A thin metallic foil of thickness 0.25 mm with a pattern of extremely small holes serves as
Question:
A thin metallic foil of thickness 0.25 mm with a pattern of extremely small holes serves as an acceleration grid to control the electrical potential of an ion beam. Such a grid is used in a chemical vapor deposition (CVD) process for the fabrication of semiconductors. The top surface of the grid is exposed to a uniform heat flux caused by absorption of the ion beam, q"s = 600 W/m2. The edges of the foil are thermally coupled to water-cooled sinks maintained at 300 K. The upper and lower surfaces of the foil experience radiation exchange with the vacuum enclosure walls maintained at 300 K. The effective thermal conductivity of the foil material is 40 W/m ∙ K and its emissivity is 0.45.
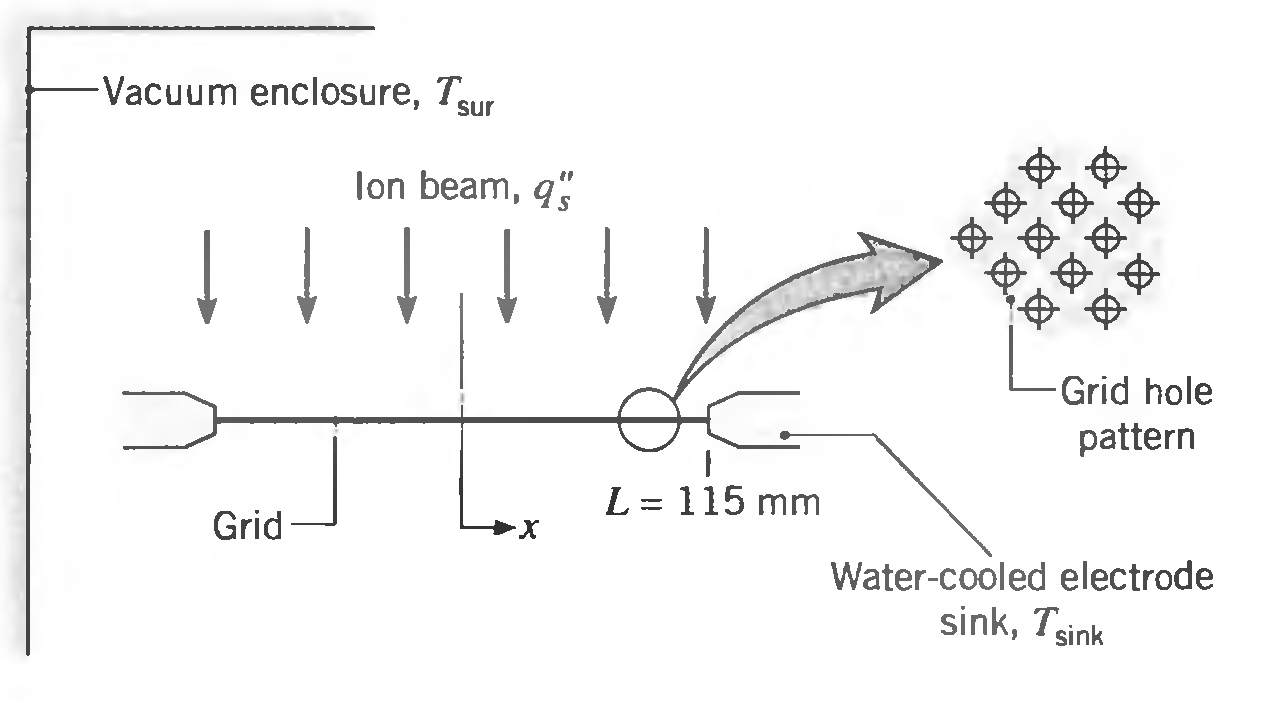
Assuming one-dimensional conduction and using a finite-difference method representing the grid by ten nodes in the x direction, estimate the temperature distribution for the grid.
DistributionThe word "distribution" has several meanings in the financial world, most of them pertaining to the payment of assets from a fund, account, or individual security to an investor or beneficiary. Retirement account distributions are among the most...
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals of Heat and Mass Transfer
ISBN: 978-0471457282
6th Edition
Authors: Incropera, Dewitt, Bergman, Lavine





