An automotive catalytic convertor is a packed bed in which a platinum catalyst is coated on the
Question:
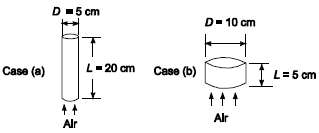
An automotive catalytic convertor is a packed bed in which a platinum catalyst is coated on the surface of small alumina spheres. A metal container holds the catalyst pellets and allows engine exhaust gases to flow through the bed of pellets. The catalyst must be heated by the exhaust gases to 300?C before the catalyst can help combust unburned hydrocarbons in the gases. The time required to achieve this temperature is critical because unburned hydrocarbons emitted by the vehicle during a cold start comprise a large fraction of the total emissions from the vehicle during an emission test. A fixed volume of catalyst is required but the shape of the bed can be modified to increase the heat-up rate. Compare the heat-up time for a bed 5 cm diameter and 20 cm long with one 10cm diameter and 5 cm long. The catalyst pellets are spherical, 5 mm diameter, have a density of 2 g/cm3, thermal conductivity of 12 W/(mK) and specific heat of 1100 J/(kg K). The packed-bed void fraction is 0.5. Exhaust gas from the engine is at a temperature of 400?C, a flow rate of 6.4 gm/s, and has the properties of air.GIVENA packed bed catalytic converter comprised of platinum coated alumina spheres with exhaust gases flowing through themTwo possible bed geometriesCase a: Diameter (Db) = 5 cm = 0.05 mLength (L) = 20 cm = 0.2 mCase b: Diameter (Db) = 10 cm = 0.1 mLength (L) = 5 cm = 0.05 mSphere density (ρp) = 2 g/cm3 = 2000 kg/m3Sphere diameter (Dp) = 5 mm = 0.005 mSphere thermal conductivity (kp) = 12 W/(m K)Void fraction (ε) = 0.5Sphere specific heat (cp) = 1100 J/(kg K)Engine exhaust gas temperature (Tg) = 400?CEngine exhaust mass flow rate (m) = 6.4 g/s = 0.0064 kg/sEngine exhaust has the properties of airASSUMPTIONSThe initial temperature of the bed (To) =20?C
Step by Step Answer:

Principles of heat transfer
ISBN: 978-0495667704
7th Edition
Authors: Frank Kreith, Raj M. Manglik, Mark S. Bohn





