The saturation concentration of dissolved oxygen in fresh-water can be calculate with the equation Where O s??
Question:
The saturation concentration of dissolved oxygen in fresh-water can be calculate with the equation
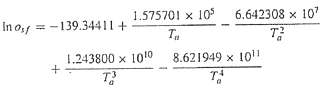
Where Os??= the saturation concentration of dissolved oxygen in freshwater at l atm (mg/L) and Ta?= absolute temperature (K). Remember that Ta = T + 273.15, where T = temperature (oC).According to this equation, saturation decreases with increasing temperature. For typical natural waters in temperate climate, the equation can be used to determine that oxygen concentration ranges from 14.621 mg/L at 0oC to 6.413 mg/L at 40oC. Given a value of oxygen concentration, this formula and the bisection method can be used to solve for temperature in oC.
(a) If the initial guesses are set as 0 and 40oC, how many bisection iterations would be required to determine temperature to an absolute error of 0.05oC?
(b) Develop and test a bisection program to determine T as a function of a given oxygen concentration to a prespecified absolute error as in (a). Given initial guesses of 0 and 40oC, test your program for an absolute error = 0.05oC and the following cases: osf = 8, 10 and 12 mg/L. Check your results.
Step by Step Answer:

Numerical Methods For Engineers
ISBN: 9780071244299
5th Edition
Authors: Steven C. Chapra, Raymond P. Canale





