Two long blocks, made up of different homogeneous materials, are at temperatures T 1 and T 2
Question:
Two long blocks, made up of different homogeneous materials, are at temperatures T1 and T2 when they are brought into contact with one another. The interface quickly reaches a temperature T0 given by, 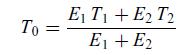 where E1 =√κ1 c1 > 0 and E2 = √κ2 c2 > 0 are called the effectivities of materials 1 and 2, where κ1 and κ2 are the thermal conductivities and c1 and c2 the specific heat per unit volume of both materials. If material 1 is very hot, but it has a low thermal conductivity κ1 and specific heat c1, and to the contrary material 2 has large thermal conductivity κ2 and specific heat c2, then the temperature of the interface T0 is almost T2, i.e. material 2 does not ‘feel the heat’ of material 1. Establish this result by using the following instructions:
where E1 =√κ1 c1 > 0 and E2 = √κ2 c2 > 0 are called the effectivities of materials 1 and 2, where κ1 and κ2 are the thermal conductivities and c1 and c2 the specific heat per unit volume of both materials. If material 1 is very hot, but it has a low thermal conductivity κ1 and specific heat c1, and to the contrary material 2 has large thermal conductivity κ2 and specific heat c2, then the temperature of the interface T0 is almost T2, i.e. material 2 does not ‘feel the heat’ of material 1. Establish this result by using the following instructions:
a) Consider an x-axis normal to the interface with x = 0 at the interface, x 0 in material 2. Let T1 (x, t) and T2 (x, t) be the solutions of the heat diffusion equation (11.35) in materials 1 and 2. Determine the boundary conditions on T1 (x, t) and T2 (x, t) at the interface.
b) Using an approach that is analogous to the one presented in § 11.4.3, show that the general solutions for the temperature profiles T1 (x, t) and T2 (x, t) are given by,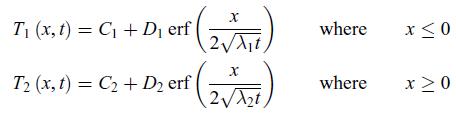
where erf (ν) is the error function defined as,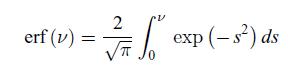 and C1, C2, D1 and D2 are constant coefficients.
and C1, C2, D1 and D2 are constant coefficients.
c) Use the boundary conditions to determine the coefficients in terms of the temperatures T0, T1 and T2. Show that the temperature T0 is given by the effusivity relation just after the two blocks have reached a common temperature at the interface.
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9781108426091
1st Edition
Authors: Jean-Philippe Ansermet, Sylvain D. Brechet





