Question:
As noted in the chapter, firms can have very distinctive cultures. Recall that Zappos has a standing offer to pay any new hire one month’s salary to quit the company after orientation. Zappos makes this offer to help ensure that those who stay with the company are comfortable in its “create fun and a little weirdness” environment. You may have taken a personality test such as Myers-Briggs or The Big Five. These tests may be useful in gauging compatibility of career and personality types. They are often available for both graduate and undergraduate students at university career placement centers. In considering the following questions, think about your next job and your longer-term career plans.
1. Review Exhibit 11.11 and circle the organizational characteristics you find appealing. Cross out those factors you think you would not like. Do you find a trend toward either the mechanistic or organic organization?
Exhibit 11.11
2. Have you been in school or work situations in which your values did not align with those of your peers or colleagues? How did you handle the situation? Are there certain values or norms important enough for you to consider as you look for a new job?
3. As you consider your career after graduation, which control-and-reward system would you find most motivating? Is this different from the controls used at some jobs you have had in the past? How do you think you would perform in a holacracy such as Zappos?
Transcribed Image Text:
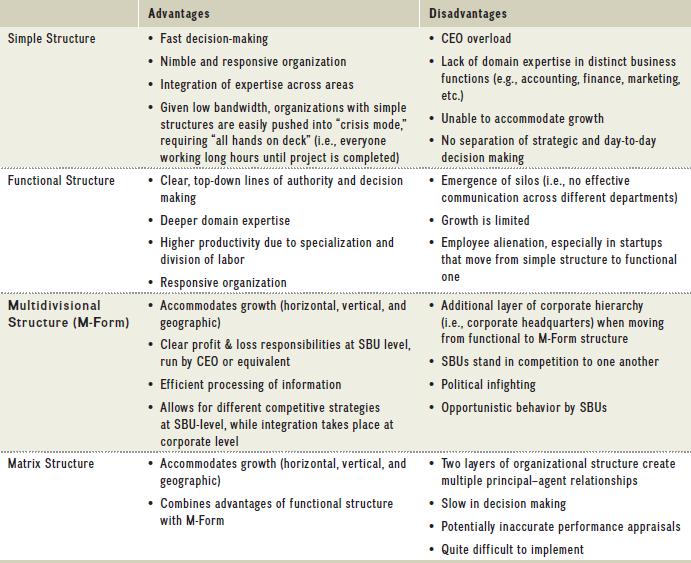
Simple Structure
Functional Structure
Multidivisional
Structure (M-Form)
Matrix Structure
Advantages
• Fast decision-making
• Nimble and responsive organization
• Integration of expertise across areas
• Given low bandwidth, organizations with simple
structures are easily pushed into "crisis mode,"
requiring "all hands on deck" (i.e., everyone
working long hours until project is completed)
Clear, top-down lines of authority and decision
making
Deeper domain expertise
• Higher productivity due to specialization and
division of labor
.
• Responsive organization
Accommodates growth (horizontal, vertical, and
geographic)
• Clear profit & loss responsibilities at SBU level,
run by CEO or equivalent
• Efficient processing of information
• Allows for different competitive strategies
at SBU-level, while integration takes place at
corporate level
• Accommodates growth (horizontal, vertical, and
geographic)
• Combines advantages of functional structure
with M-Form
Disadvantages
• CEO overload
• Lack of domain expertise in distinct business
functions (e.g., accounting, finance, marketing.
etc.)
• Unable to accommodate growth
No separation of strategic and day-to-day
decision making
Emergence of silos (i.e., no effective
communication across different departments)
• Growth is limited
Employee alienation, especially in startups
that move from simple structure to functional
one
• Additional layer of corporate hierarchy
(i.e., corporate headquarters) when moving
from functional to M-Form structure
• SBUS stand in competition to one another
• Political infighting
Opportunistic behavior by SBUS
Two layers of organizational structure create
multiple principal-agent relationships
Slow in decision making
Potentially inaccurate performance appraisals
Quite difficult to implement







