The article Polyhedral Distortions in Tourmaline (A. Ertl, J. Hughes, et al., The Canadian Mineralogist, 2002: 153162)
Question:
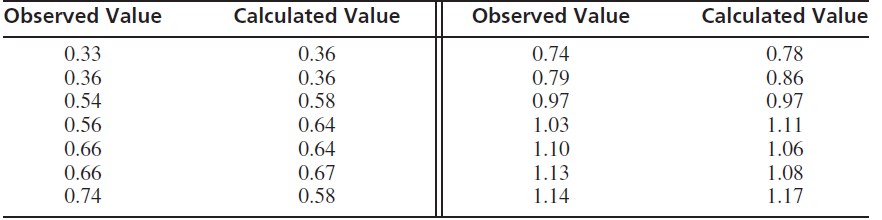
a. Assume that the observed value y is an unbiased measurement of the true value. Show that if the calculated value x is accurate (i.e., equal to the true value), then y = x + ε, where ε is measurement error.
b. Compute the least-squares line y = β̂0 + β̂1x.
c. Show that if the calculated value is accurate, then the true coefficients are β0 = 0 and β1 = 1.
d. Test the null hypotheses β0 = 0 and β1 = 1.
e. Is it plausible that the calculated value is accurate? Or can you conclude that it is not? Explain.
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Question Posted:





