Question: (Lloyd's mirror) A point source of narrowband light is placed at distance (s) above a perfectly reflecting planar mirror. At distance (d) away, the interference
(Lloyd's mirror) A point source of narrowband light is placed at distance \(s\) above a perfectly reflecting planar mirror. At distance \(d\) away, the interference fringes are observed on a screen, as shown in Fig. 5-4p. The complex degree of (self-) coherence of the light is
\[ \gamma_{o}(\tau)=e^{-\pi \Delta u|\tau|} e^{-j 2 \pi \bar{v} \tau} \]
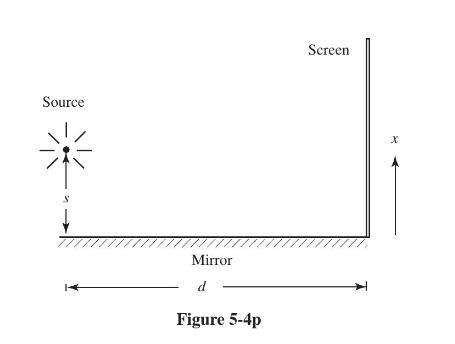
Adopting the assumptions \(s \ll d\) and \(x \ll d\), and taking account of a sign change of the field on reflection (polarization assumed parallel to the mirror), find
(a) The spatial frequency of the fringe.
(b) The classical visibility of the fringe as a function of \(x\), assuming equal strength interfering beams.
Source S Mirror d Figure 5-4p Screen X
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (158 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To analyze the problem with Lloyds mirror setup we can break it down into two parts a finding the spatial frequency of the fringe and b determining th... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


