In Section 61, Figure 62 (c) shows an air-tunable capacitor as one example of the capacitor types.
Question:
In Section 6–1, Figure 6–2
(c) shows an air-tunable capacitor as one example of the capacitor types. This type of device can vary its capacitance similar to how a potentiometer can vary its resistance.
Changing the capacitance in a circuit can change the frequency at which it operates. Suppose we are given the circuit in Figure P6–73 with a capacitor connected in parallel with an inductor. There are no other devices in the circuit. The capacitor has an initial voltage vCð0Þ = V0 V and the inductor’s initial current is iLð0Þ = 0A.
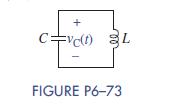
The differential equation for the voltage across the capacitor in this circuit is given by
![]()
We will learn more about solving this type of differential equation in the next chapter and beyond. The solution to this differential equation is
![]()
UsingMATLAB, plotonasemi-logscale (logarithmiconthehorizontal and linear on the vertical) the radian frequency of vCðtÞ versus the capacitance of the circuit. Use capacitances scaled logarithmically from 0:001 to 1 μF. In a separate MATLAB figure, use the subplot command to plot vC(t) versus time for C = 0:001 μF, 0:01 μF, 0:1 μF, and 1 μF. Using the plots you created and your knowledge of how a capacitor stores charge, explain why changing the capacitance of a parallel LC circuit changes the frequency at which it oscillates.
Step by Step Answer:

The Analysis And Design Of Linear Circuits
ISBN: 9781119235385
8th Edition
Authors: Roland E. Thomas, Albert J. Rosa, Gregory J. Toussaint





