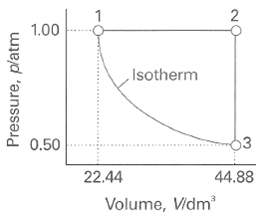
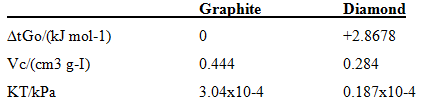
Physical Chemistry 7th Edition Peter Atkins - Solutions
Discover comprehensive solutions for "Physical Chemistry 7th Edition" by Peter Atkins with our expertly curated resources. Access an online answers key, detailed answers, and a solutions manual to aid your study. Our solutions PDF offers step-by-step answers and solved problems for a deeper understanding. Enhance your learning with our test bank and chapter solutions, all tailored to support your needs. Whether you're seeking an instructor manual or a textbook guide, our platform provides everything you need. Enjoy the convenience of free download options, empowering you to excel in your physical chemistry endeavors.
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()