A single-stage evaporator system is used to concentrate 10,000 kg/h of an NaOH solution from 10% to
Question:
A single-stage evaporator system is used to concentrate 10,000 kg/h of an NaOH solution from 10% to 35%. The feed is heated up using the residual heat from the condensed steam before entering the evaporator. The concentrated solution is cooled down using water in a second heat exchanger.
Finally, the evaporated water is condensed in direct contact with water (see Fig. P4.19).
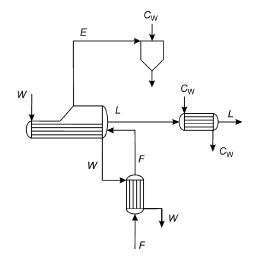
The hot utility is a saturated steam at 3.2 atm, which condenses at the evaporator and exits the heat exchanger at 40C. The evaporation chamber is maintained at 150 mmHg vacuum with respect to 760 mmHg. The liquid from the direct contact cooling device is at dew point. The NaOH solution is fed to the system at 20C and to the evaporator at 50C. The cooling water used to cool down the concentrated solution enters at 20C and leaves at 35C. The global heat transfer coefficient is 2000 kcal/(m2 hC). Determine:
a. Solution boiling point.
b. Flowrate of hot utility.
c. Evaporator area.
d. Required cooling water.
e. Area of the heat exchangers. The global heat transfer coefficients are 800 and 400 kcal/ (m2 hC) for the feed heated and the solution cooler, respectively.
Step by Step Answer:

Industrial Chemical Process Analysis And Design
ISBN: 9780081010938
1st Edition
Authors: Mariano Martín





