Question:
The White Ocean Company is an office products distributor that must decide what to do with delinquent credit-sales accounts. Mr. Bob Smith, the credit manager, divides accounts into the following categories: (1) accounts not past due, (2) accounts 30 days or less past due, (3) accounts 31 to 60 days past due, (4) accounts 61 to 90 days past due, and (5) accounts more than 90 days past due. For simplicity, assume that all transactions for each account fall neatly into the same category. Mr. Smith decides what to do about these customer accounts based on the history of the account in general and also the activity during the account€™s delinquency period. Sometimes, for example, the customer will not communicate at all. At other times, however, the customer will either write to state that a cheque is forthcoming or make a partial payment. Mr. Smith tends to be most understanding of customers who make partial payments because he considers such payments acts of good faith. Mr. Smith is less understanding of those customers who only promise to pay or who simply ignore follow-up bills from the company. Mr. Smith has four potential actions to take in cases of credit delinquency. First, he can simply wait (i.e., do nothing). Second, he can send an initial letter to the customer, inquiring about the problem in bill payment and requesting written notification of a payment schedule if payment has not already been made. Third, he can send a follow-up letter indicating that a collection agency will be given the account if immediate payment is not forthcoming.
Fourth, he can turn the account over to a collection agency. Of course, Mr. Smith prefers to use one of the first three actions rather than turn the account over to a collection agency because his company receives only half of any future payments when the collection agency becomes involved.
a. Create a decision table for the White Ocean Company and provide a set of reasonable decision rules for Mr. Smith to follow. For now, ignore the influence of a customer€™s credit history.
b. Expand the decision table analysis you have prepared in question (a) to include the credit history of the customer accounts. You are free to make any assumptions you wish about how this history might be evaluated by Mr. Smith.
Transcribed Image Text:
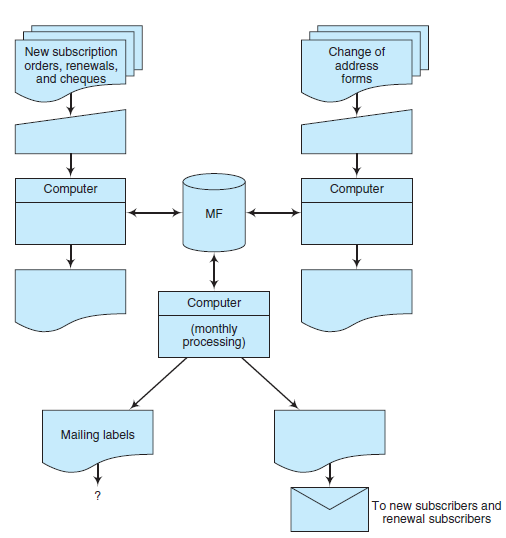
New subscription orders, renewals, and cheques Change of address forms Computer Computer MF Computer (monthly processing) Mailing labels To new subscribers and renewal subscribers







