Question: An nth-order rate law is often used to model chemical reactions that solely depend on the concentration of a single reactant: where c = concentration
An nth-order rate law is often used to model chemical reactions that solely depend on the concentration of a single reactant:
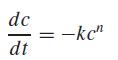
where c = concentration (mole), t = time (min), n = reaction order (dimensionless), and k = reaction rate (min−1 mole1−n). The differential method can be used to evaluate the parameters k and n. This involves applying a logarithmic transform to the rate law to yield,
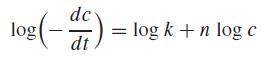
Therefore, if the nth-order rate law holds, a plot of the log(−dc/dt) versus log c should yield a straight line with a slope of n and an intercept of log k. Use the differential method and linear regression to determine k and n for the following data for the conversion of ammonium cyanate to urea:

dc dt -kch
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (154 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To determine the values of k and n for the given reaction we can use the differential method and lin... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


