If the elephant were to snorkel in salt water, which is more dense than freshwater, would the
Question:
(a) Yes€”that depth would increase, because the pressure would be lower at a given depth in salt water than in freshwater;
(b) yes€”that depth would decrease, because the pressure would be higher at a given depth in salt water than in freshwater;
(c) No, because pressure differences within the submerged elephant depend on only the density of air, not the density of the water;
(d) No, because the buoyant force on the elephant would be the same in both cases.
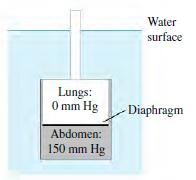
An elephant can swim or walk with its chest several meters underwater while the animal breathes through its trunk, which remains above the water surface and acts like a snorkel. The elephant€™s tissues are at an increased pressure due to the surrounding water, but the lungs are at atmospheric pressure because they are connected to the air through the trunk. The figure shows the gauge pressures in an elephant€™s lungs and abdomen when the elephant€™s chest is submerged to a particular depth in a lake. In this situation, the elephant€™s diaphragm, which separates the lungs from the abdomen, must sustain the difference in pressure between the lungs and the abdomen. The diaphragm of an elephant is typically 3.0 cm thick and 120 cm in diameter.
Step by Step Answer:

University Physics with Modern Physics
ISBN: 978-0133977981
14th edition
Authors: Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman





