Question: In Examples 17.3 and 17.5, crystallizer heat addition is by an external heat exchanger through which magma circulates, as in Figure 17.16. If instead the
In Examples 17.3 and 17.5, crystallizer heat addition is by an external heat exchanger through which magma circulates, as in Figure 17.16. If instead the heat is added to the feed, determine the new feed temperature. Which is the preferred way to add the heat?
Example 17.3
Concentrate from an evaporation system is 4,466 lb/h of 37.75 wt% MgSO4 at 170°F and 20 psia. It is mixed with 9,860 lb/h of a saturated aqueous recycle filtrate of MgSO4 at 85°F and 20 psia and sent to a vacuum crystallizer, operating at 85°F and 0.58 psia, to produce water vapor and a magma of 20.8 wt% crystals and 79.2 wt% saturated solution. The magma is sent to a filter, from which filtrate is recycled. Determine the lb/h of water evaporated and the maximum crystal production rate in tons/day on a dry basis.
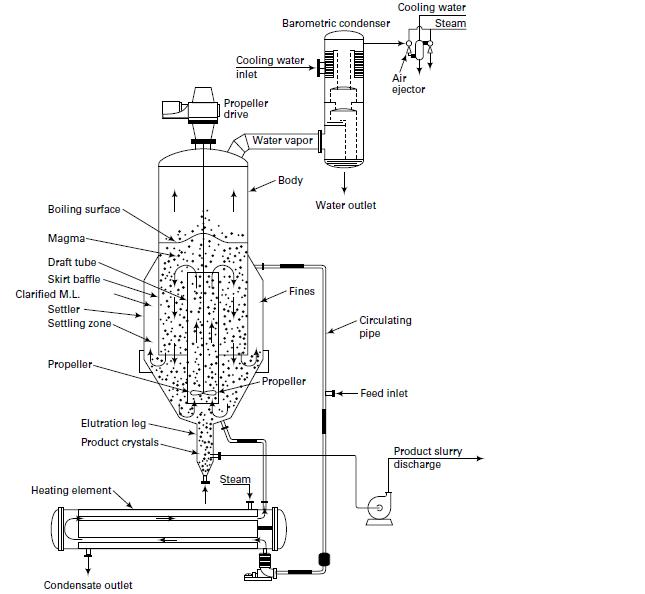
Boiling surface- Magma- Draft tube- Skirt baffle Clarified M.L. Settler Settling zone Propeller Elutration leg- Product crystals. Heating element- Condensate outlet Cooling water inlet Propeller drive Barometric condenser Steam Water vapor Body Fines Propeller Water outlet Cooling water Steam Air ejector Circulating pipe Feed inlet Product slurry discharge
Step by Step Solution
3.50 Rating (160 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The given process in Example 173 involves a vacuum crystallizer where the heat addition is through an external heat exchanger However to determine the ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


