GaAs has cubic symmetry, leading to the piezoelectric tensor shown in Table 3.4, with e 41 =
Question:
GaAs has cubic symmetry, leading to the piezoelectric tensor shown in Table 3.4, with e41 = 1.6×10−5 C/cm2.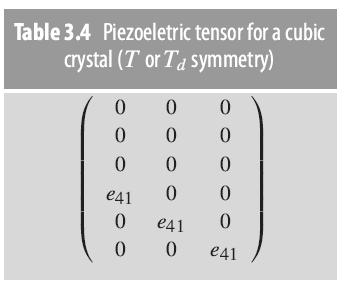
The elastic constants of GaAs are C11= 11.8 × 1011 dyne/cm2, C12 = 5.3 × 1011 dyne/cm2, and C44 = 5.9 × 1011 dyne/cm2. For a voltage of 5 V applied in the [100] direction across a slab of GaAs with thickness 1 mm, what strain will be created, assuming there is no applied stress?
Suppose that you want to generate an electric field by applying a stress to a GaAs crystal. What is a possible direction for a stress that would generate an electric field? Can you do this with a stress in the [100] direction?
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





