Question: For the normal distribution 2k = 2k (2k)! / (k! 2k) and 2k+1 = 0, k = 0, 1, . . . . Use this
For the normal distribution μ2k = σ2k (2k)! / (k! 2k) and μ2k+1 = 0, k = 0, 1, . . . . Use this result to analyze the two estimators where mk = 1/n Σni=1 (xi ?? x)k. The following result will be useful. Asy Cov [??nmj, ??nmk] = μj + k ?? μjμk + jkμ2μj??1 μk??1 ?? jμj??1μk+1 ?? kμk??1μj+1. Use the delta method to obtain the asymptotic variances and covariance of these two functions assuming the data are drawn from a normal distribution with mean μ and variance σ2. Under the assumptions, the sample mean is a consistent estimator ofμ, so for purposes of deriving asymptotic results, the difference between x and μ may be ignored. As such, no generality is lost by assuming the mean is zero, and proceeding from there. Obtain V, the 3 × 3 covariance matrix for the three moments, then use the delta method to show that the covariance matrix for the two estimators is where J is the 2 x 3 matrix of derivatives.
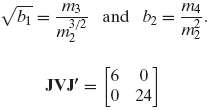
b = m3 3/2 m JVJ' = and by: b [60 0 24 m4 m m
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (192 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
For the normal distribution 24 2kk2 and 21 0 k 0 1 Use this result to analyze the two estimators M3 ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
3-M-E-E-A (132).docx
120 KBs Word File


