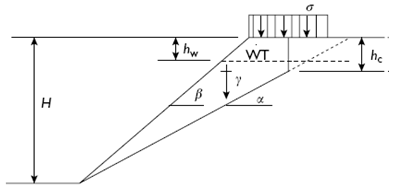
A generic diagram of a slope in a jointed rock mass that is threatened by a planar
Question:
A generic diagram of a slope in a jointed rock mass that is threatened by a planar block slide is shown, in the sketch. Although not shown, bench height is 55 ft (16.76 m).
Given that Mohr–Coulomb failure criteria apply, the clay-filled joints constitute 93%
of the potential shear failure surface, no tension cracks have yet appeared and:
1 slope height H =? ft (m);
2 failure surface angle α = 32◦;
3 slope angle β = 49◦;
4 friction angle (rock) φr = 38◦
5 cohesion (rock) cr = 1000 psi (6.90MPa);
6 friction angle (joint) φj = 27◦;
7 cohesion (joint) cj = 10 psi (0.069MPa);
8 specific weight γ = 158pcf (25.0kN/m3);
9 tension crack depth hc = 0.0 ft (m);
10 water table depth hw = 0.0 ft (m);
11 seismic coefficient ao = 0.00;
12 surcharge s = 0.0 psf (kPa)
Find the maximum pit depth possible without drainage.
Step by Step Answer:






