Question: For a spherical planet with mass M, volume V, and radius R, derive an expression for the acceleration due to gravity at the planets surface,
For a spherical planet with mass M, volume V, and radius R, derive an expression for the acceleration due to gravity at the planet€™s surface, g, in terms of the average density of the planet, r = M/V, and the planet€™s diameter, D = 2R. The table gives the values of D and g for the eight major planets:
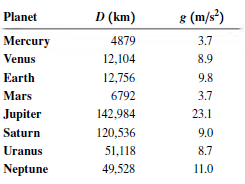
(a) Treat the planets as spheres. Your equation for g as a function of r and D shows that if the average density of the planets is constant, a graph of g versus D will be well represented by a straight line. Graph g as a function of D for the eight major planets. What does the graph tell you about the variation in average density?
(b) Calculate the average density for each major planet. List the planets in order of decreasing density, and give the calculated average density of each.
(c) The earth is not a uniform sphere and has greater density near its center. It is reasonable to assume this might be true for the other planets. Discuss the effect this nonuniformity has on your analysis.
(d) If Saturn had the same average density as the earth, what would be the value of g at Saturn€™s surface?
8 (m/s) D (km) Planet Mercury 4879 3.7 Venus 12,104 8.9 Earth 12,756 9.8 6792 Mars 3.7 Jupiter 142,984 23.1 120,536 Saturn 9.0 51,118 Uranus 8.7 11.0 Neptune 49,528
Step by Step Solution
3.48 Rating (171 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
IDENTIFY and SET UP At the surface of a planet g GMR 2 and average density is mV where V 43 R 3 for ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


