Figure P3.26 shows a boiler and turbine from a coal-fired steam power plant. Water enters the boiler
Question:
Figure P3.26 shows a boiler and turbine from a coal-fired steam power plant. Water enters the boiler at 5 MPa, 100°C at a mass flow rate of 400 kg/s. Steam leaves the boiler at 5 MPa, 650°C. The steam then passes through a turbine with an isentropic efficiency of 86% and exhausts to a pressure of 10 kPa. The turbine is connected to an electrical generator with an efficiency of 94%. The boiler is fired using coal with a heat of combustion of 21,000 kJ/kg. The coal is combusted with dry atmospheric air entering the furnace after passing through a preheater. The air enters the furnace at 1 atm, 300°C at a volumetric flow rate of 400 m3/s. The products of combustion leave the furnace at 1 atm, 700°C. Determine the
a. Power delivered by the electrical generator (MW)
b. Mass-based air-fuel ratio in the boiler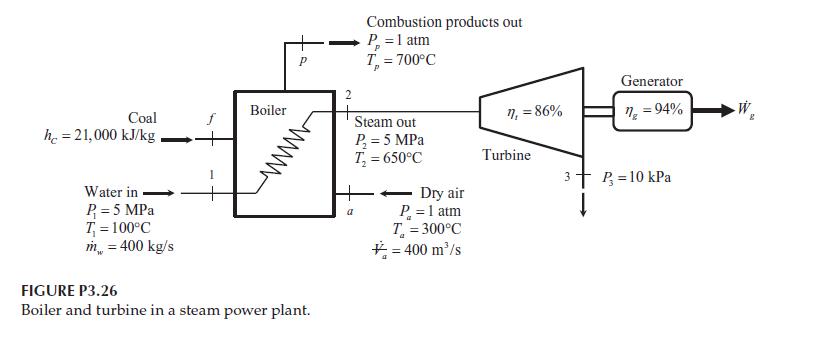
c. Total mass of coal used in one year, assuming the plant runs continuously all year long and the power delivery is constant at the value computed in part (a).
Express your answer in tons.
The cost of delivered coal to the plant is $48.52/ton, and the utility company sells energy at a rate of $0.10/kWh. Assuming that the power delivery remains constant year-round at the value computed in part (a), and all of the energy delivered by the generator can be sold, determine the following,
d. The annual cost of coal to operate the power plant
e. The annual income realized from the sale of energy delivered by the generator
f. The annual profit made by the utility company due to the sale of energy
Step by Step Answer:

Thermal Energy Systems Design And Analysis
ISBN: 9781138735897
2nd Edition
Authors: Steven G. Penoncello





