Repeat Example 7.10 except consider the case when the operating pressures in both the shell and the
Question:
Repeat Example 7.10 except consider the case when the operating pressures in both the shell and the tube side are 100 barg. Explain why the pressure factor for the heat exchanger is much smaller than for any of the process vessels shown in Figure 7.6.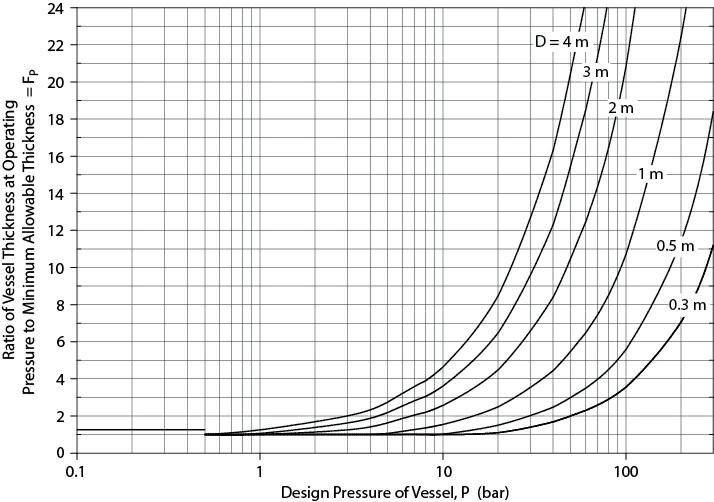
Example 7.10
Find the bare module cost of a floating-head, shell-and-tube heat exchanger with a heat transfer area of 100 m at the end of 2016. The operating pressure of the equipment is 1.0 bar, with both shell and tube sides constructed of carbon steel. The cost curve for this heat exchanger is given in Appendix A, Figure A.5, and is repeated as Figure 7.4. It should be noted that unlike the examples shown in Figures 7.1 and 7.2, the log-log plot of cost per unit area versus area is nonlinear. In general this will be the case, and a second-order polynomial is normally used to describe this relationship.
Figure A.5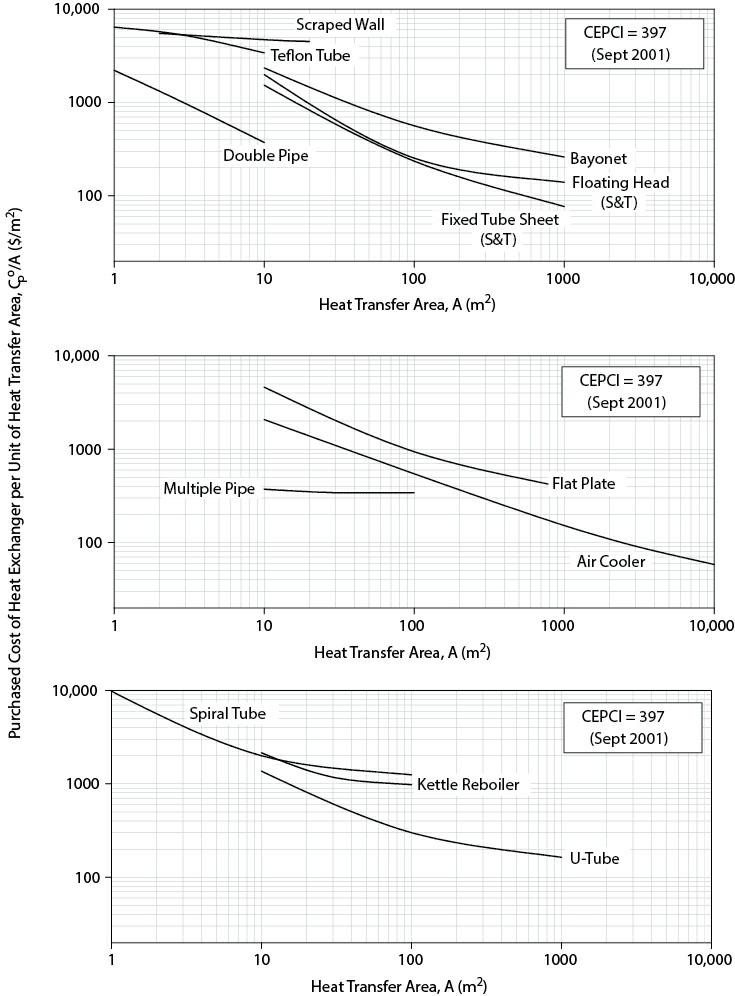
Figures 7.1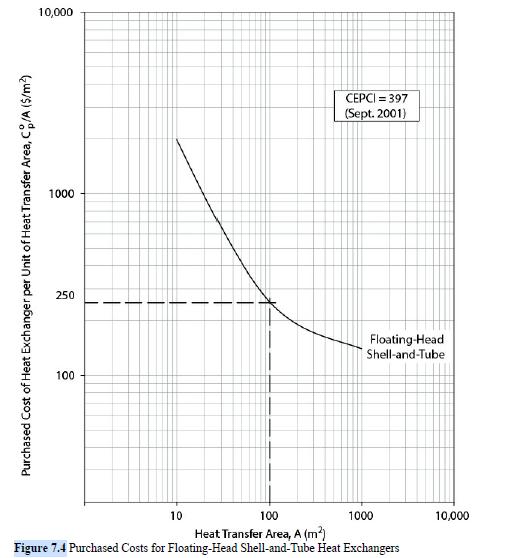
Figures 7.2
Step by Step Answer:

Analysis Synthesis And Design Of Chemical Processes
ISBN: 9780134177403
5th Edition
Authors: Richard Turton, Joseph Shaeiwitz, Debangsu Bhattacharyya, Wallace Whiting





