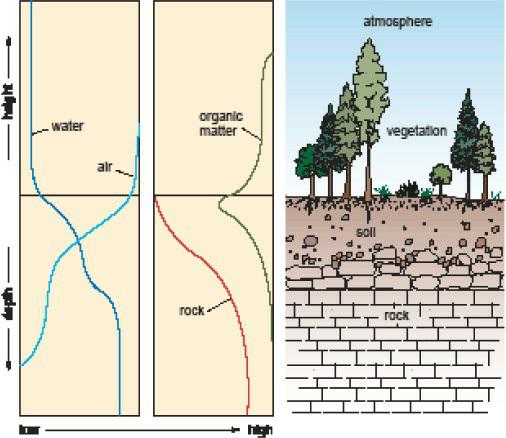
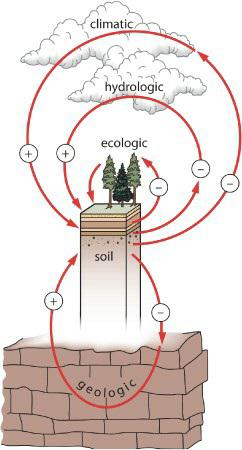
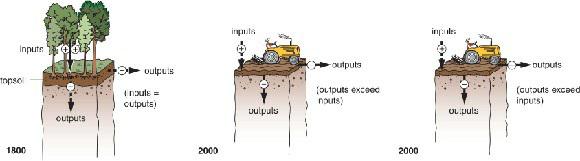
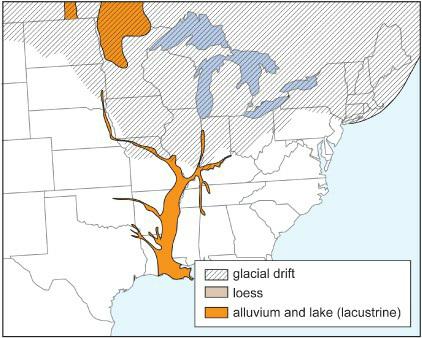
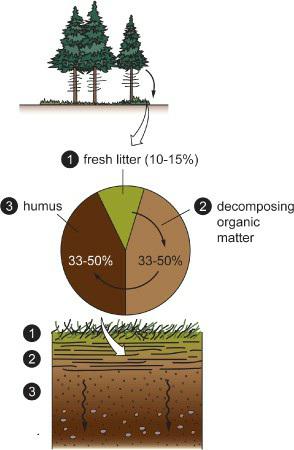
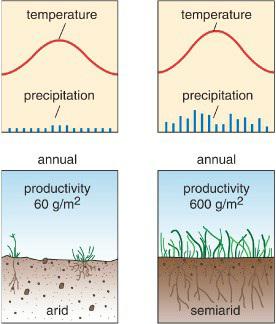
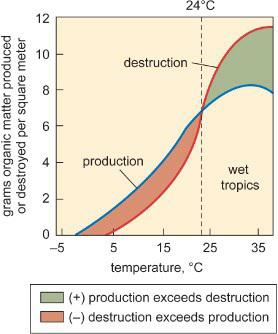
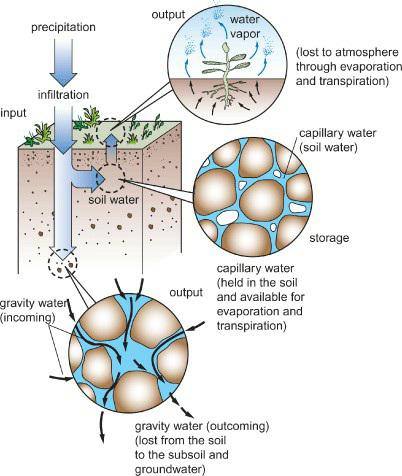
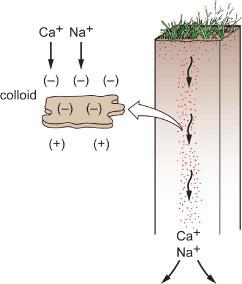
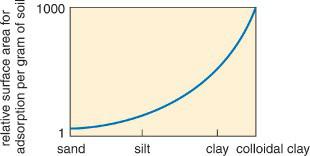
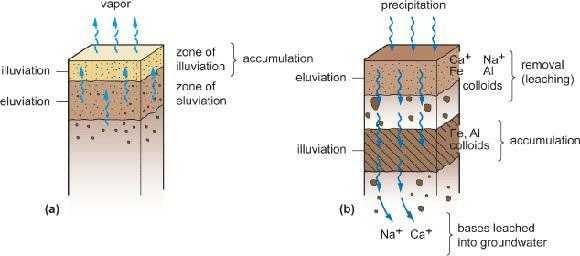
Physical Geography Great Systems And Global Environments 1st Edition William M. Marsh, Martin M. Kaufman - Solutions
Unlock the secrets of "Physical Geography: Great Systems and Global Environments" by William M. Marsh and Martin M. Kaufman with our comprehensive online resources. Access the complete answers key and solutions manual to enhance your understanding. Our solutions PDF provides step-by-step answers to all solved problems, offering a valuable instructor manual for educators. Dive into the textbook's questions and answers, exploring chapter solutions and test bank materials to thoroughly prepare for exams. Enjoy the convenience of a free download to enrich your learning experience with precise and detailed explanations.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()