Question: A non-angler, curious to know what counts as a good day of fishing (F) at the lake and puzzled by the phenomenon that it can
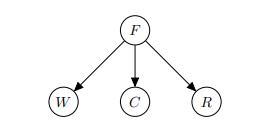
A non-angler, curious to know what counts as a good day of fishing (F) at the lake and puzzled by the phenomenon that it can sometimes be a good day even when no fish are caught, decides to create a naive Bayes model with F as the Boolean class variable and three features: whether it rained (R), how many fish were caught (C) with values {none, some, lots}, and whether it was windy (W). A naive Bayes net is shown in Figure S12.1.
a. Here are some plausible probability tables estimated from (entirely made up) data:
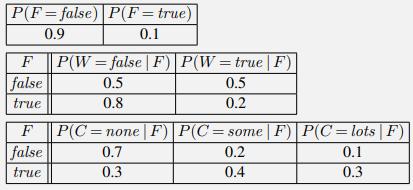
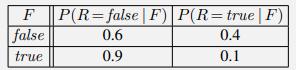
Given this model, calculate the following probabilities:
(i) P(F = true | R = true, C = none, W = true).
(ii) P(F = true | R = false, C = lots, W = false).
(iii) P(F = true | R = true, C = some, W = false).
b. Derive symbolic expressions for the following probabilities in terms of P(R | C), P(C | F), P(W | F), and P(F):
(i) P(R).
(ii) P(R | C, W).
(iii) P(R, C, W | F).
c. Comment on the plausibility of the conditional independence assumptions made by the naive Bayes model.
Figure S12.1 A naive Bayes model for fishing.
P(F= false) P(F= true) 0.9 0.1 P(W = false | F)| P(W = true | F) 0.5 0.5 0.8 0.2 F false true F false true P(C=none | F)| P(C = some | F)| P(C = lots | F)| 0.2 0.1 0.4 0.3 0.7 0.3
Step by Step Solution
3.44 Rating (157 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a i ii iii b i ii iii PR FPC FPW F c The assumptions of the mo... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


