A robot arm consists of rigid links connected by joints allowing the relative motion of neighboring links.
Question:
A robot arm consists of rigid links connected by joints allowing the relative motion of neighboring links. The dynamic model for a robot arm can be derived using Lagrange's equations
\[\frac{\mathrm{d}}{\mathrm{d} t}\left(\frac{\partial T}{\partial \dot{\theta}_{i}}\right)-\frac{\partial T}{\partial \theta_{i}}+\frac{\partial V}{\partial \theta_{i}}=\tau_{i}, \quad i=1,2, \ldots, n\]
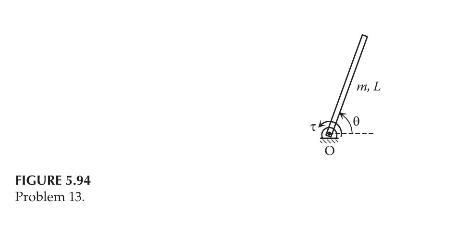
where: \(\theta_{i}\) is the angular displacement of the \(i\) th joint \(\tau_{i}\) is the torque applied to the \(i\) th joint \(n\) is the total number of joints Consider a single-link planar robot arm, as shown in Figure 5.94. Use Lagrange's equations to derive the dynamic model of the robot arm. Assume that the motion of the robot arm is constrained in a vertical plane, and the joint angle varies between \(0^{\circ}\) and \(360^{\circ}\).
Step by Step Answer:

Modeling And Analysis Of Dynamic Systems
ISBN: 9781138726420
3rd Edition
Authors: Ramin S. Esfandiari, Bei Lu





