A bowler throws a bowling ball of radius R = 11 cm along a lane. The ball
Question:
A bowler throws a bowling ball of radius R = 11 cm along a lane. The ball (Figure) slides on the lane with initial speed vcom,0 = 8.5 m/s and initial angular speed w0 = 0. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the ball and the lane is 0.21. The kinetic frictional force f k acting on the ball causes a linear acceleration of the ball while producing a torque that causes an angular acceleration of the ball. When speed v com has decreased enough and angular speed w has increased enough, the ball stops sliding and then rolls smoothly.(a) What then is v com in terms of w? During the sliding, what are the balls?(b) Linear acceleration and(c) Angular acceleration?(d) How long does the ball slide?(e) How far does the ball slide?(f) What is the linear speed of the ball when smooth rollingbegins?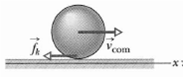
Step by Step Answer:

Fundamentals of Physics
ISBN: 978-0471758013
8th Extended edition
Authors: Jearl Walker, Halliday Resnick





