Question: The financial information shown in the following table was presented for Massive Enterprises Ltd. for the year ending May 31, 20X1. Statement of Income Sales
The financial information shown in the following table was presented for Massive Enterprises Ltd. for the year ending May 31, 20X1.
Statement of Income
Sales………………… $1,700,000
Cost of sales…………… 830,000
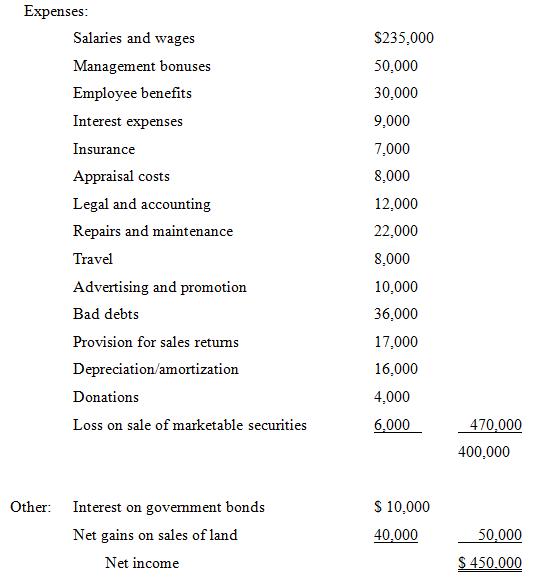
Additional Information:*
* All relates to the statement of income.
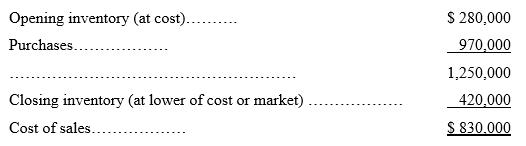
The closing inventory at the end of the previous year was valued at the lower of cost or market, which amounted to $270,000.
2. The salaries and wages of $235,000 included salaries of $95,000 to the president, $80,000 to the president’s spouse (who worked as a full-time manager), and $15,000 to a full-time housekeeper, who looked after the children so that the president and the president’s spouse could work full-time in the business.

4. Employee benefits:

5. Interest expense included interest of $8,000 on a bank loan that was used to purchase new equipment during the previous year. In addition, $1,000 of interest arising from deficient income tax instalments was paid to the CRA.

7. Appraisal costs:

8. Legal and accounting expenses:

9. Repair and maintenance costs:

10. Travel costs (incurred for sales personnel):

11. Advertising and promotion costs:

12. Bad debts expense of $36,000 represented an increase in the reserve for doubtful accounts receivable arising from the sale of merchandise.
13. As a result of past experience, the company began a new policy of providing a reserve of 1% of sales for expected future returns of defective merchandise sold. Although the year’s provision was $17,000, only $12,000 of merchandise was returned.
14. The depreciation/amortization expense of $16,000 was based on the estimated useful life of depreciable property owned (equipment and vehicles). Capital cost allowance and amortization of eligible capital expenditures for tax purposes have been correctly calculated as $19,000 in total.
15. The loss on sale of securities resulted from the sale of shares in public corporations. These were acquired several years earlier using excess funds not needed for the business.
16.The net gain on the sale of land of $40,000 consisted of the following:
• Property 1, which was acquired three years earlier at a cost of $100,000 as a potential site for a new head office building. However, new leased space became available, thus eliminating the need for a new building. Because of this, the land has been sold at the market price of $160,000.
• Property 2, which was purchased four years earlier with excess corporate funds after it was learned that a new shopping centre was being planned for the area. The company believed that the new shopping centre would enhance property values and purchased the land at a cost of $90,000 in the hope that it could be sold at a substantial profit. But the shopping centre proposal was cancelled and the land was sold in the current year for $70,000.
Required:
1. For the year ended May 31, 20X1, determine the company’s net income from business for tax purposes.
Expenses S235,000 50,000 30,000 9.000 7,000 8.000 12,000 22,000 8.000 0.000 36,000 17,000 16,000 4.000 6.000 Salaries and wages Management bonuses Employee benefit Interest expenses Insurance Appraisal costs Legal and accounting Repairs and maintenance Travel dvertising and promotion Bad debts Provision for sales retums Depreciation/amortization Donations Loss on sale of marketable securities 470,000 400,000 Other 10,000 Interest on government bonds Net gains on sales of land 40.000 50.000 Net income Legal fees: To collect an account receivable Cost of amending the Articles of Incorporation Costs of issuing a new class of preference shares S 400 1,000 and debentures 3,000 Accounting Tax consultations for a submission to a federal govemment task force on sales tax reform 2,000 Annual audit fees 5.600 $12.000
Step by Step Solution
3.29 Rating (164 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The question requires the determination of net income from business Therefore other items such as pr... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
691-L-B-L-I-T-E (664).docx
120 KBs Word File


