Repeat Example 5.20, and determine a mathematical model for the single-link robot arm shown in Figure 5.97
Question:
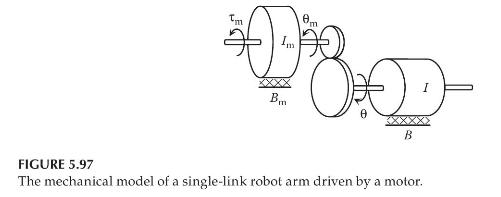
Repeat Example 5.20, and determine a mathematical model for the single-link robot arm shown in Figure 5.97 in the form of a differential equation of motion in the load variable \(\theta\).
Data From Example 5.20:
The mechanical model of a single-link robot arm driven by a motor can be represented as a gear–train system, as shown in Figure 5.97, in which two rotational subsystems are coupled with a pair of gears with negligible inertia. The mass moments of inertia of the motor and the load are Im and I, respectively. The coefficients of torsional viscous damping of the motor and the load are Bm and B, respectively. τm is the torque generated by the motor. Assume that the gear ratio is N = r1/r2. Derive the differential equation of motion in terms of the motor variable θm.
Step by Step Answer:

Modeling And Analysis Of Dynamic Systems
ISBN: 9781138726420
3rd Edition
Authors: Ramin S. Esfandiari, Bei Lu





