An orifice meter (see Figure 3.2-1) is to be calibrated for the measurement of the flow rate
Question:
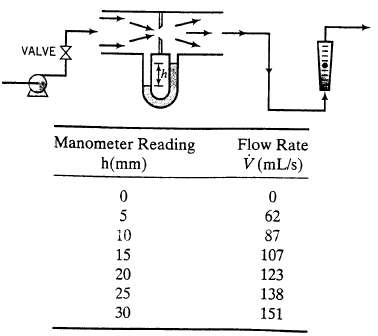
An orifice meter (see Figure 3.2-1) is to be calibrated for the measurement of the flow rate of a stream of liquid acetone. The differential manometer fluid has a specific gravity of 1.10. The calibration is accomplished by connecting the orifice meter in series with a rotameter that has previously been calibrated for acetone, adjusting a valve to set the flow rate, and recording the flow rate (determined from the rotameter reading and the rotameter calibration curve) and the differential manometer reading, h. The procedure is repeated for several valve settings to generate an orifice meter calibration curve of flow rate versus h. The following data are taken.
(a) For each of the given readings calculate the pressure drop across the orifice, ?P (mm Hg).
(b) The flow rate through an orifice should be related to the pressure drop across the orifice by the formula V = K (?P)n verify graphically that the given orifice calibration data are correlated by this relationship, and determine the values of K and n that best fit the data.
(c) Suppose the orifice meter is mounted in a process line containing acetone and a reading = 23 mm is obtained. Determine the volumetric, mass, and molar flow rates of acetone in the line.
Step by Step Answer:

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes
ISBN: 978-0471720638
3rd Edition
Authors: Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau





