Question: If the voltage rather than the current is kept constant, what happens as the temperature increases from 25°C to 150°C? (a) At first the current
If the voltage rather than the current is kept constant, what happens as the temperature increases from 25°C to 150°C?
(a) At first the current increases, then it decreases.
(b) The current increases.
(c) The current decreases, eventually approaching zero.
(d) The current does not change unless the voltage also changes.
The current€“voltage characteristics of a forwardbiased p-n junction diode depend strongly on temperature, as shown in the figure. As a result, diodes can be used as temperature sensors. In actual operation, the voltage is adjusted to keep the current through the diode constant at a specified value, such as 100 mA, and the temperature is determined from a measurement of the voltage at that current.
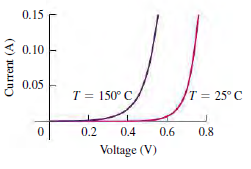
0.15 0.10 0.05 T = 150 C T = 25 C 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 Voltage (V) Current (A)
Step by Step Solution
3.32 Rating (170 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
IDENTIFY and SET UP On the graph shown with the introduction draw a vertical line ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


