Question: A dilute aqueous solution of H2SO4 (Solution A) is to be mixed with a solution containing 90.0 wt% H2SO4 (Solution B) to produce a 75.0
A dilute aqueous solution of H2SO4 (Solution A) is to be mixed with a solution containing 90.0 wt% H2SO4 (Solution B) to produce a 75.0 wt% solution (Solution C).
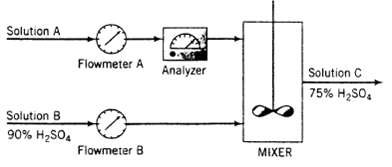
The flow rate and concentration of Solution A change periodically, so that it is necessary to adjust the flow rate of Solution B to keep the product H2S04 concentration constant. Flow meters A and B have linear calibration plots of mass flow rate (m) versus meter reading (R) which pass through the following points:
Flow meter A: mA = 150lbm/h, RA = 25
mA 500lbm/h, RA = 70
Flow meter B: mB = 200lbm/h, RB = 20
mB = 8(X) lbm/h. RB = 60
The analyzer calibration is a straight Line on a semi log plot of % H2SO4(x) on a logarithmic scale versus meter reading (Rx) on a linear scale. The line passes through the points (x = 20%, Rx 4.0) and (x 100%. Rx = 10.0).
(a) Calculate the flow rate of Solution B needed to process 300lbm/h of 55% H2 SO4 (Solution A) and the resulting flow rate of Solution C. (The calibration data are not needed for this part.)
(b) Derive the calibration equations for mA (RA), mB(RB), and x(Rx. Calculate the values of RA RB, and R corresponding to the flow rates and Concentrations of part (a).
(c) The process technician's job is to read Flow meter A and the analyzer periodically, and then to adjust the flow rate of Solution B to its required value. Derive a formula that the technician can use for R8 in terms of RA and R. and then check it by substituting the values of part(a).
Solution A Solution B 90% HSO4 o Flowmeter A Flowmeter B Analyzer MIXER Solution C 75% HSO4
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (162 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a 300lbh 055lb HSO41bm 045lb HOlb mg lbmh 0901b HSO41bm 010lb HOlb ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (2 attachments)
13-E-C-E-C-P (120).pdf
180 KBs PDF File
13-E-C-E-C-P (120).docx
120 KBs Word File


